Unit C: Atoms, elements, and Compounds 5.1: From Particles to Solutions
advertisement

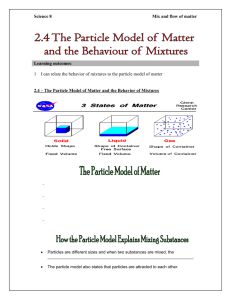
Unit C: Atoms, elements, and Compounds 5.1: From Particles to Solutions pg. 175 Key Concepts: 3. Pure substances have characteristic physical properties. Particle Theory of Matter Particle theory of Matter: a theory that describes the composition and behaviour of matter. 1. All matter is made up of tiny particles that have empty spaces between them. 2. Different substances are made up of different kinds of particles. 3. Particles are in constant random motion. 4. The particles of a substance move faster as its temperature increases. 5. Particles attract each other. Adding or taking away heat can cause the particles of matter to increase or decrease their random motion. Solids have their particles held closed together in a rigid shape, yet they are still vibrating (motion). Changes of state are caused by temperature changes. Solids become liquid as heat is added. The particles gain thermal energy and move further apart changing from a solid to a liquid. Continuous increase in temperature causes the liquid to become a gas as the particles move even further apart. Figure 1: all matter is made up of particles. Figure 2: The particle theory describes the different behaviours of solids, liquids, and gases. Pure Substances Pure Substance: a substance that is made up of only one type of particle. - Matter is made up of many types of particles. - Some matter is made up of one type of particle and are known as pure substances. - e.g.: distilled water Mixtures Mixture: a substance that is made up of at least two different types of particle. - Matter that is made up of more then one type of particles are known as mixtures. - e.g.: salt dissolved in water, salt water. - Mixtures can be either solids, liquids, or gases. Mechanical Mixtures and Solutions Mechanical Mixture: a mixture in which you can distinguish between different types of matter. Solution: a uniform mixture of two or more substances. - There are two types of mixtures, mechanical mixtures and solutions. - Mechanical mixtures, the substances that make them up do not disappear. They are distinguishable from each other. - Solutions, the substances disappear and are not distinguishable and can not be seen with the naked eye. - Solutions consist of a solvent and one or more solute. The solvent does the dissolving and the solute is dissolved in the solvent. - Gas and Liquid solutions are clear, mechanical mixtures are opaque. Alloys Alloys: a solid solution of two or more metals. - Tin is a metal and Lead is a metal, on their own they are pure, made up of one type of particle. When mixed together they form an alloy, a solid solution. Figure 8: The classification of Matter Evidence of Learning: Students can … - explain the main ideas of the particle theory of matter. - describe the difference between a pure substance and a mixture. - describe the difference between a mechanical mixture and a solution. - explain the composition of an alloy. Check Your Learning: Questions 1 – 10, page 178 Summary: - The particle theory of matter describes the composition and behaviour of matter. - A pure substance is made up of only one type of particle. - A mixture is made up of at least two different types of particles. - A mechanical mixture contains more than one type of particle, and the different types of particles are visible. - A solution contains more than one type of particle but the different types of particles cannot be distinguished visually. - An alloy is a solution composed of to or more metals.