Chapter 13 Objectives Part A - Monopolistic Competition
advertisement

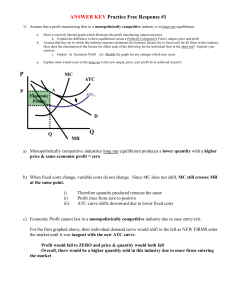
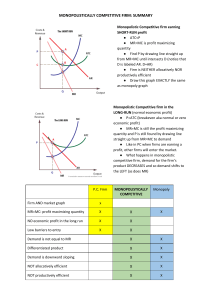
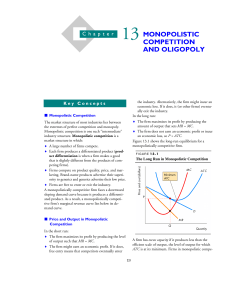
Chapter 13 Objectives Part A - Monopolistic Competition 1. Identify the characteristics of monopolistic competition. 2. Identify the relationship between price, marginal revenue, marginal cost, and average total cost for a monopolistically competitive firm in long-run equilibrium. 3. Identify the profit level for a monopolistically competitive firm in long-run equilibrium. 4. Explain what is meant by “excess capacity” in a monopolistically competitive industry. 5. Explain why monopolistically competitive firms’ demand curves are not perfectly elastic. Why are they able to raise price and not lose all of their customers? 6. Identify and explain the factors that affect the elasticity of a monopolistically competitive firm’s demand curve. (Under what circumstances will customers be more likely to switch to other firms’ products.) 7. Explain why monopolistically competitive firms advertise? What effects does advertising have on their demand curves? Part B - Oligopoly 8. Identify the characteristics of oligopoly. (p. 286) 9. Explain what it means that firms in an oligopolistic industry are “mutually interdependent.” (p. 286). 10. How can mergers help firms achieve greater efficiency? (p. 287) 11. Define game theory. (p. 289) 12. Explain what a cartel is and why cartels are difficult to maintain. (293) 12. Explain the effect that collusion will have on price in oligopoly. (293-295) 14. Identify the factors that make collusion difficult to maintain in oligopoly. (295) The following objectives are not in your textbook specifically, and will be covered in class. 15. Use a payoff matrix to identify two firms’ dominant strategies. 16. Use a payoff matrix to identify two firms’ profits in the case of both collusion and independent action. 17. Define: “Nash equilibrium.” 18. Given a payoff matrix, identify the state of Nash equilibrium.