Name:_____________ Chemistry 112 Third Hour Exam
advertisement

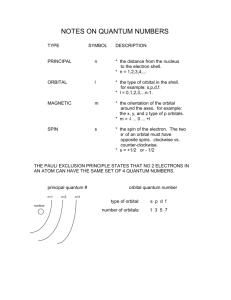
Name:_____________ Chemistry 112 Third Hour Exam Remember- Show all work for partial credit 1. (10 points) A sample of air expands from 2L to 4L in volume at a constant pressure of 2.4 atm. At the same time the gas is heated with 500 J of energy. What is the )E for this system. w= -P)V = -2.4atm ×2L = - 4.8 l@atm -4.8 l@atm × 101.3 J/l@atm = -486.24 J E=q+w = +500 J -486 J =14 J 2. (10 points) What is the difference between a state function and a path function. Give an example of each State Function: A variable or property that only depends on the current state of a system. Examples: )H or )E Path Function: A variable or property of that depends on the path taken between two state of a system. Examples: w or q 2 3. During cold weather I occasionally use a hand & pocket warmer. Basically these are sealed packages of iron filings, which, when you open the package and expose it to air, undergoes the reaction: 4Fe(s) + 3O2(g) 62Fe2O3(s) + 4H2O(l) )H= -1652 kJ A. (5 points) Assume the hand warmer contains 25 g of Fe, how much heat will this release? 25 g Fe × 1 mol/55.85 g Fe = .4476 mol Fe X kJ heat − 1652 kJ heat = ; .4476 molFe 4 mol Fe X = − 185 kJ B. (5 points) To model the effect of the hand warmer on my hands, I will assume that my hands contain about 2000 g of water that is at 15oC. Using this model, how warm will my hands get, (what is the final T?) after all the heat from the warmer is transferred to the water. (Specific heat capacity of water = 4.18 J/(oC@g)) Heat = Specific Heat Capacity × g × )T 185,000 J = 4.18 J/(oC@g)× 2000 × )T )T = 185000/(4.18×2000) = 22.1oC Tfinal = Tinitial + )T = 15+22.1 = 37.1oC 4. I am going to run the reaction A + B 6C inside a constant pressure calorimeter. A. (2 points) What is the name of the energy I will be measuring? )H or enthalpy B. (4 points) The calorimeter contains 50g of water that is initially at 25oC. After the reaction the temperature of the water is 15.5oC. How much energy was produced (or absorbed) in this reaction. (Specific heat capacity of water = 4.18 J/(oC@g)) Heat = Specific Heat Capacity × g × )T = 4.18 × 50 ×(25-15.5) = 1985.5 water got colder so this is an endothermic reaction so sign should be positive = + 1985.5 J C. (4 points) If the reaction mixture contained .005 moles each of A and B, what was the energy released (or absorbed) per mole of reactant. 1985.5 J/.005 mol = X J/1 mol =397100 J or 397.1kJ 3 5. (10 points) Estimate )Hrxn for the reaction NaCl(s) 6 Na+(aq) + Cl-(aq) from the following heat of formation ()Hf in kJ/mol) Na(s)=0, Na+(aq) = -240, NaCl(s) = -411, Cl2(g)=0, Cl2(aq) = -23, Cl-(aq) = -167 )Hrxn = 3np)Hfp - 3nr)Hfr =[1(-240) + 1(-167)]-(1)-411 = -407 + 411 = 4 kJ 6. (10 points) Given the following data: C2H2(g) + 5/2 O2(g) 6 2CO2(g) + H2O(l) C(s) + O2(g) 6 CO2(g) H2(g) + 1/2 O2(g) 6 H2O(l) )H = -1300kJ )H = -394kJ )H = -1300kJ Calculate )H for the reaction 2C(s) + H2(g) 6 C2H2(g) )H RXN 1 reversed: 2CO2(g) + H2O(l)6 C2H2(g) + 5/2 O2(g) RXN 2 x2: 2C(s) + 2O2(g) 6 2CO2(g) RXN 3 as is: H2(g) + 1/2 O2(g) 6 H2O(l) SUM 2C(s) + H2(g) 6 C2H2(g) +1300 -394(2) -1300kJ -788 kJ 7.(5 points) An FM radio station transmits at a frequency of 95.9 MHz. What is the wavelength associated with this frequency? c= 8< 3x108m/s = 8 95.9x106 s-1 (Hz = s-1) 8 = 3x108/95,9x106 = 3.13m B. (5 points) What is the energy associated with a single photon of energy at this frequency? E=h< = 6.626x10-34 J@s x 95.9x106 s-1 = 6.35x10-26 J 4 8. (10 points) The Bohr equation for a hydrogen atom is: E = − 2.178x10 − 18 Z2 J 2 n Using this equation, calculate the energy needed to move an electron from the n=1 orbital to the n=4 orbital. Would ths correspond to light being emitted or absorbed by a hydrogen atom? E at n=1 E at n=4 12 −18 E = − 2.178 x10 J 2 1 E = − 2.178x10 = -2.178x10-18 −18 12 J 2 4 = -0.135x10-18 )E = Ef - Ei = -0.135x10-18 - ( -2.178x10-18) = + 2.043x10-18 J; + so E must be absorbed 9 (10 points) Name the 4 quantum numbers used to describe the orbitals of an atom, give range of values associated with each quantum number and the physical property of the orbital associated with each quantum number. Principle Quantum Number (n): gives overall energy or size of orbital; n is an integer >0 Angular Momentum Quantum Number (Q) : gives shape of orbital; integers from 0 to n-1 Magnetic Quantum Number mQ: Gives orientation of orbital; integers from -Q to +Q Electron Spin Quantum Number ms: Spin of electron; +1/2 or -1/2 10. (10 points) Define the terms Photon - a single unit or packet of energy Standing wave - a wave that does not travel through space but remains at one location Node - In an orbital it is a region in which the probability of finding an electron is zero Degenerate Orbital - orbitals that have the same energy