Hospital Ownership and Financial Performance: An Integrative Research Review Yu-Chu Shen
advertisement

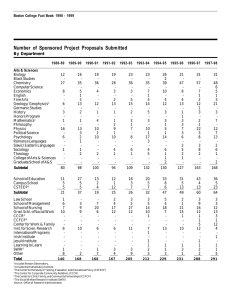
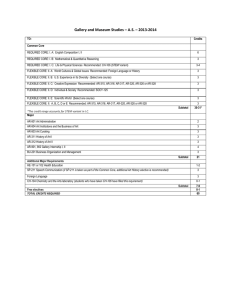
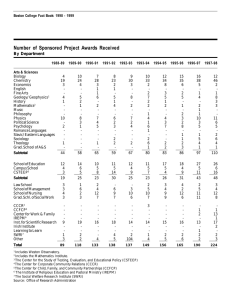
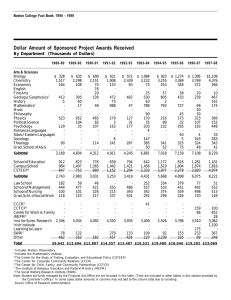
Hospital Ownership and Financial Performance: An Integrative Research Review Academy Health Annual Research Meeting Boston, June 28, 2005 Yu-Chu Shen Naval Postgraduate School and NBER Karen Eggleston, Joseph Lau, Christopher Schmid Tufts University Funded by grant #050953 under the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation’s Changes in Health Care Financing and Organization (HCFO) Initiative Research Objective • Does ownership affect hospital financial performance (cost, revenue, profit, efficiency)? • Competing theories with contrasting • predictions Hundreds of empirical studies to date with conflicting findings • • policymakers have little clear evidence economics of ownership and behavior imperfectly understood Scope of the Integrative Review Synthesize the main findings of the empirical literature between January 1990 and July 2004 on hospital ownership and performance (published or unpublished) Examine multivariate empirical studies of US acute general short stay hospitals; Examine studies that compare differences between for-profits and nonprofits, between nonprofits and government, or both. Scope of the Integrative Review We start with 1434 potentially relevant studies, and end up with 141 studies for the integrative review. Focus on four broad categories of performance measures: financial performance (cost, revenue, profit, and efficiency) quality / patient outcomes uncompensated care or community benefits Staffing Presentation Is Focused On Four Financial Measures Number of studies analyzed the outcome Number of articles with usable information Outcomes Reviewed Operating cost Patient revenue and returns on assets 22 19 14 11 Profit margin 17 14 Cost and technical efficiency 19 15 Integrative Review Research Questions 1. What is the magnitude of the difference between NFP and FP— what is the effect size? 2. How precise or reliable is this estimated effect size? 3. How do differences in analytic methods and other study features affect the estimates of effect size? Categorizing Analytical Methods Three types of methodology rigor Type 3: if a study meets both of the following conditions: (a) uses panel estimation or explicitly accounts for potential selection problem (b) includes two of the following three sets of controls: patient level, hospital level, market level Type 2: if meets EITHER (a) or (b) Type 1: if meets NEITHER (a) nor (b) Cost: Summary of N-F Effect Size By Method Types Effect size (95% CI) Study method_level==0 gautam1996 Method Type 1 % Weight 0.11 ( 0.04, 0.18) 5.3 wang2001 0.23 ( 0.01, 0.45) 1.6 shukla1997 0.27 ( 0.05, 0.49) 1.6 0.16 ( 0.06, 0.25) 8.5 campbell1990 -0.23 (-0.38,-0.08) 2.7 goes1995 -0.08 (-0.12,-0.04) 6.3 -0.03 (-0.08, 0.02) 6.0 Subtotal method_level==1 fournier1997 connor1998 Method Type 2 -0.01 (-0.03, 0.02) 6.8 becker2002 0.04 ( 0.01, 0.06) 6.7 clement1997 0.04 ( 0.00, 0.08) 6.3 lawrence1990 0.12 ( 0.03, 0.20) 4.6 -0.01 (-0.05, 0.04) 39.4 shen2003b -0.06 (-0.08,-0.04) 6.8 wilcox-gok2002 -0.05 (-0.10, 0.00) 6.1 -0.04 (-0.05,-0.02) 6.9 0.00 (-0.02, 0.03) 6.8 mark1999 0.02 ( 0.01, 0.03) 7.0 zeckhauser1995 0.05 (-0.00, 0.11) 5.8 bazzoli2000 0.08 ( 0.02, 0.14) 5.7 potter2001 Subtotal method_level==2 carey2000 carey1997 Method Type 3 0.11 ( 0.10, 0.13) 6.9 Subtotal 0.01 (-0.03, 0.06) 52.0 Overall 0.02 (-0.01, 0.05) 100.0 FP is less costly -.48845 0 Effect size FP is more costly .488456 Revenue: Summary of N-F Effect Size By Method Type Study Effect size (95% CI) method_level==0 molinari1993 shukla1997 wang2001 Subtotal 0.21 ( 0.06, 0.36) 0.28 ( 0.06, 0.50) 0.35 ( 0.14, 0.57) 0.26 ( 0.16, 0.37) 4.5 2.4 2.4 9.3 0.04 ( 0.02, 0.06) 0.07 ( 0.04, 0.11) 0.08 (-0.07, 0.23) 0.12 ( 0.10, 0.14) 0.08 ( 0.03, 0.13) 13.1 12.0 4.2 13.1 42.4 -0.02 (-0.04, 0.00) 0.00 (-0.06, 0.06) 0.02 ( 0.01, 0.03) 0.04 (-0.01, 0.09) 0.01 (-0.02, 0.03) 13.2 10.3 13.6 11.2 48.3 0.06 ( 0.03, 0.10) 100.0 method_level==1 connor1998 clement1997 gapenski1993 younis2001 Subtotal method_level==2 shen2003b bazzoli2000 mark1999 wilcox-gok2002 Subtotal Method Type 1 Method Type 2 Method Type 3 Overall FP-.57406 generates less revenue 0 Effect size FP generates more .574063 revenue % Weight Revenue: Summary of N-F Effect Size By Covered Region Study Effect size (95% CI) national==0 wilcox-gok2002 gapenski1993 Single state molinari1993 sample shukla1997 wang2001 Subtotal 0.04 (-0.01, 0.09) 0.08 (-0.07, 0.23) 0.21 ( 0.06, 0.36) 0.28 ( 0.06, 0.50) 0.35 ( 0.14, 0.57) 0.17 ( 0.05, 0.29) 11.2 4.2 4.5 2.4 2.4 24.8 national==1 shen2003b bazzoli2000 mark1999 connor1998 clement1997 younis2001 Subtotal -0.02 (-0.04, 0.00) 0.00 (-0.06, 0.06) 0.02 ( 0.01, 0.03) 0.04 ( 0.02, 0.06) 0.07 ( 0.04, 0.11) 0.12 ( 0.10, 0.14) 0.04 (-0.00, 0.08) 13.2 10.3 13.6 13.1 12.0 13.1 75.2 0.06 ( 0.03, 0.10) 100.0 National sample Overall FP-.57406 generates less revenue 0 Effect size FP generates more .574063 revenue % Weight Profit Margin: Summary of N-F Effect Size By Method Type Effect size (95% CI) Study method_level==0 molinari1993 shukla1997 wang2001 Subtotal method_level==1 gapenski1993 goes1995 picone2002 clement1997 connor1998 thorpe2001 Subtotal method_level==2 bazzoli2000 mark1999 wilcox-gok2002 shen2003b zeckhauser1995 Subtotal Method Type 1 Method Type 2 Method Type 3 Overall FP earns lower profit -.49741 0 Effect size % Weight 0.20 ( 0.06, 0.35) 0.22 ( 0.00, 0.44) 0.28 ( 0.06, 0.50) 0.23 ( 0.12, 0.33) 3.5 1.9 1.9 7.4 -0.09 (-0.24, 0.06) -0.03 (-0.07, 0.00) 0.02 ( 0.02, 0.03) 0.04 ( 0.00, 0.08) 0.06 ( 0.03, 0.08) 0.28 ( 0.25, 0.32) 0.06 (-0.02, 0.13) 3.3 8.8 9.9 8.8 9.5 9.0 49.2 0.01 (-0.05, 0.07) 0.02 ( 0.00, 0.03) 0.02 (-0.02, 0.07) 0.02 ( 0.00, 0.04) 0.05 (-0.01, 0.10) 0.02 ( 0.01, 0.03) 7.7 9.9 8.3 9.6 8.0 43.4 0.06 ( 0.02, 0.09) 100.0 FP earns higher profit .497418 Profit Margin: Summary of N-F Effect Size By Covered Region Study Effect size (95% CI) national==0 gapenski1993 goes1995 wilcox-gok2002 zeckhauser1995 molinari1993 Single state shukla1997 wang2001 sample Subtotal -0.09 (-0.24, 0.06) -0.03 (-0.07, 0.00) 0.02 (-0.02, 0.07) 0.05 (-0.01, 0.10) 0.20 ( 0.06, 0.35) 0.22 ( 0.00, 0.44) 0.28 ( 0.06, 0.50) 0.05 (-0.01, 0.12) 3.3 8.8 8.3 8.0 3.5 1.9 1.9 35.7 national==1 bazzoli2000 mark1999 shen2003b picone2002 clement1997 connor1998 thorpe2001 Subtotal 0.01 (-0.05, 0.07) 0.02 ( 0.00, 0.03) 0.02 ( 0.00, 0.04) 0.02 ( 0.02, 0.03) 0.04 ( 0.00, 0.08) 0.06 ( 0.03, 0.08) 0.28 ( 0.25, 0.32) 0.06 ( 0.02, 0.11) 7.7 9.9 9.6 9.9 8.8 9.5 9.0 64.3 0.06 ( 0.02, 0.09) 100.0 National sample Overall FP earns -.49741lower profit 0 Effect size FP earns higher .497418 profit % Weight Efficiency: Summary of N-F Effect Size By Covered Region Study Effect size (95% CI) national==0 li2001 chirikos2000 chirikos1994 ferrier1996 sari2003 Subtotal 0.09 (-0.00, 0.18) 0.11 ( 0.07, 0.15) 0.12 (-0.03, 0.26) 0.19 ( 0.11, 0.26) 0.30 ( 0.24, 0.37) 0.16 ( 0.08, 0.25) 6.5 7.4 5.4 6.9 7.0 33.3 -0.17 (-0.20,-0.14) -0.12 (-0.16,-0.07) -0.11 (-0.13,-0.09) -0.07 (-0.10,-0.04) -0.06 (-0.11,-0.02) -0.06 (-0.10,-0.02) -0.06 (-0.11,-0.01) 0.08 ( 0.05, 0.11) 0.12 ( 0.08, 0.17) -0.05 (-0.11, 0.01) 7.5 7.3 7.6 7.5 7.3 7.4 7.3 7.5 7.3 66.7 0.02 (-0.04, 0.08) 100.0 national==1 rosko1999 brown2003 rosko2001b folland2001 koop1997 ozcan1992 zuckerman1994 burgess1996 rosko2001a Subtotal Single state sample National sample Overall FP is less efficient -.37047 0 Effect size FP is more efficient .370474 % Weight What Do We Learn? (1) Evidence is pretty conclusive regarding revenue and profit margins Most studies find for-Profits earn more revenue (per admission) and have higher profit margins There is little evidence of any difference in cost between FP and NFP hospitals Evidence is mixed regarding efficiency. Single state (Florida) analyses find FP more efficient, national analyses tend to find FP less efficient. What Do We Learn? (2) Functional forms and analytical methods matter Weaker methods and functional forms tend to predict larger differences between not-for-profits and for-profits National samples tend to produce more conservative estimates of effect size than single state analyses