CLADOGRAM ANALYSIS
advertisement

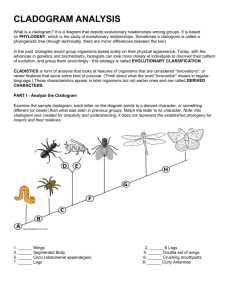
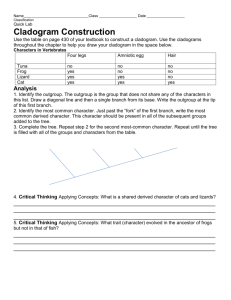
CLADOGRAM ANALYSIS What is a cladogram? It is a diagram that depicts evolutionary relationships among groups. It is based on PHYLOGENY, which is the study of evolutionary relationships. Sometimes a cladogram is called a phylogenetic tree (though technically, there are minor differences between the two). In the past, biologists would group organisms based solely on their physical appearance. Today, with the advances in genetics and biochemistry, biologists can look more closely at individuals to discover their pattern of evolution, and group them accordingly - this strategy is called EVOLUTIONARY CLASSIFICATION CLADISTICS is form of analysis that looks at features of organisms that are considered "innovations", or newer features that serve some kind of purpose. (Think about what the word "innovation" means in regular language.) These characteristics appear in later organisms but not earlier ones and are called DERIVED CHARACTERS. PART I - Analyze the Cladogram Examine the sample cladogram, each letter on the diagram points to a derived character, or something different (or newer) than what was seen in previous groups. Match the letter to its character. Note: this cladogram was created for simplicity and understanding, it does not represent the established phylogeny for insects and their relatives. 1. ______ Wings 2. ______ 6 Legs 3. ______ Segmented Body 4. ______ Double set of wings 5. ______ Cerci (abdomenal appendages) 6. ______ Crushing mouthparts 7. ______ Legs 8. ______ Curly Antennae PART II - Create Your Own Cladogram To make a cladogram, you must first look at the animals you are studying and establish characteristics that they share and ones that are unique to each group. For the animals on the table, indicate whether the characteristic is present or not. Based on that chart, create a cladogram like the one pictured above. Cells Backbone Legs Slug Catfish Frog Tiger Human DRAWING OF YOUR CLADOGRAM Hair Opposable Thumbs Constructing a Cladogram Objective: Students will construct a cladogram using descriptions and information about 7 imaginary animals. Students will determine which traits are derived traits, and identify synapomorphy and automorphy of characteristics. Tips for constructing your cladogram 1. Use the times to determine the positioning of the species. Older organisms will appear first on the cladogram 2. Determine features that are shared among organisms - these are synapomorphies - Place an S on these features to help you keep track 3. Determine features that are unique to organisms - these are automorphies - Place an A on these features 4. There may be several ways to represent this cladogram, remember that cladistics and systematics is inexact, do not worry if yours looks different from others. Description of Species Species 1 - Fossils of this species date back to 30,000 years ago. The organism has a single antenna that is branched (like a Y). It has two eyes positioned on top of the head a non segmented body Species 2 - Fossils of this species date back to 8,000 years ago. This organism has branched antennae, 3 body segments, the middle segment has fleshy appendages with a bendable joint. Species 3 - Fossils of this species date back to 25,000 years ago. The organism has a branched antenna (like a Y), body is divided into 2 segments, and eyes positioned on the top of the head. In addition, the last segment of the body has a long curley tail. Picture Species 4 - Fossils of this species date back to 10,000 years ago. This organism has branched antennae, 2 body segments, eyes positioned on the top of the head, fleshy appendages on the last segment have a bendable joint. Species 5 - Fossils of this species date back to 50,000 years ago. The organism has a single antennae, two eyes positioned on top of a head and a non segmented body. Species 6 - Fossils of this species date back to 20,000 years ago. This organism has branched antennae, 2 body segments, eyes positioned on the top of the head, and small flesh appendages on the last segment. This organism also has a ridge of spines on the last segment. Species 7 - Fossils of this species date back to 31,000 years ago. The organism has a single branched antennae (like a Y) and a club like structure at the end of the branches of the antennae. It has two eyes positioned on top of the head and a non segmented body.