Document 13202885
advertisement

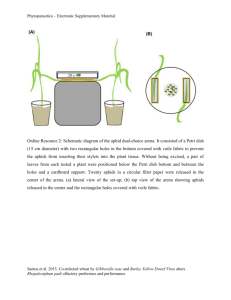
Resisting the currant-lettuce aphid Rosemary Collier, Warwick Crop Centre, School of Life Sciences Currant-lettuce aphid Nasonovia ribisnigri • Heteroecious - primary winter woody host and secondary summer herbaceous host • Holocyclic - asexual and sexual reproduction • Possibly anholocyclic sometimes surviving on lettuce and other related hosts including chicory, speedwell and hawkweed Control • Feeding location makes control difficult • Currently: – Insecticides with several different modes of action e.g. • Imidacloprid seed treatment • Systemic insecticide spirotetramat (Movento) – Resistant lettuce varieties • Introduced in 1998 • Introgressed a resistance gene (Nr) from the wild lettuce species L. virosa into commercial varieties of the cultivated lettuce L. sativa Resistance-breaking aphids (Rb) • Reported first in 2007 in continental Europe • Investigated by breeding companies – Rb Nasonovia developed on all lettuce varieties with Nr gene – Rb Nasonovia multipy more slowly than WT aphid on lettuce with no Nr gene – No significant differences between Rb aphids originating in France or Germany • Now in the UK Research on Nasonovia at Warwick • HDC project: Biology and control – Gemma Hough • HortLINK project: Control with pesticides and biopesticides • VeGIN: Identifying sources of resistance in diversity set Technique: • Infest test plants with fixed numbers of new-born nymphs • Cover plants with bread bags • Count aphids after a specific period of time Survival of WT and RB aphids – Gemma Hough Development time of WT and Rb aphids at different temperatures – Gemma Hough 50 45 5 °C Development t ime t o adult (days) 40 10 °C 35 15 °C 30 20 °C 25 25 °C 20 15 10 5 0 Rb Aphid + Saladin (Sus) Rb Aphid + Eluarde (Nr) Rb Aphid + Rotary (Nr) WT Aphid + Saladin WT Aphid + Eluarde WT Aphid + Rotary (Sus) (Nr) (Nr) Aphid t ype (Rb or WT) and lettuce variety (Sus or N r) At lower temperatures a few WT aphids overcome resistance Number of WT aphids recovered from tests on lettuce diversity set after 3 weeks (5 at start) Mean t otal number oper plant 500 400 300 Mapping parent 200 100 0 95 96 14 85 92 93 87 2 62 71 1 84 22 37 60 38 61 57 8 54 64 5 9 51 40 10 24 32 81 42 68 16 70 17 73 15 36 3 77 59 43 56 35 29 58 34 86 25 Range: 1.4 – 442 aphids per plant Number of WT aphids recovered from tests on lettuce diversity set after 3 weeks Mean t otal number per plant 600 500 400 300 200 100 0 21 7 75 90 63 13 88 26 30 31 11 44 4 67 74 91 12 28 33 23 78 52 79 69 47 18 41 49 39 50 89 6 80 83 76 82 48 19 45 46 53 72 66 20 94 55 65 Range: 1.4 – 442 aphids per plant Number of Rb and WT aphids recovered from tests on lettuce diversity set after 3 weeks 450 Mean total number per plant 400 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 95 96 14 85 92 93 87 2 62 71 84 37 60 38 61 57 8 54 64 5 9 51 40 10 24 32 81 42 68 16 70 17 73 15 36 77 59 43 56 35 29 58 34 86 25 27 Wild type aphids Resistance-breaking aphids Number of Rb and WT aphids recovered from tests on lettuce diversity set 1400 Mean total number per plant 1200 1000 800 600 400 200 0 21 7 75 90 63 13 88 26 30 31 11 44 67 74 91 12 28 33 23 78 52 79 69 47 18 49 39 50 89 6 80 83 76 82 48 19 45 46 53 72 66 20 94 55 65 Wild type aphids Resistance-breaking aphids Future work • The most resistant line was the wild species L. virosa. If a mapping population was available – then this could be followed up to map the resistance. • Failing that a backcross programme could be initiated – we have SNPs for all wild species. Future work • Based on the screen, one of our mapping parents showed some resistance – this will need to be confirmed • The mapping population could be used to map the resistance. There may be transgressive segregation for the trait in the population – meaning some lines may perform even better than the resistant parent • With the new SNP markers being genotyped in the population we can then map the trait using a new linkage map, and get informative markers that can be used for marker assisted selection in subsequent generations • These markers are linked to sequence so these will aid the mapping process • The markers have also been screened in the Salinas x Serriola (Michelmore) population, the alignment of common markers will open up the wealth of genomic resources at UC Davis Chicory and endive screen (Peter Walley & Gemma Hough) 21 Chicorium instybus and 29 Chicorium endivia Aphid numbers (Endive and Chicory) 1000 900 800 700 600 500 400 300 200 100 0 50 9 46 13 47 37 25 26 38 27 45 32 31 33 36 48 44 35 39 7 16 43 6 20 49 41 22 40 19 3 10 30 Thank you to: Defra Horticultural Development Company Gemma Hough Peter Walley Marian Elliott