CULTURE Chapter 1 Section III
advertisement

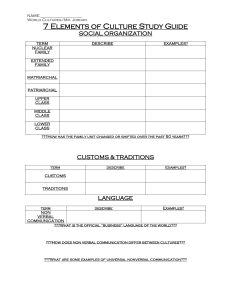
CULTURE Chapter 1 Section III What is culture? Culture All the things that make up a people’s entire way of life. 7 Elements of Culture Social Organization Customs and Traditions Language Arts and Literature Religion Forms of Government Economic Systems SCLARFE Social Organization Purpose: Help people of a culture work together to meet basic needs What are basic needs? Social Organization Family Patterns Nuclear Family Parts: Wife, Husband, Children Typical in industrial societies What are some other industrial societies? United States – Family Arrangements Purple – 2000 Blue 1970 What does this show us? Extended Family Several generations living in one household. Generations? Characteristics: May not have a lot of money Common in farming societies Respect for elders Patriarchal/Matriarchal Families Patriarchal Families Men exercise more authority than women Typical the eldest male is decision maker. Matriarchal Families Women exercise more authority than men. Social Classes Purpose: Rank people in order of status. Basis: Money Occupation Education Ancestry Land Owned Animals Owned Religious leader Social Mobility The ability to move amongst classes Was it always this way? Is it this way everywhere? How might one rise in society? Family and Society 5 Minutes Write about your families history: How did you come to be where you are today. Think about Family Structure Think about Social Classes Do you know? If not, consider another families history, or make-up a logical history one might be a part of. Customs and Traditions Rules and Behavior How to sleep How to greet How to eat SOCIAL NORMS – Customs and Traditions What are some differences between our culture and other cultures customs and traditions? Language The CORNERSTONE of culture How would you communicate thoughts, feelings, and knowledge without it? INDIA OVER 700 Languages! Government recognizes 15 official languages. Should the U.S. have an official language? Arts and Literature Products of the human imagination. Teach a culture’s beliefs and values. Example? Folk Tales Art and Literature Help promote pride and unity Religion Helps a culture answer questions about the meaning and purpose of life. Monotheism – the worship of one God Polytheism – the worship of more than one God The Major Religions Hinduism Buddhism Judaism Islam Christianity What kind of problems has religion caused? Sources of Religious Conflict Internal Fighting within a religion External Fighting outside of religion (against another) Forms of Government Government 1) Refers to People who hold power in a society 2) Refers to Society’s Laws Political Institutions Government Why are governments formed? Types of Government Democracy Republic People have supreme power Government can only act with the people’s consent People choose leaders who represent them Dictatorship A ruler or group holds power by force Sometimes will claim to be republics Economic Systems Economics How people use limited resources to satisfy their wants and needs. 3 Basic Questions 3 Basic Economic Questions What goods and services should be produced? How should the goods and services be produced? For whom should the goods and services be produced? Traditional Economy People produce most of what they need to survive. For thousands of years most cultures had traditional economies. Market Economy Individuals answer the three basic economic questions by buying and selling goods and services. Businesses/Manufacturers decide what to produce based on what people will buy. Command Economy Government controls what goods and services are produced, and what they will cost. Mixed Economy Individuals make some economic decisions and the government makes others. Example? Causes of Culture Change Technology Changing Environment New Ideas Diffusion The movement of ideas or customs from one place to another Peaceful Diffusion War/Forced Diffusion Subculture Group of people within a society that share certain beliefs, values, and customs. Ethnocentrism Judging other cultures by the standards of one’s own. Racism Believing one racial group is NATURALLY SUPERIOR than another racial group. Essay – 40% Name and explain the 7 elements of culture. Be sure to provide an example of each and justify how it fits the category.