PERMIT FOR UNDERGRADUATE STUDENTS TO USE ENGINEERING
advertisement
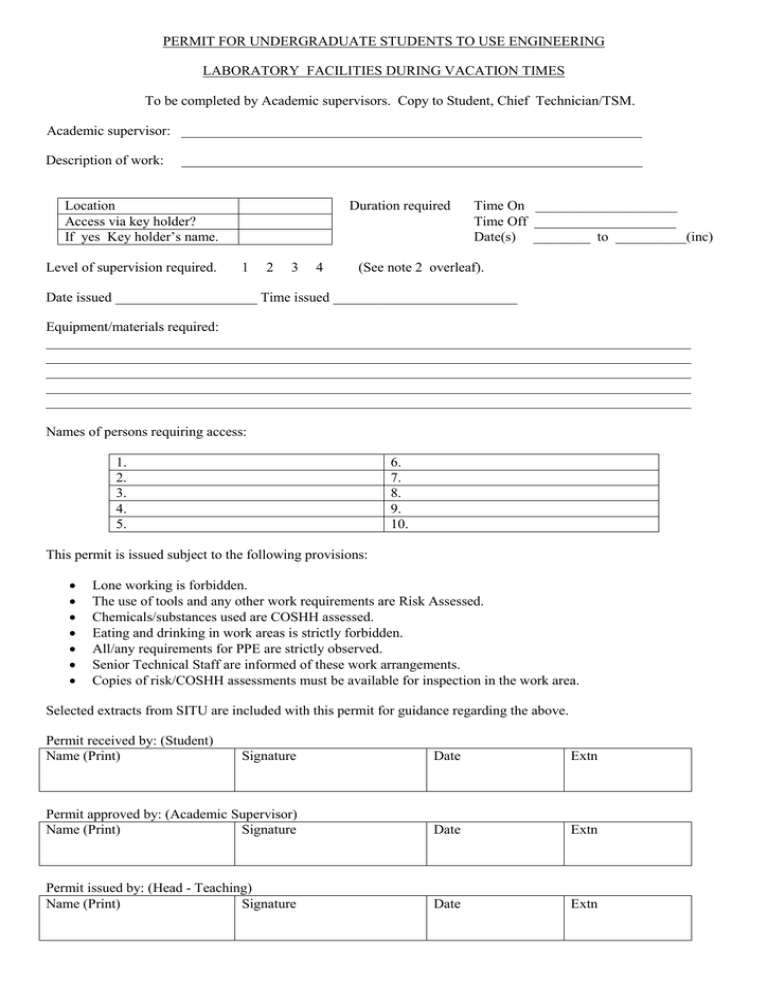
PERMIT FOR UNDERGRADUATE STUDENTS TO USE ENGINEERING LABORATORY FACILITIES DURING VACATION TIMES To be completed by Academic supervisors. Copy to Student, Chief Technician/TSM. Academic supervisor: _________________________________________________________________ Description of work: _________________________________________________________________ Location Access via key holder? If yes Key holder’s name. Level of supervision required. Duration required 1 2 3 4 Time On ____________________ Time Off ____________________ Date(s) ________ to __________(inc) (See note 2 overleaf). Date issued ____________________ Time issued __________________________ Equipment/materials required: ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ Names of persons requiring access: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. This permit is issued subject to the following provisions: Lone working is forbidden. The use of tools and any other work requirements are Risk Assessed. Chemicals/substances used are COSHH assessed. Eating and drinking in work areas is strictly forbidden. All/any requirements for PPE are strictly observed. Senior Technical Staff are informed of these work arrangements. Copies of risk/COSHH assessments must be available for inspection in the work area. Selected extracts from SITU are included with this permit for guidance regarding the above. Permit received by: (Student) Name (Print) Signature Date Extn Permit approved by: (Academic Supervisor) Name (Print) Signature Date Extn Permit issued by: (Head - Teaching) Name (Print) Signature Date Extn SELECTED EXTRACTS FROM S.I.T.U. FOR GUIDANCE. 2. CONTROL AND SUPERVISION 2.1 GENERAL 1 Departments must assess the need for supervision of staff, students, visitors and others who may be at risk. 2 Supervision and controls must be sufficiently stringent to, so far as is reasonably practicable, prevent accidents and illhealth. 3 There are four main levels of supervision: 1) work requiring continuous supervision (Eg Undergraduate practicals); 2) work requiring periodic supervision; 3) work which may not be started without the advice/permission of the supervisor; and 4) work requiring little or no supervision. 4 No detailed rules can be given on what is or is not adequate supervision. Each activity must be evaluated individually. 5 Factors to be considered include: risks of activities facilities and equipment; and training, experience, competence and personalities of people supervised. 6 Direct supervision means that there must be a competent person to: point out safety requirements before work starts; and be available within close proximity for consultation at all times. 7 Departments must decide on controls necessary to protect workers and others at risk. 8 Staff and students must be told what is expected of them and how they will be supervised. 9 People responsible for safety supervision and management must regularly inspect areas under their jurisdiction to ensure that acceptable standards are being maintained. 10 Supervision arrangements must be reviewed: if circumstances change; if there is an accident or incident; and periodically at pre-determined intervals. 11 Departments must ensure that supervisors: are identified; are trained and competent; and have documented responsibilities. 12 Suitable deputising arrangements must be made, where necessary, in case of illness or absence of staff. 2.3 UNDERGRADUATE SUPERVISION 1 Undergraduates must be adequately supervised at all times. 2 Health and safety instruction must be an integral part of Undergraduate courses. 3 Sufficient attendants must be present during practical classes to ensure that students are adequately supervised from the point of view of health and safety. 4 All undergraduates must be given a copy of the leaflet Safety in Laboratories - Instructions to Undergraduates and must sign and return the last page before they start practical work. Copies can be obtained from the Safety Office. 6. HYGIENE 1 If hazardous substances are handled, a sink should be set aside exclusively for hand washing. Soap, towels etc. must be available. Hands must be washed thoroughly after handling hazardous substances and before leaving the laboratory. 2 Smoking is not permitted in laboratories and workshops (see SITU Part 2). 3 Eating, drinking, chewing, application of cosmetics (apart from hand cream), licking labels and similar operations are not permitted in laboratories, workshops and other areas where potentially hazardous substances are used or stored. 4 The following should not be brought into such areas: food and drink. eating or drinking utensils; smoking materials; and cosmetics (excluding hand cream). personal belongings should be kept to the minimum and street clothing segregated from protective clothing. 5 Mouth pipetting (even of harmless substances) is not permitted. 6 Rooms must be adequately ventilated. 7 Potentially contaminated surfaces must be decontaminated as soon as practicable. 8 Safety signs must be observed (see SITU Part 2). 7.3 STUDENTS 1 Undergraduates must never work alone in laboratories or workshops, even on projects. 2 Postgraduate students may not work alone unless they have obtained prior permission from their supervisor. 3 The supervisor must define the type of work which may be carried out by the student working alone and any special conditions or restrictions that may apply. Written instructions should be issued. 7.5 COMPANIONS 1 Lone working may be avoided by the use of a companion. 2 Not everybody is a suitable companion. Companions need not have a detailed knowledge of the work but they must be familiar with the hazards; know what to do in an emergency; know location of phones, alarm points, extinguishers etc; be familiar with exits and building layout; and know how to summon help. 3 If reliance is placed on calling for assistance from someone some distance away, playing radios etc by either party is forbidden.

