FS-6700-7 (11/99) U.S. Department of Agriculture 1. WORK
advertisement

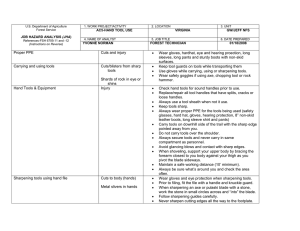
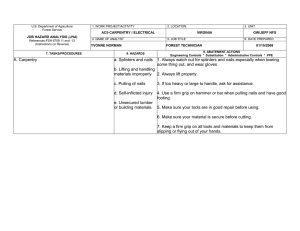
FS-6700-7 (3/98) U.S. Department of Agriculture Forest Service JOB HAZARD ANALYSIS (JHA) References-FSH 6709.11 and -12 (Instructions on Reverse) 7. TASKS/PROCEDURES A. Ergonomics for powered hand tools 1. WORK PROJECT/ACTIVITY 2. LOCATION Unity Auto Shop Unity Ranger District Compound 4. NAME OF ANALYST 5. JOB TITLE Robert P. Glover 8. HAZARDS PHYSICAL: Preventing fatigue and muscular or skeletal injuries resulting from extensive tool use, and work station design. Maintenance Worker FS-6700-7 (11/99) 3. UNIT Unity R. D. 6. DATE PREPARED 03-05-2001 9. ABATEMENT ACTIONS Engineering Controls * Substitution * Administrative Controls * PPE 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. Select tools that can be used without bending the wrist. Hand tools should allow the operator to grasp, hold, and use the tool with the wrist held straight. Select the tool with the workplace layout and job design in mind. Remember sometime a tool is correct for one operation and incorrect for another. Use the right tool for the job. Ensure it is the right size and has sufficent power to do the job safely. When there is a choice select a tool of low weight. Select low vibrating tools. Choose tools with vibration-absorbing handles. Choose hand tools that have the center of gravity within or close to the handle. Select tools with rounded and smooth handles that you can grip easily. Choose tools with double handles to permit easier holding and better manipulation of the tool. Select tools with a trigger strip rather than a button. Ensure the tool is well maintained and in good repair. Frequently-used tools that weigh more than 1 lb. Should be counter-balanced. Hold the tool close to your body. Do not over reach. Keep good balance and proper footing at all times. This will help the operators to control the tool bettter, especiallly in response to unexpected situations. Rest your hands by putting the tool down when not using it. Reduce power to the lowest setting that can complete the job safely. This action reduces tool vibration at the source. FS-6700-7 (3/98) 21. Consider wearing anti-vibration gloves. B. Pneumatic tools / Air hoses C. Use of hand tools (hammer, screw drivers, pliers, hand saws, wrenches etc.) a. Eye injury, hearing loss b. damaged tools and hoses c. exceeding manufactured psi for tools. d. Use of air nozzel to clean filters or saw parts. a. Cracked handles or splinters b. Damaged or mushroom heads c. Loose heads 1. 2. 3. 4. Keep hand tools clean and good working condition. Worn or broken tools shall be replaced and tagged. Hand tools will be inspected annually. When done with tools they will be returned to their proper location. 1. 2. 4. 1. Always select the right tool for the job. Tools with edges and blades must always be sharp and with teeth going the right direction. Use tools and service equipment only for the tasks for which they are designed. Keep power tool guards and safety devices in place and functional. Wear safety goggles or face shield. b. Defective equipment 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Keep drill air vents clear to maintain adequate ventilation. Keep drill bits sharp Keep all cords free of the cutting area during ues. Inspect cords for frays or damage before each use. Do not use a bent drill bit. c. Not opertating the drill properly 1. Select the bit or attachment suitable for the size of drill and the work being done. Ensure that the bit or attachments are properly seated and tightened in the chuck. Use only bits and attachments that turn true. Use the auxillary (second) handle for large work or continuous operations. Disconnect power supply befor changing or adjusting bit or attachments. Secure woodpiece being drilled to prevent movement. Slow the rate of feed just before breaking thru the surface. Drill a small pilot hole before drilling large holes. Do not exceed the manufacturer’s recommended maximum drilling capacities. a. Using the wrong tool for the job b. Dull Tools D. Powered Drills 1. Use of face shield / goggles and hearing protection is mandatory when operating pneumatic tools 2. Check all hoses for defective parts before operation. 3. Read manufctures suggested psi before operation. 4. Do not use if heads are cracked or mushroomed. 5. Check safety clips or retainer on all tools and supply lines. 6. Never kink an air hose. 7. Never point the nozzle at another person. 8. Never use the nozzle to clean off clothes. 9. Never use a nozzle above 10psi rating. a. Sight loss 3. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. FS-6700-7 (3/98) 10. Do not use a hole saw cutter without the pilot drill. 11. Do not use high speed steel (HSS) bits without cooling or using lubrication. 12. Do not attempt to free a jammed bit by starting or stopping the drill. Unplug the drill and then remove the bit from the workpiece. 13. Do not reach under or around stock being drilled. 14. Do not over reach. 15. Always keep proper footing or balance. 16. Do not straddle a drill or position your body to apply pressure that may exceed the drills capabilities or capacity. E. Portable grinders a. Hearing and sight loss, hands, and burns 1. 2. 3. 4. b. Defective equipment 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. c. Not operating the portable grider properly 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. F. Toxics a. Improper storage b. Improper ventilation c. Improper use d. Failure to read MSDS e. Failure to use proper PPE Wear safety face protection to protect from flying debris (goggles , safety glasses, or face shield). Wear hearing protection that is suitable for the level and frequency of the noise you are exposed to in the work area. Wear gloves for protection of hands. Wear apron for the protection from flying debri and burns. Replace damaged guards because if an abrasive wheel breaks while rotating it can cause serious injury. Do not operator without guards. Check that the grinder does not vibrate or operate roughly. Inspect all wheels for cracks and defects before operating. The maximum speed in revolutions per minute (RPM) is marked on every wheel. Never exceed this speed Insure that mounting flange surfaces are clean and flat. Stand away from the wheel when starting grinding. Warn co-workers to do the same. Run newly mounted wheels at operating speed for 1 minute before grinding. Avoid using grinders near flammable materials. Do not clamp grinder in a vice for grinding hand-held work. Do not use liquid coolant with portable grinders. Do not force wheel onto grinder or change mounting hole size. Do not tighten the mounting nut excessively. 1. Insure proper ventilation by fan or other means. 2. Make sure you check the MSDS for ventilation requirements. 3. Wear protective clothing as listed in MSDS 4. Properly store and tag toxic materials. FS-6700-7 (3/98) G. Equipment and vehicle maintenance - shop a. Moving parts b. Lifting items c. Wrong tool for the job. d. Not using correct PPE 1. Stay clear of all moving parts of vehicle or equipment. 2. Restrain any loose clothing or hair that may catch in moving parts. 3. Use lifting devices when possible or request assistance if needed. 4. Use proper tools and procedures to accomplish work. 5. Always wear required PPE as needed according to the task to be performed. H. Equipment and vehicle maintenance - field a. No communications by phone or radio. b. Failure to check out on sign out board. 1. Never work on equipment in the field by yourself. 2. Have an assistant or equipment operator work with you. 3. Always sign out to where you are going. 4. Make sure you have a workable phone or radio with you. I. Jacks J. Use of creepers K. Housekeeping a. Air jack 1. Use hearing protection when using air jack. b. Defective equipment 1. Use only jacks that are maintained in good operating condition. c. Not operating the jack correctly. 1. Place the jack securely on a dry, level, clean surface at right angles to the load. 2. Position the jack at the jack point recommended by the vehicle manufacturer 3. Shift vehicles with automatic transmissions to park or lower gear, if it has a standard transmission, and apply the parking brake. 4. Do not overload a jack beyond its capacity. 5. All lifts must be vertical. 6. Do not position yourself where you could be pinned between the operation handle and the wall if the vehicle or jack moves accidentally. 7. Place safety stands under the vehicle to support the vehicle if an employee must work under the vehicle. 8. Ensure That the safety stands are in good working condition and positioned properly, and are the correct load capacity. 9. Do not get under a vehicle that is supported by a jack only. a. Not using creeper correctly. 1. Before using creeper make sure the proper stands are in postion in case of jack failure or movement. 2. Keep feet clear of other traffic. 5. Secure creepers in a wall rack when not in use. 6. Do not leave creepers leaning against wall where they could be a tripping hazard. 1. Clean all spills immediately. 2. Mark spills and wet area. 3. Mopping or sweeping debris from floors. a. Common causes of slips. 1. Wet or oily surfaces 2. Ocassional spills 3. Weather FS-6700-7 (3/98) hazards b. Trips 1. Obstructed view 2. Poor lighting 3. Clutter in your way 4. Uncovered cable 5. Uneven walking surface c. Falls 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 1. 2. d. Imporoper cleanup and storage. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. M. Housekeeping a. Common causes of slips. 4. Wet or oily surfaces 4. 5. 6. Removing obstacles from walkways and always keeping them from clutter. Covering cables that cross walkways. Keep work areas and walkways well lit. Replacing used light bulbs and faulty switches. Always closing file cabinets and storage cabinet doors. Reduce the risk of slipping and falling on wet floors by: a. Take your time and pay attention to where you are going. b. Adjust your stride to a pace that is suitable for the walking surface and the task you are doing. c. Walk with feet pointed slightly outward. d. Make wide turns a corners. Reduce the risk of tripping and falling a. Always using installed light sources that provide sufficient light for your task. b. Using a flashlight if you enter a dark room where there is no light. c. Ensure that things you are carrying or pushing do not prevent you from seeing any obstructions, spills, etc. d. Make sure dock safety chains are in place when not in use. Empty trash containers regularly. Discard rags, paper and other items soaked with flammable materials (such as oil, gas or solvents) in approved metal containers. Label flammable and combustable materials clearly and store in separate place, away from heat and ignition sources. Use only approved safety containers for flammable and combustable liquids. Store compressed gas cylinders upright and secure with a chain or brackets. Close valves of empty cylinders. Make sure sure valve protection cap is in place. Clean all spills immediately. Mark spills and wet area. Mopping or sweeping debris from floors. FS-6700-7 (3/98) 5. 6. Ocassional spills Weather hazards b. Trips 6. Obstructed view 7. Poor lighting 8. Clutter in your way 9. Uncovered cable 10. Uneven walking surface c. Falls 6. Removing obstacles from walkways and always keeping them free from clutter. 7. Covering cables that cross walkways. 8. Keep work areas and walkways well lit. 9. Replacing used light bulbs and faulty switches. 10. Always closing file cabinets and storage cabinet doors. 3. 4. d. Improper cleanup and storage. 1. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. Reduce the risk of slipping and falling on wet floors by: a. Take your time and pay atteention to where you are going. b. Adjust your stride to a pace that is suitable for the walking surface and the task you are doing. c. Walk with feet pointed slightly outward. d. Make wide turns a corners. Reduce the risk of tripping and falling a. Always using installed light sources that provide sufficent light for your task. b. Using a flashlight if you enter a dark room where there is no light. c. Ensure that things you are carrying or pushing do not prevent you from seeing any obstructions, spills, etc. d. Make sure dock safety chains are in place when not in use. Empty trash containers regularly. Discard rags, paper and other items soaked with flammable materials (such as oil, gas or solvents) in approved metal containers. Label flammable and combustable materials clearly and store in separate place, away from heat and ignition sources. Use only approved safety containers for flammable and combustable liquids. Store compressed gas cylinders upright and secure with a chain or brackets. Close valves of empty cylinders. Make sure sure valve protection cap is in place. FS-6700-7 (3/98) 10. LINE OFFICER SIGNATURE Previous edition is obsolete 11. TITLE (over) 12. DATE FS-6700-7 (3/98) JHA Instructions (References-FSH 6709.11 and .12) The JHA shall identify the location of the work project or activity, the name of employee(s) involved in the process, the date(s) of acknowledgment, and the name of the appropriate line officer approving the JHA. The line officer acknowledges that employees have read and understand the contents, have received the required training, and are qualified to perform the work project or activity. Blocks 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6: Self-explanatory. Block 7: Identify all tasks and procedures associated with the work project or activity that have potential to cause injury or illness to personnel and damage to property or material. Include emergency evacuation procedures (EEP). Block 8: Identify all known or suspect hazards associated with each respective task/procedure listed in block 7. For example: a. Research past accidents/incidents. b. Research the Health and Safety Code, FSH 6709.11 or other appropriate literature. c. Discuss the work project/activity with participants. d. Observe the work project/activity. Emergency Evacuation Instructions (Reference FSH 6709.11) Work supervisors and crew members are responsible for developing and discussing field emergency evacuation procedures (EEP) and alternatives in the event a person(s) becomes seriously ill or injured at the worksite. Be prepared to provide the following information: a. Nature of the accident or injury (avoid using victim's name). b. Type of assistance needed, if any (ground, air, or water evacuation). c. Location of accident or injury, best access route into the worksite (road name/number), identifiable ground/air landmarks. d. Radio frequencies. e. Contact person. f. Local hazards to ground vehicles or aviation. g. Weather conditions (wind speed & direction, visibility, temperature). h. Topography. i. Number of individuals to be transported. j. Estimated weight of individuals for air/water evacuation. The items listed above serve only as guidelines for the development of emergency evacuation procedures. e. A combination of the above. Block 9: Identify appropriate actions to reduce or eliminate the hazards identified in block 8. Abatement measures listed below are in the order of the preferred abatement method: JHA and Emergency Evacuation Procedures Acknowledgment We, the undersigned work leader and crew members, acknowledge participation in the development of this JHA (as applicable) and accompanying emergency evacuation procedures. We have thoroughly discussed and understand the provisions of each of these documents: a. Engineering Controls (the most desirable method of abatement). For example, ergonomically designed tools, equipment, and SIGNATURE DATE SIGNATURE DATE furniture. b. Substitution. For example, switching to high flash point, non-toxic solvents. Work Leader c. Administrative Controls. For example, limiting exposure by reducing the work schedule; establishing appropriate procedures and practices. d. PPE (least desirable method of abatement). For example, using hearing protection when working with or close to portable machines (chain saws, rock drills, and portable water pumps). e. A combination of the above. Block 10: The JHA must be reviewed and approved by a line officer. Attach a copy of the JHA as justification for purchase orders when procuring PPE. Blocks 11 and 12: Self-explanatory. HERE IS THE JHA AND THE UNITY RANGER DISTRICT SHOP RULES FOR USE OF TOOLS IN THIS SHOP FS-6700-7 (3/98) PORTABLE TOOL CABINET 1. ALL TOOLS WILL BE SIGNED OUT AND CHECKED IN . 2. ALL TOOL WILL BE CLEANED BEFORE RETURNED TO CABINET. 3. THE FOLLOWING PEOPLE WILL HAVE KEY TO ISSUE TOOLS. Bob Glover Eddie June Greenwood Joe Greenwood Kevin Reilly 4. ALL TOOLS THAT ARE DEFECTIVE WILL BE TAGGED AND PUT OUT OF SERVICE. 5. BEFORE USUING A TOOL, THE EMPLOYEE WILL REVIEW JHA FOR WOOD SHOP AND SIGN IT: THESE THREE SECTIONS MUST BE COVERED EEACH TIME A TOOL IS USED. SECTION A ERGONOMICS FOR HAND TOOLS SECTION B WOOD WORKING MACHINES SECTION M HOUSEKEEPING PLUS THE SECTION FOR THE TOOL BEING USED HERE IS THE JHA TOOL INDEX: SECTION TOOL C TABLE SAW D USE OF PUSH STICK E RADIAL ARM SAW F BAND SAW FS-6700-7 (3/98) G USE OF HAND TOOLS H POWERED DRILLS I BELT SANDERS J PORTABLE GRINDERS K MITRE SAW L CIRCULAR SAW 6. THE FOLLWING TOOLS MAY BE USED BY CERTIFIED EMPLOYEE’S ONLY (THESE TOOLS ARE LOCKED OUT TO PREVENT UNAUTHORIZED USE) TABLE SAW RADIAL ARM SAW BAND SAW CERTIFIED OPERATORS BOB GLOVER KEVIN REILLY JOE GREENWOOD JIM COX BILL ROUNSVILLE 7. PAY ATTENTION TO DIAGRAMS AT WORK STATION FOR THESE TOOLS. 8. IF YOU ARE NOT SURE ABOUT A TOOL ASK.