AP Physics Vectors Worksheet 2 Vector Addition
advertisement

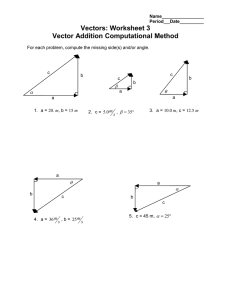
Name Period Date AP Physics Vectors Worksheet 2 Vector Addition Computationally determine the resultants. Be sure each resultant has both a magnitude and a direction. 1. You walk 15 m East , then 25 m at 30. North of East . What is your displacement? a. Begin by sketching a vector diagram of the situation needed to find the resultant displacement. b. Sketch the perpendicular components for each vector shown below, and then calculate these perpendicular components. 15 m 25 m 30.º c. Calculate the perpendicular components of the resultant, sketch a new vector diagram using these components, and then calculate the resultant displacement. AP Vectors Worksheet 2 page 2 2. You are flying in a plane moving 150. m at 65 North of West, when a 40. m wind s s begins to blow at 40. North of East . What is your resultant velocity? a. Begin by sketching a vector diagram of the situation needed to find the resultant velocity. b. Sketch the perpendicular components for each vector shown below, and then calculate these perpendicular components. 40. m/s 40.º 150. m/s 65º c. Calculate the perpendicular components of the resultant, sketch a new vector diagram using these components, and then calculate the resultant velocity. AP Vectors Worksheet 2 page 3 3. Velocities A and B are as shown. Calculate both in unit vector notation and in polar coordinates (magnitude and direction) A B . A 15 m y 40.o 20.o x B 9 .0 m s s AP Vectors Worksheet 2 page 4 4. A particle undergoes three successive displacements in a plane as follows: 4.00 m due Southwest , 5.00 m East , and 6.00 m in a direction 60.0 North of East . a. Find the magnitude and direction of the resultant displacement. b. Find the displacement that would be required to bring the particle back to the starting position. AP Vectors Worksheet 2 page 5 5. Two displacements are given by a 4iˆ 3 ˆj kˆ and b iˆ ˆj 4kˆ where both are in meters. Find the following in unit vector notation. a. a b b. a b c. A vector c such that a b c 0 . 6. Two displacements are given by a 4.0 m iˆ 3.0 m ˆj and b 6.0 m iˆ 8.0 m ˆj . Find the magnitudes and directions of the following. a. a b. b c. a b d. b a AP Vectors Worksheet 2 page 6 e. a b f. How do the orientations of (d) and (e) compare? 7. You walk 22 m South , then 15 m at 35 South of West , then 8.0 m at 20. South of East. What is your displacement?