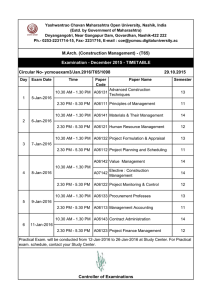
DOCUMENT #: GSC15-GRSC8-08 FOR: Presentation SOURCE:
advertisement
DOCUMENT #: GSC15-GRSC8-08 FOR: Presentation SOURCE: ETSI AGENDA ITEM: GRSC8 4.3 CONTACT(S): Markus Mueck, TC RRS Chair Reconfigurable Radio Systems (RRS) Presenter: Gabrielle Owen, TC ERM Chair Global Standards Collaboration (GSC) GSC-15 Overview Role and Structure of ETSI RRS Cognitive Radio Activities in RRS • • • • Cognitive Radio Approach Cognitive Pilot Channel Functional Architecture Novel activities related to: TV White Spaces Software Defined Radio Activities in RRS • Mobile Device SDR Architecture • Reconfigurable Base Stations Related Activities in ETSI ERM / STF386 Conclusions 2 Role and Structure of ETSI RRS TC RRS’ main responsibility is to carry out standardization activities related to Reconfigurable Radio Systems encompassing both Software Defined Radio (SDR) and Cognitive Radio (CR). TC RRS is building on the following Working Group structure: • WG1 focuses on “System Aspects” and develops proposals from a system aspects point of view for a common framework in TC RRS; • WG2 focuses on SDR technology with a particular interest in “Radio Equipment Architecture” and proposes common reference architectures for SDR/CR radio equipments; • WG3 focuses on "Cognitive Management and Control"; the group addresses functionalities for Reconfigurable Radio Systems which are related to the Spectrum Management and Joint Radio Resource Management across heterogeneous access technologies; • WG4 focuses on “Public ETSI TC RRS Safety” and collects and defines the related RRS WG2: WG3: requirements from relevant WG1: Reconfigurable WG4: Cognitive RRS System Radio RRS Public stakeholders in the Public Management Aspects Equipment Safety and Control Architecture Safety and Defense domain. 3 RRS Cognitive Radio Approach Centralized and Decentralized CR System (CRS) Concepts • Objective: Provision of more efficient and flexible use of spectrum by Obtaining knowledge of the radio operational environment and location, Deciding on the gathered information and acting based on this decision, Learning from the results obtained. • Four CRS deployment examples are proposed: dedicated spectrum, shared spectrum, secondary usage in dedicated spectrum, and spectrum dedicated for CRS. • The overall ETSI RRS cognitive radio system concept is shown on the right hand side. 4 Cognitive Pilot Channel (CPC) & Functional Architecture (FA) in RRS CPC Scope: The Cognitive Pilot Channel (CPC) serves mainly to support the user terminal for an efficient discovery of the available radio accesses in a heterogeneous wireless environment. FA Scope: Network with heterogeneous access technologies Reconfigurable UEs / Mobile Devices and Reconfigurable Base Stations; Functional Architecture addresses generic framework on possible SON (3GPP TS 36.300) evolution concepts, etc. New activities started on TV White Spaces. Database DSM Dynamic Spectrum Management MS DSONPM Dynamic Self-Organising Network Planning and Management MC CCM Configuration Control Module MJ CJ JRRM Joint Radio Resource Management CR JR RAT 1 RAT 2 … RAT n 5 Software Defined Radio Activities SDR in Mobile Devices: RRS has proposed the SDR architecture illustrated on the right hand side with the following capabilities: • Multiradio configuration capability; • Multiradio operation capability; • Multiradio resource sharing capability. Interface definitions are currently ongoing. SDR in Reconfigurable Base Stations: The following general requirements are derived: • • • • • • Transition from one standard to a new; Multi-standard use, frequency re-farming; Spectrum trading & secondary spectrum usage; Dynamic capacity optimization depending on load; Network planning and adaptation, antenna tuning; Backhaul reconfiguration for flat architecture. 6 Related Activities in TC ERM / STF 386 Development of cognitive interference mitigation techniques for use by PMSE devices (Programme Making and Special Events) Achieve co-existence of high audio quality PMSE devices using often a 100% transmitter duty cycle emission profile with victim radio services such as Services in L-Band or Broadcast Services and future Land Mobile Services and applications in UHF frequency range that is currently under investigation under the “Digital Dividend” discussions in Bodypack for ENG EC, ECC and ETSI fora See also separate presentation on cognitive-PMSE (C-PMSE). 7 Conclusions Cognitive Radio / Software Defined Radio Activities are well advanced within ETSI; SDR mainly focuses on Mobile Device Architecture & Interface definitions between distinct stakeholder domains (Device / Component Manufacturer, etc.); CR mainly focuses on devices operating in a heterogeneous context, flexible & dynamic spectrum/resource management and TV White Space operation as a future topic; There are close ties between TC RRS and TC ERM & STF386 on cognitive interference mitigation techniques for use by PMSE devices . 8 Supplementary Slides 9 References / Further reading ETSI Reconfigurable Radio Systems – Status and Future Directions on Software Defined Radio and Cognitive Radio Standards, Markus Mueck, Antti Piipponen, George Dimitrakopoulos, Kostas Tsagkaris, Fernando Casadevall, Panagiotis Demestichas, Jordi Pérez-Romero, Oriol Sallent, Gianmarco Baldini, Stanislav Filin, Hiroshi Harada, Merouane Debbah, Thomas Haustein, Jebns Gebert, Benoist Deschamps, Paul Bender, Michael Street, Kari Kalliojärvi, Sithamparanathan Kandeepan, Jaswinder Lota, Aawatif Hayar, IEEE Communications Magazine, September, 2010 ETSI TR 102 802: “Reconfigurable Radio Systems (RRS); Cognitive Radio System Concept”, 2009 ETSI TR 102 680: "Reconfigurable Radio Systems (RRS); SDR Reference Architecture for Mobile Device", 2009 ETSI TR 102 681: " Reconfigurable Radio Systems (RRS)); Radio Base Station (RBS) Software Defined Radio (SDR) status, implementations and costs aspects, including future possibilities ", 2009 ETSI TR 102 682: "Reconfigurable Radio Systems (RRS); Functional Architecture for Management and Control of Reconfigurable Radio Systems", 2009 10 References / Further reading, cont’d ETSI TR 102 683: “Reconfigurable Radio Systems (RRS); Cognitive Pilot Channel (CPC)”, 2009 ETSI TR 102 745: “Reconfigurable Radio Systems (RRS); User Requirements for Public Safety”, 2009 ETSI TR 102 733: “Reconfigurable Radio Systems (RRS); System Aspects for Public Safety”, 2009 ETSI TR 102 799: “Operation methods and principles for spectrum access systems and quality control of used spectrum for PMSE technologies and the guarantee of a high sound production quality on selected frequencies utilising cognitive interference mitigation techniques”, 2010. Draft ETSI TR 102 800: “Protocols for spectrum access and sound quality control systems using cognitive interference mitigation techniques”, 2010. 11