π Δ σ
advertisement

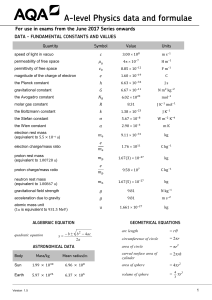
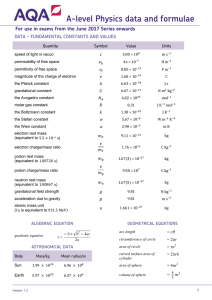
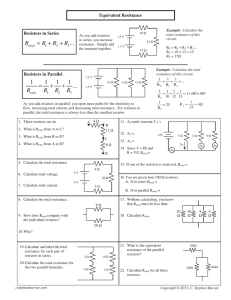
IM Syllabus (2013): Physics Data and Formulae Booklet The following equations may be useful in answering some of the questions in the examination. Uniformly accelerated motion: Circular motion: v = u + at 1 s = ut + at 2 2 2 2 v = u + 2as ⎛u+v⎞ s=⎜ ⎟t ⎝ 2 ⎠ Useful formulae: F = kΔx F σ = A Δl ε= l Hooke's law: Stress: Strain: Young's modulus: Y= σ ε Energy stored in a stretched wire: E= 1 2k ( Δl ) 2 Fields due to point sources: Period: T = 2π r v Momentum: p=mv Newton’s second law: F = ma Kinetic energy: KE = Gravitational potential energy: PE = Δ ( mgh ) Mechanical work done: W = FΔd 1 2 mv 2 Vibrations and waves: Q1 Q2 Force between point charges: F= Force between point masses: M M F = G 12 2 r 4πε 0 r 2 Current electricity: Acceleration in s.h.m.: a = –k x Period: T = 2π Velocity of a wave: v = fλ k Electromagnetism: Current: I = nAve Ohm’s law: V = IR Resistors in series: RTOTAL = R1 + R2 + … Power: a= Mechanics: Materials: Resistors in parallel: v2 r Centripetal acceleration: 1 RTOTAL = E= Electric field strength: 1 1 + + ... R1 R 2 2 P = IV = I R = V 2 R F q Electric potential (uniform field): V = E d Energy of a particle accelerated by an electric field: QV = Δ ( 1 2 mv 2 ) Force on a moving charge: F = BQv Magnetic flux: Φ = BA Force on current: F = BIl Emf induced in a moving conductor: E = Blv 1 IM Syllabus (2013): Physics Induced emf: Charge on capacitor: Q = CV Parallel-plate capacitor: C= ε 0ε r A d Root mean square for sinusoidal alternating current I V and voltage: I rms = 0 ; V rms = 0 2 2 Physics of nuclei and atoms: Ray optics: Magnification: dt Alternating current: Capacitance: Thin lenses: E = − N dΦ 1 1 1 = + (real is positive) f u v 1 1 1 = − (Cartesian) f v u v h m = = i (real is positive) u ho m=− Radioactivity: A = λN Mass-energy relation: E = mc 2 Line spectra: ΔE = hf = hc λ h v = − i (Cartesian) u ho Mathematical Formulae: Surface area of a sphere: S = 4π r 2 Volume of a sphere: V= Surface area of a cylinder: S = 2π rh + 2π r 2 Volume of a cylinder: V = π r 2h 4 3 πr 3 The following constants may be useful in answering some of the questions in the examination. Acceleration of free fall on and near the Earth’s surface g = 9.81 m s−2 Gravitational field strength on and near the Earth’s surface g = 9.81 N kg−1 Coulomb’s law constant k = 1/(4πεo) = 8.99 × 109 N m2 C−2 Charge of an electron e = −1.60 × 10−19 C Mass of an electron me = 9.11 × 10−31 kg Electronvolt 1 eV = 1.60 × 10−19 J Gravitational constant G = 6.67 × 10−11 N m2 kg−2 Permittivity of free space εo = 8.85 × 10−12 F m−1 Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10−34 J s Speed of light in a vacuum c = 3.00 × 108 m s−1 Unified atomic mass unit u = 1.66 ×10−27 kg 2