Document 12822801
advertisement

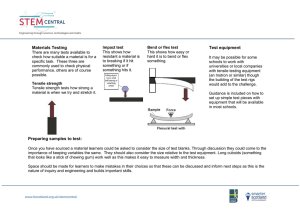
It is the maximal stress required to fracture a structure. The three basic types of strength are: 1- Tensile strength. 2- Compressive strength. 3- Shear strength. It is the maximal tensile stress the structure will withstand before rupture. Tensile strength is measured by subjecting a rod, wire or dumbbell shaped specimen to a tensile loading (unilateral tension test). Brittle materials are difficult to test by using the unilateral tension test. Instead, an indirect tensile test called diametral compression test is used. In this method, a compressive load is placed on the diameter of a short cylindrical specimen. ( ) It is the deformation that results from the application of a tensile force. The flexural strength of a material is obtained when one loads a simple beam, simply supported (not fixed) at each end, with a load applied in the middle, such a test is called (three-point bending test). Flexural strength test is especially useful in comparing denture base materials in which a stress of this type is applied to a specimen of denture acrylic with masticatory loads. It is the resistance to motion of one material body over another. If an attempt is made to move one body over the surface of another, a restraining force to resist motion is produced; this restraining force is the (static) frictional force and results from the molecules of the two objects bonding where their surfaces are in close contact. Figure (1-20): Microscopic area of contact between two objects. The frictional force, which resists motion, is proportional to the normal force and the coefficient of friction. It is a loss of material resulting from removal and relocation of materials through the contact of two or more materials Tooth brushing with a dentifrice may cause wear of teeth. Adhesion is the force which causes two different substances to attach when they are brought in contact with one another. When the molecules of the same substance hold together; the forces are said to be cohesion.