Stuff I Should Know (Page 2) 2nd DRAFT
advertisement

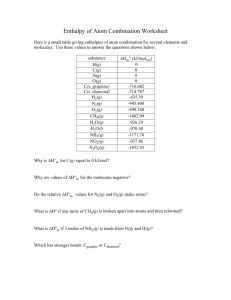
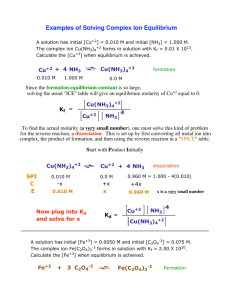
Stuff I Should Know (Page 2) 2nd DRAFT Complex Ions & Common Ligands Ligands polar molecules & anions Central Ions transition metals and Al3+ Examples usually twice the number of ligands as the charge on the central ion. Key Words: “excess, concentrated” Organic Chemistry & Functional Groups alkanes alkenes Cn H2n+2 Cn H2n alcohol NH3 , H2 O, OH−, CN−, Cl− Ag +, Cu 2+, Ni2+, Zn2+, etc. & Al3+ Ag(CN)2 −, Cu(NH3 )4 2+, Ni(OH)4 2−, Zn(NH3 )4 2+, Al(OH)6 3− alkynes Cn H2n−2 aromatics (benzene) C6 H6 ketone ether aldehyde Odd example: Fe3+ + SCN− FeSCN2+ Reaction with Acid: Cu(NH3 )4 2+ + H+ → Cu 2+ + NH4 + nuclear chem alpha 4 2 He beta/electron 0 −1 carboxylic acid ester amine amide e neutron 1 0 n positron Substituted benzene: ortho = 1,2 meta = 1,3 0 +1 para = 1,4 e Lewis Acids & B ases BF3 + NH3 → BF3 NH3 acid anhydrides (oxides of nonmetals, CO2 ) basic anhydrides (oxides of metals, MgO) MgO + CO2 → MgCO3 decomposition reactions: MgCO3 → MgO + CO2 Strange Examples: P4 O10 + H2 O → H3 PO4 Electrochemical Cells anode cathode oxidation reduction + side − side lower E° higher E° e− leave e− enter Strange Ions: (nitride, N3−) (hydride, H−) Li + N2 → Li3 N LiH + H2 O → H2 + Li+ + OH− SN & hybridization & shape Steric Number hybridization 1 s 2 sp 3 sp2 4 sp3 5 sp3 d 6 sp3 d2 Flame Test Colors Barium – green Sodium – yellow Copper – blue (w/ green) Potassium – lavender Strontium – red Lithium – red Calcium – orange Quantum Numbers 1, 2, 3, … n l 0 … (n−1) ml −l … +l ms +½, −½ l IMF’s London dipole−dipole hydrogen bonding 0 = s, 1 = p, 2 = d, 3 = f Writing Lewis Structures hint: use one valence electron to connect F’s or Cl’s then determine lone pairs (Ex: XeF4 ) metallic ionic Product−Favored Reactions ∆G < 0 E° > 0 Keq > 1 covalent network IMF BP FP Hvap Hfus IMF BP FP Hvap H fus VP VP Orders of Reactions & Graphs That Give Straight Lines 0 Order 1st Order 2nd Order [R] vs. Time ln[R] vs. Time 1/[R] vs. Time slope = -k slope = -k slope = k Bond Orders bond B.O. single 1 σ double 2 σ+π triple 3 σ+π+π basic shape −− linear r planar tetrahedral r bipyramidal octahedral nonpolar molecules, ex: CH4 , He polar molecules, ex: H2 S, SO2 H−F, H−O−, H−N−, NH3 , H2 O amines and alcohols metals, Ag, Pb salts, NaCl, Ca CO3 (Note: “ates” contain covalent bonds) C(graphite), C(diamond), SiO2 , WC, Si, SiC (Note: graphite = London, too) Activity of Metals (Four Groups) Metals React with… Groups I & II H2 O ex: Li + H2 O → Li+ + OH− + H2 Non-oxidizing Acid, ex: HCl all others Zn + 2HCl → H2 + ZnCl2 Oxidizing Acid, HNO3 or H2 SO4 (conc.) Cu, Ag, Hg Cu + HNO3 → NO2 + H2 O + Cu 2+ Au, Pt, Ir Aqua Regia (HNO3 + HCl)