Solutions to End of Chapter Problems
Solutions to End of Chapter Problems
1.
What is the greatest advantage that digital communication has over analog communication?
Relative noise immunity.
2.
Describe the function of a regenerative repeater.
Receive a noisy digital signal, determine the 0s and 1s, and retransmit the “clean” digital signal. This allows digital signals to be transmitted over long distances without error.
3.
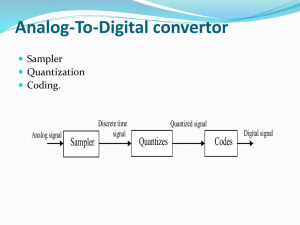
What is the cause of aliasing in the A/D process?
Sampling too slowly. An analog signal must be sampled faster than the Nyquist rate to prevent aliasing.
4.
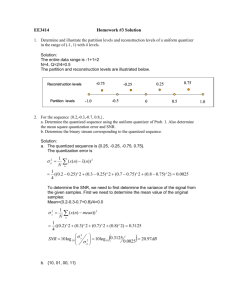
Why does a 5-bit quantizer produce a better approximation to an analog signal than a 3-bit quantizer?
A 5-bit quantizer has a smaller voltage resolution which can more accurately represent the signal’s voltage range.
With a 5-bit quantizer, the voltage range is divided into 2 5 =32 partitions, as opposed to 2 3 =8 partitions for the 3bit quantizer. The analog sample will be quantized to a value closer to its analog value.
5.
A music signal has frequency content from 0 Hz up to 18.75 kHz. What sampling frequency must be exceeded for successful A/D conversion? What is another name for the minimum sampling frequency?
The minimum sample frequency is called the Nyquist Rate, f
N
, and is equal to 2 times the max frequency in the signal. Here, f
N
= 2(18.75 kHz) = 37.5 kHz.
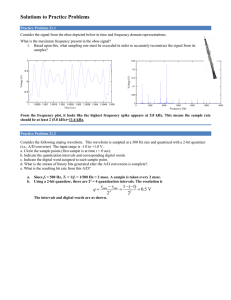
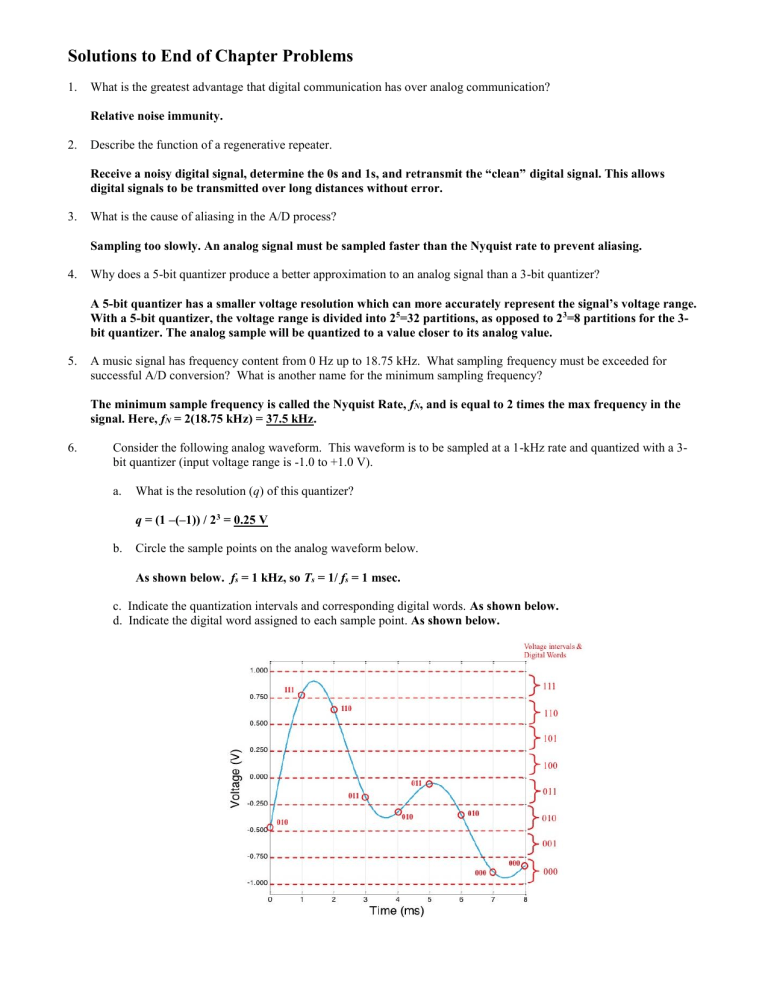
6. Consider the following analog waveform. This waveform is to be sampled at a 1-kHz rate and quantized with a 3bit quantizer (input voltage range is -1.0 to +1.0 V). a.
What is the resolution ( q ) of this quantizer? b.
Circle the sample points on the analog waveform below. q = (1 –(–1)) / 2 3 = 0.25 V
As shown below. f s
= 1 kHz, so T s
= 1/ f s
= 1 msec. c. Indicate the quantization intervals and corresponding digital words. As shown below. d. Indicate the digital word assigned to each sample point. As shown below.
e. When a receiver receives the transmitted bits, D/A is used to recover the analog signal, but the recovered signal is not the same as the original analog signal. What is the term to describe this difference and what can be done to minimize this difference?
This is called “quantization error”, which is minimized by using more bits to represent each sample
(larger value of N ). For example, use a 4-bit quantizer vice a 3-bit quantizer.
7. Consider the following analog waveform. This waveform is to be sampled at a 1.333333 MHz rate and quantized with a 3-bit quantizer (input voltage range is -2.0 to +2.0 V). a.
What is the resolution ( q ) of this quantizer? q = (2 –(–2)) / 2 3 = 0.5 V b.
Circle the sample points on the analog waveform below.
As shown below. f s
= 1.33333 MHz, so T s
= 1/ f s
= 0.75 μsec. c. Indicate the quantization intervals and corresponding digital words. As shown below.
d. Indicate the digital word assigned to each sample point. As shown below.