Heat Transfer CH 4 Prentice Hall p.115-117
advertisement

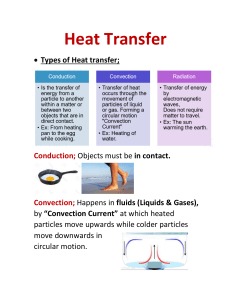
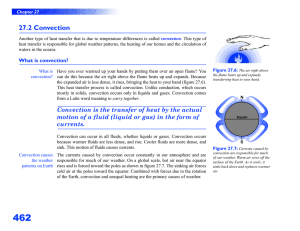
Heat Transfer CH 4 Prentice Hall p.115-117 Heat • The energy transferred from a hotter object to a colder object. – The hotter something is, the faster its molecules are moving. – Does ice have heat? Heat Transfer • Three ways it is transferred: – Conduction – Radiation – Convection Conduction • Heat transfer by direct contact of particles of matter • Particles bump into each other and transfer their energy heating them up. Radiation Climate • The transfer of energy through empty space • Moves in waves – Sunlight – Open fire. Safety Convection • Heat transfer by the circular movement of particles (liquids and gasses) • Particles transfer heat • Caused by differences in density. How Convection Works Density = Mass / Volume • Heated Fluids: – Move faster and bump into other particles – They spread out increasing the volume – Density decreases. How Convection Works • Cooling Fluids – Move slower – They come together, decreasing the volume – Density increases. Convection Lab Convection and Sea The Ocean Floor The Ocean Floor