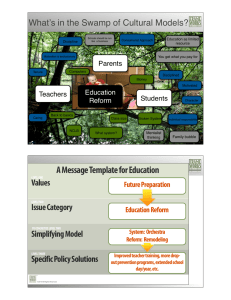
Implications for Consumer Engagement in National Health Reform: Cautionary Tales and New
advertisement

Implications for Consumer Engagement in National Health Reform: Cautionary Tales and New Opport nities Opportunities Marilyn y Moon, Ph.D. Vice President and Director, Health Program June 29, 2010 Health Reform – A Movement T Toward dV Value-Driven l D i Health H lth C Care Reforms insurance system Requires quality reporting and advancement Promotes innovations Funds research and establishes knowledge centers Fortifies patients’ roles as partners in care Health Reform Will Require Consumer Engagement to be Successful Choose among health plan options Hold providers accountable Respond p to “value based” p purchasing g and p plans Understand evidence-based findings and implications for changes in care Monitor security of personal health information Seek p preventive care Practice healthy behaviors H lth C Health Care C Consumer Needs N d Access Meaningful g information Resources to act Social and emotional support Confidence Time Assurances of privacy and security Transparency Challenges to Consumer E Engagement t System complexity Communication barriers Changes to traditional employer-employee relationship New concepts p to consumers Proliferation of information and information sources Changes to traditional provider-patient relationship Effect of Health Reform on C Consumers Will Vary V Differential impacts on consumers based on Education Income Culture Skills Familiarity with system Confidence Advocacy Patients Have Beliefs That Challenge Key Goals of Evidence-based Health Care Patients believe: More care is better Newer care is better More costlyy care is better Their physicians know best Treatment ea e dec decisions so sa and d health care quality should not be discussed in terms of costs ““I don’t ’ see how extra care can be harmful to your health health. Care would only benefit you.” “Because if you’re “B ’ going i to have a doctor that’s better he better, he’llll charge more.” Patients Are Unfamiliar With Key Tenets of Evidence-based Health Care Unfamiliar U f ili with ith th the tterms 8 “medical evidence,” quality guidelines guidelines,” and “quality “quality standards” Only 49% said they had heard about medical research and only 34% had ever had a physician discuss the topic with them “Of Of course my doctor uses evidence-based medicine. He makes decisions based on the available evidence— things like my test results and medical history history.” Facilitators for Consumer E Engagement t Tools State Health Insurance Exchanges State websites to aid consumer decision-making Quality reporting Innovations Demonstration D t ti projects j t Health Home innovations Meaningful use Telehealth e e ea t Use Approaches and Venues A Appropriate i t to t Audience A di Need N d tto fifind d outt where h people l gett information Develop user-centric materials Adapt materials to site Be aware of cultural sensitivity Use multiple contacts Incorporate perspective of friends and family