Universal Gravitation Worksheet 5 m x kg
advertisement

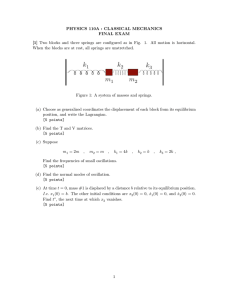
Name Period Date Universal Gravitation Worksheet 5 6 22 1. The Earth’s moon has a radius of 1.74 x10 m and a mass of 7.36 x10 kg . a. What is the free-fall acceleration of an object dropped at the surface of the moon? Draw a force diagram for the object. b. How much would a 1500. kg spaceship weigh at the surface of the Earth? What about at the surface of the moon? 2. A certain planet has a radius that is twice that of the Earth and a mass that is only half that of the Earth. What would be the free-fall acceleration at the surface of this planet? (Hint: Use proportional thinking.) v 3. Assume that the diagram to the right represents the circular orbit around the Earth of a satellite at an altitude of 1000. km above the surface of the Earth. The Earth has a mean radius 24 6 of 6.38 x10 m and a mass of 5.98 x10 kg . a. Draw a force diagram of the satellite in orbit. b. Draw a motion map for one complete orbit of the satellite. Universal Gravitation Worksheet 5 page 2 c. What is the radius of the orbit of the satellite? d. What is the orbital speed of the satellite given its circular orbit? e. What is the orbital period of the satellite? f. Is this satellite being accelerated? How do you know? If so, what is the direction and magnitude of the acceleration? 4. The earth's orbit around the sun is very nearly circular, with an average radius of 1.50 x1011 m . Assume the mass of the earth is 5.98 x10 24 kg and the mass of the 30 sun is 1.99 x10 kg . a. What is the period of the Earth’s orbit around the sun in seconds? b. What is the average speed of the earth in its orbit around the sun? c. What is the magnitude of the earth's average acceleration in its orbit around the sun? Show your work. d. With what force does the sun attract the earth?