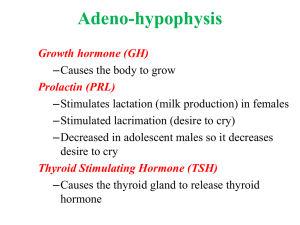
Diagnosing Endocrine Problems
advertisement

Diagnosing Endocrine Problems PHYSIOLOGY OF DISEASE AND TREATMENTS Addison’s Disease Cause Cortex portion of adrenal gland underactive Symptoms Low blood sugar, low blood Na+, loss of water, tiredness, and yellowing of the skin Use of cortisone Myxedema Cause Occurs in Adults Thyroid gland is underactive Decreases the production of thyroxin Symptoms Lowered metabolism, changes in skin texture, puffiness of the face, a decrease in mental abilities Treatment Use of thyroid extract Myxedema Acromegaly Cause The pituitary gland over secretes human growth hormone in adults Symptoms Bones thicken, especially in the hands, the feet, and the face Treatment No available treatment Cretinism Cause Little to no thyroxin is produced from birth Symptoms In infants, face swells, lips become large, and tongue becomes thick Physical and mental growth is stunted Treatment Use of thyroid extract Dwarfism Cause Pituitary gland under secretes human growth hormone Symptoms Stunted growth Relative size of body parts is normal Treatments Use of growth hormone before skeletal growth is completed Hypoglycemia Causes Pancreas produces too much insulin Symptoms Low blood sugar levels, dizziness, intense hunger, and weakness Treatment Control of blood sugar by diet Hyperthyroidism Causes Thyroid is overactive, producing too much thyroxin Symptoms High metabolic rate, excitability, rapid speech, anxiety, increased appetite, and weight loss Treatment Medication to stop production of thyroxin; surgery if thyroid is enlarged Hypothyroidism Cause Thyroid is underactive, producing too little thyroxin Symptoms Low metabolic rate, dry skin, reduced alertness, and weight gain Treatment Use of thyroid extract Diabetes Mellitus Causes Little or no insulin is produced by the islets of Langerhans in the pancreas Symptoms Uncontrolled blood sugar levels, excessive urination, weakness, excessive appetite, and weight loss Treatment Careful planning of diet Exercise Regular injections of insulin Diabetes insipidus Cause Posterior lobe of pituitary gland is underactive, producing too little vasopressin Very uncommon Due to head injury or tumor Symptoms Excessive thirst and increased urination Kidney’s unable to conserve water Treatments Careful planning of diet Complete the case studies on the back! Bellwork Matching: They may have more than one answer. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. TSH FSH ADH OT GH LH Luteinizing hormone Labor contractions, milk ejection Stimulates body cell division Thyroid stimulating hormone Oxytocin Antidiuretic Hormone Ovulation, formation of corpus luteum h. Follicle stimulating hormone i. Reabsorption of water, elevation of blood pressure and volume j. Estrogen secretion, sperm maturation k. Secretion of thyroid hormones l. Promotes long bone growth a. b. c. d. e. f. g. Outline for Endocrine Test Performance enhancing drugs EPO, testosterone, blood doping, GH, steroids, Effects as a performance enhancing drug Possible side effects of drugs Label organs/glands of endocrine system Hypothalamus, pineal, pituitary gland, parathyroid, thyroid, thymus, pancreas, adrenal, ovaries, testes Hormones: actions/functions and site of production Aldoesterone, cortisol, epinephrine, GnRH, estrogen, insulin, glucagon, PTH, melatonin, ADH, oxytocin, FSH, LH, testosterone, thymosin, cacitonin, HCG