Software quality This lecture
advertisement

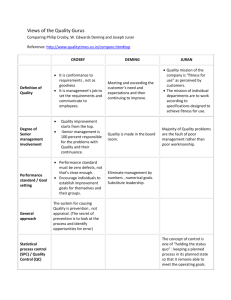
Software quality by Kristian Sandahl This lecture • Perspectives of quality • Quality factors • Two examples: – Reliability – Usability • How to use inspections • Process improvement paradigms Perspectives of quality • Transcendent – something we learn to recognize • Product-based – measurable variable • Usage-based – in the eyes of the beholder • Manufacturing-based – conformance to requirements • Value-based – market sets the value Many opinions ⇒ Statistical techniques Quality factors • • • • • • • • • Correctness Reliability Efficiency Usability Integrity Maintainability Flexibility Testability Security • • • • • • • • • Price? Portability Reusability Interoperability Survivability Safety Manageability Supportability Replaceability Functionality Reliability • The probability that the software executes with no failures during a specified time interval • Approximation: MTTF/(1+MTTF) • Reliability engineering: – Goal failure intensity – Operational profiles – Statistical Usage Testing Usability • Relevance • Efficiency • Attitude • Learnability Usability engineering: – Task analysis – Prototyping (HI-FI, LO-FI) Data collection from inspections • • • • • Number of defects Classes of defects Severity Number of inspectors Number of hours Inspections in quality assurance • • • • Appraisal – defect detection Assurance – prediction of defects Control – adjust the process Improvement: reduce variation, increase precision Analysis Inspection data Design Coding Test-cases Inspection Inspection Inspection data data data Inspection data Research – predicting troubles • Regression analysis from empirical material • Often a linear combination between size and complexity • Size can be measured in: – lines of code (KLOC) – function points – Halstead software science Measuring complexity • • • • Cyclomatic number V(G) = e – n + 2 e = number of edges (arcs) n = number of nodes Due to McCabe(76) Example I 2 III 1 II 3 IV 5 4 V 6 VI 7 8 VII 9 VIII 10 11 IX 12 X 13 14 XI V(G) = 14 – 11 + 2 = 5 CMM 5: Optimising 4: Managed 3: Defined 2: Repeatable 1: Initial Each level has key process areas. QIP 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Set quantifiable goals Select processes Run processes Measure objectives Analyse measurements Package experience