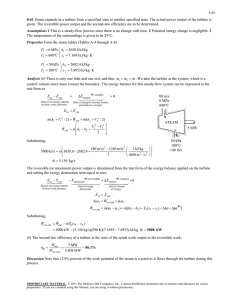
6-35 are to be determined. are negligible.
advertisement
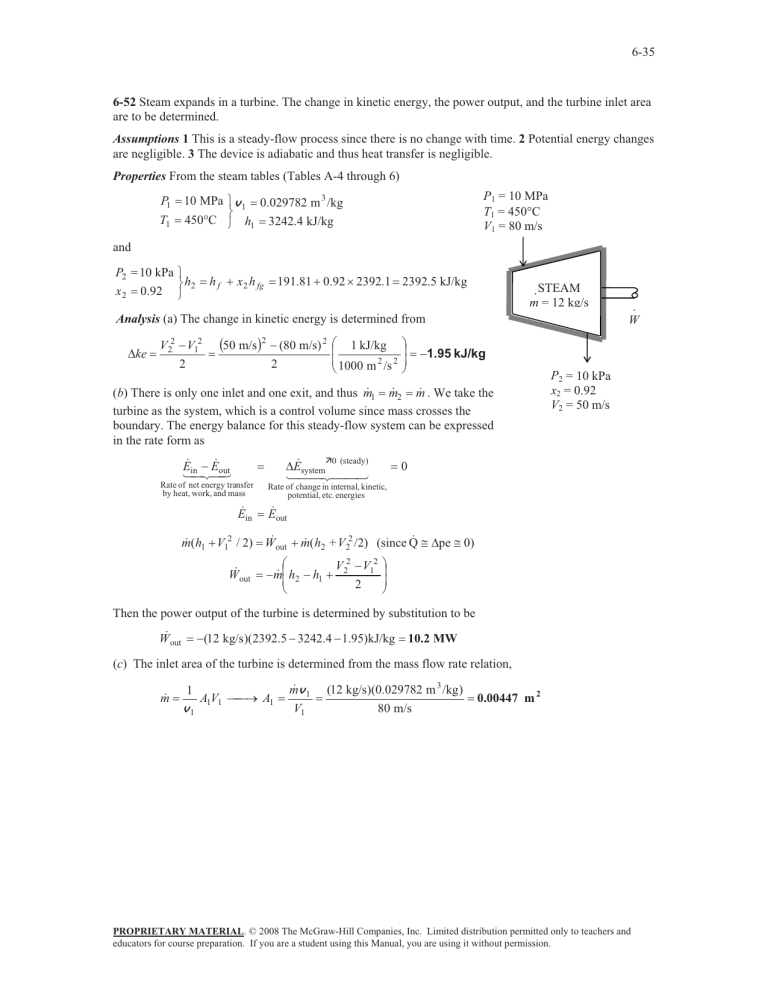
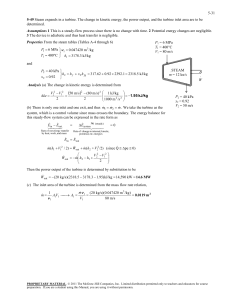
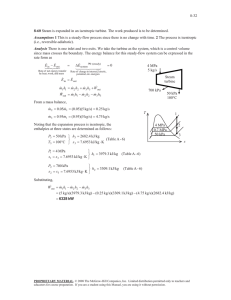
6-35 6-52 Steam expands in a turbine. The change in kinetic energy, the power output, and the turbine inlet area are to be determined. Assumptions 1 This is a steady-flow process since there is no change with time. 2 Potential energy changes are negligible. 3 The device is adiabatic and thus heat transfer is negligible. Properties From the steam tables (Tables A-4 through 6) P1 T1 P1 = 10 MPa T1 = 450qC V1 = 80 m/s 10 MPa ½ v 1 0.029782 m 3 /kg ¾ 450qC ¿ h1 3242.4 kJ/kg and P2 x2 10 kPa ½ ¾ h2 0.92 ¿ h f x 2 h fg 191.81 0.92 u 2392.1 2392.5 kJ/kg · STEAM m = 12 kg/s Analysis (a) The change in kinetic energy is determined from 'ke V 22 V12 2 50 m/s 2 (80 m/s) 2 2 § 1 kJ/kg ¨ ¨ 1000 m 2 /s 2 © · ¸ ¸ ¹ 1.95 kJ/kg 1 m 2 m . We take the (b) There is only one inlet and one exit, and thus m turbine as the system, which is a control volume since mass crosses the boundary. The energy balance for this steady-flow system can be expressed in the rate form as E in E out 'E systemÊ0 (steady) Rate of net energy transfer by heat, work, and mass Rate of change in internal, kinetic, potential, etc. energies E in · W P2 = 10 kPa x2 = 0.92 V2 = 50 m/s 0 E out # 'pe # 0) m (h1 V12 / 2) W out m (h2 + V 22 /2) (since Q W out § V 2 V12 m ¨ h2 h1 2 ¨ 2 © · ¸ ¸ ¹ Then the power output of the turbine is determined by substitution to be W out (12 kg/s)(2392.5 3242.4 1.95)kJ/kg 10.2 MW (c) The inlet area of the turbine is determined from the mass flow rate relation, m 1 v1 o A1 A1V1 m v 1 V1 (12 kg/s)(0.029782 m 3 /kg ) 80 m/s 0.00447 m 2 PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. © 2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Limited distribution permitted only to teachers and educators for course preparation. If you are a student using this Manual, you are using it without permission.