Science Journal of Medicine and Clinical Trials Published By ISSN: 2276-7487
advertisement

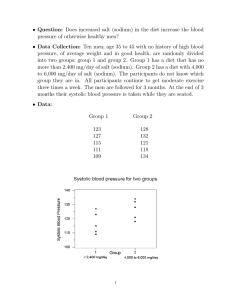
Science Journal of Medicine and Clinical Trials ISSN: 2276-7487 Published By Science Journal Publication http://www.sjpub.org © Author(s) 2015. CC Attribution 3.0 License. Research Article International Open Access Publisher Volume 2015, Article ID sjmct-168, 4 Pages, 2015. doi: 10.7237/sjmct/168 A Study on the Natriuretic Effect of Vernonia Amygdalina Ethanolic Extract on Wistar Rats By Odeyinka Odewusi Email: yinksdadon@yahoo.com Phone: +2347030282270 Accepted 05 May, 2014 Abstract- The hypothesis for this research was that intraperitoneal injection of V.amygdalina extract would bring about an increase in sodium excretion and perhaps a reduction in plasma concentration of sodium.Estimation of sodium concentration was carried out on blood samples collected from four group of rats injectedperitoneally with varying concentrations of V amygdalina in normal saline,each group consisting of eight rats.The mean plasma sodium level of groups i, ii, iii and control are 142.38±2.26 mmol/L ,141.0±1.20 ,139.7±1.19 and 137.88±0.83 respctively.These values reveal a proportionate decline in plasma sodium level in response to increasing dosage of extract .V amygdalina aqueous extract perhaps possess natriuretic properties which if harnessed can be used in the treatment of retentive disorders of sodium metabolism. Keywords ;Natriuretic , Sodium ,V .amygdalina , Introduction The balance of sodium is divided into two and depicted by the internal and external balance respectively.The internal balance of Na concerns the distribution between the various body compartments.This internal balance of Na is regulated by osmolality of either the extracellular or intracellular fluid.On the other hand the external balance matches input with output so that the total Na in the body is kept constant(whitby et al. 1989).This research work focuses on the external balance and the regulatory mechanisms that pertains to sodium metabolism.The primary organ that regulates extracellular Na+is the kidney.In addition to the kidney as the main organ that regulates plasma sodium levels,the following mechanisms are the regulators of Na+ excretion from the body (i)glomerular filtration rate(whitbyet al. 1989,Bolarin 2010) (ii)The rennin angiotensinaldosterone system (thrasher et al. 1994 ,Bolarin 2000) (iii)Natriuretic peptides and (iv)dopamine release from the kidney(Bolarin 2010).Recent advances in medicine are comfirming thatanalytes not thought of possess natriuretic properties .For example both oxytocin and secretinare now known to have natriuretic effects on the kidney(Cheng et al. 2009 ),preliminary to this is the work of waldum et al.( 1980) which observed a decrease in Na+reabsorption rate when secretin was administered.Barbezat et al.( 1972 )had earlier reported a significant increase in Na+ excretion when secretin was infused into dogs.Similarly ,oxytocin ,an hormone that has a similar structure to vassopresin(Terashimaet al. 1999) has a natriuretic effect in rats(Dicker and Heller 1946) and dogs(Brooks and Pickford 1958).Later in 1975 Ahmad et al. reported several cases of hyponatraemia when oxytocin was used to induce labour.These research works brings up the insinuation that natriuretic substances are likely to abound in nature. Retentive disturbances of sodium homeostasis such as hypervolaemia,SIADH and oedema are routinely treated with the use of diuretics.These drugs cause an increase in sodium excretion and their use are not without side effects .For example, Loop diuretics cause metabolic alkalosis,carbonicanhydrase inhibitors cause metabolic acidosis(Heuselet al 1999), whitby et al 1989 went on to state that thiazide diuretics cause glucose intolerance.In light of these, new lines of drugs needs to be discovered and characterized as there is an ever increasing need to limit toxic drugs(Lown, 1993).If this is to be done resort to phytochemicals could be the solution.Information on the active ingredients and curative actions of the medicinal plants was acquired by the introduction of European scientific methods(Herbon, 1998). Vernoniaamygdalina is a Nigerian plant, the extract of which have been reported to possesshepatoprotective properties(Adesanoyeet al, 2010),chemotherapeutic effects against breast cancer cells(Luoet al. 2010),antibacterial effect(Ojiezehet al. 2010).Oyagbemi and Adejimi (2012) and Adedapo et al. (2007) reported its anticoccicidal and antihelminthic activities respectively.Not more than nothing has been said about its natriureticproperty.It should be noted that the presence of phytochemicals is the rationale underlying the inclusion of plant parts in various native medicinal preparations(Egwaikhideet al. 2009).This research work is therefore designed to assess and ascertain the effect of aqueous extract of Vernoniaamygdalina on renal handling of sodium. Materials and Methods Sources of plantmaterials: VAmygdalina leaves and young shoots was collected from forest lands adjoining AcheiversUniversity,Owo,Ondostate,WesternNigeria.The botanist in the plant science unit of the biological sciencesdepartment identified the plants. Bitter leafextraction:The sample leaves were washed with water ,dried at room temperature for two and a half weeks and grounded into powder using a blender.200g of the ground leaf was dissolved in 1litre of absolute ethanol the extraction process was carried out in a soxhlet extractor for 5hours.The extract obtained was condensed and later dried at 40oC for 1 week in an oven. Preparation of standard bitter leaf extract solution:200mg of the bitter leaf extract was dissolved in 5ml of sterile normal saline at a temperature of 50C.This was then made up to 10ml to make a 200mg/10ml(20mg/ml) bitter leaf extract stock solution.5mg/ml How to Cite this Article: Odeyinka Odewusi, “A Study on the Natriuretic Effect of Vernonia Amygdalina Ethanolic Extract on Wistar Rats”, Science Journal of Medicine and Clinical Trials, Volume 2015, Article ID sjmct-168, 4 Pages, 2015. doi: 10.7237/sjmct/168 Science Journal of Medicine and Clinical Trials (ISSN: 2276-7487) and 10mg/ml bitter leaf solution was prepared by appropriate dilution of stock with normal saline. Laboratory animals :Thirty two (32)wistar rats weighing between 195 – 220g were used in this research.These animals were obtained from the animal house and were reared under standard animal management practices throughout the duration of research.The animals were fed with chow pellets and waterad libitum in standard quantity all through. Grouping and dosage of experimental animals: were divided into four treatment groups(I -IV) of eight(8) rats each.Each rat in groups I ,II and III were supplemented through intraperitoneal injection with2.5mg/100g body weight/day, 5mg/100g body weight/day and ,10mg/100g body weight/daybitter leaf extract solution respectively for 10 days ,so that the effect observed if due to treatment,should likely show a multiplying effect.Group IV (control)was not supplemented but each rat was injected intraperitoneally with 1ml normal saline for 10 days. Group Control Group I Group II Group III MeanSD(mmol/L) 142.38±2.26 141.0±1.20 139.0±1.19 137.88±0.83 Student’s t NA 1.672 4.473 8.419 Page 2 Blood sample collection: Blood samples were collected by puncture of ocular vein with heparinized capillary tube.Once the vein is punctured,blood flows by capillary action and this was collected into lithium heparinized blood sample containers.The blood was centrifuged,the supernatant plasma removed into plain blood sample containers and refridgerated at 4oC for estimation of sodium Sodium ion estimation was carried out using flame photometry. Statistical analysis was done using SPSS ,the student’s t was the statistical tool of choice ,values are expressed as mean ± SD.Significance was tested at P < 0.05 Results Table 1 showing the mean plasma concentration,the standard deviation (SD),the p value and students’ t when the plasma sodium level of the supplemented groups were compared with that of un supplemented group P value NA 0.138 0.003 0 Remarks NA Not significant Significant Significant NA means not applicable Graph 1. indicating the mean plasma sodium in response to various doses of VAmygdalinaadministered. How to Cite this Article: Odeyinka Odewusi, “A Study on the Natriuretic Effect of Vernonia Amygdalina Ethanolic Extract on Wistar Rats”, Science Journal of Medicine and Clinical Trials, Volume 2015, Article ID sjmct-168, 4 Pages, 2015. doi: 10.7237/sjmct/168 Page 3 Science Journal of Medicine and Clinical Trials (ISSN: 2276-7487) Discussion Levine et al in 1998 defined natriuresis as the discharge of sodium through urine.As far as the human physiology is concerned three types of natriuretic substance have been identified so far,they are (i) Atrialnatriuretic peptide (ii) Brain natriuretic peptide (iii) C-type natriureticpeptide(levine et al. 1998).It is of opinion that more natriuretis substances still abound in nature yet to be tapped.Various research works have culminated in making the phytochemical constituents of V.amygdalinaknown.It has been known to contain carbohydrates, saponins, alkaloids, tannins, proteins and steroids, flavonoids and glycosides(Ugwuoke et al 2010).The presence of alkaloids in plant parts have been known to confer diuretic properties on them. The mean plasma sodium level of groups I,II ,III and the controlgroup as shown in table 1 are 142.38±2.26 mmol/L ,141.0±1.20 ,139.7±1.19 and 137.88±0.83respctively.These values clearly shows a progressive decline in plasma sodium level as the dose administered increases.This would imply that the phytochemical constituent of A.amygdalinahas a multiplying effect on sodium excretion.The student’s t and the P values when the plasma sodium levels of groups I ,II and III are compared with that of the unsupplemented group are (1.672 ,.138) ,(4.473 , .003) and (8.419 , .000) respectively (Table 1).This also shows that the variation or difference in plasma sodium levels when the control group is compared with group I is statistically insignificant.On the other hand when the plasma sodium level of the groups II and III are compared with that of the control group the difference is of statistical significance.Further illustrating the natriuretic response of rats to aqueous V .amygdalina extract is Graph 1 above.Insummary ,this researchwork ventured into and found out that crude aqueous extract of V amygdalinapossess natriuretic properties and ,that the natriuresis conferred is dose dependent.It is the opinion of the conductors of this research thatthe natriuretic effect of V amygdalinais most probably linked to its effect on renal water handling since diuresisfavours the excretion of sodium. Conclusion and Recommendation As it has been clearly stated above,this research work ascertained that the peritoneal administration of V amygdalinaaqueous extractfavours sodium excretion in rats.The phytochemical constituents responsible for this characteristic could be isolated ,purified and characterized.The resultant drug when administered would probably have little or lesser side effects than most synthetic drugs presently in use.Other approach to these research would be finding out if the V amygdalinahas an effect on renal water handling. Reference 1. 2. AdedapoAA,OmoloyeOA,Ohore OG (2007).Studies on the antihelminthic activity on vernonia amygdalina on puppies. Asian J.Pharmacol. Vet. Res.74:31-36 AdesanoyeOA,Farombi EO( 2010).Hepatoprotective effects of vernoniaamygdalina(astereaceae) in rats treated with carbon tetrachloride.Exp. Toxicol.Pathol. 62(2): 197-206. 3. Baron DN, Newman F & Warrick A (1958)The effects of secretin onurinary volume and electrolytes in normal subjects and patients with chronic pancreatic disease. Experientia14 30–31. 4. Bolarin DM (2010). The Kidney:Bolarin’s aids to chemical pathology,1st edition O&A publications, Ibadan. pp.340-378. 5. Barbezat GO, Isenberg JI & Grossman MI (1972) Diuretic action of secretin in dog. Proceedings of the Society for Experimental Biology andMedicine 139 211–215. 6. Brooks FP , Pickford MT (1958) The effect of posterior pituitaryhormones on the excretion of electrolytes in dogs. Journal ofPhysiology 3 468–493. 7. Carrie Y Y Cheng, Jessica Y S Chu and Billy K C Chow (2009)Journal of Molecular Endocrinology 43, 81– 92www.endocrinology-journals.org 8. Dicker SE , Heller H (1946) The renal action of posterior pituitaryextract and its fractions as analysed by clearance experiments onrats. Journal of Physiology 104 353–360 9. HerbornJB(1998).Phytochemical methods: A guide to modern techniques of plant analysis,2nd EditionHall,New York.pp.5-11 10. Heusel JW ,Siggaard-Anderson O,Scott MG(1999):Physiology and disorders of water,electrolyte, and acid-base metabolism:In Tietz textbook of clinical chemistry(eds) Burtis CA and Ashwood E.WBsaunders,Philadelphia,Pennsylvania pp10951124 11. Levin ER, Gardner DG, Samson WK (1998). "Natriuretic peptides". The New England Journal of Medicine 339 (5): 321–8. doi:10.1056/NEJM199807303390507. PMID 9682046 12. LownJW( 1993):”Discovery and development anthracycline,antitumour,antibiotic”RoyalSosiety Chemistry pp165. of of 13. Luo X ,OyugiDA,Lin C, Izevbigie EB ,.Lee KS(2010).Isolation and characterization of the antibreast c carcinoma cell growth components of vernoniaamygdalina extracts. Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood) 235:1472-1478. 14. Maunsback.A.B,Marples. D,Chin. E et al(1997):Aquaporin water channel expression in human kidney.Journal of the American society of nephrologists;1-14 . 15. Newman DJ,Price CP(2009):Renal function and nitrogen metabolites:In Tietz textbook of clinical chemistry.WBsaunders,Philadelphia,Pennsylvania pp 120412701. 16. OjiezehTI,NwachukwuSE,Udoh SJ(2010):Antimicrobial effect of citrus aurantifolia juice and Vernonia amygdalina on common bacteria isolates.Derpharmachemica 17. Oyagbemi T O andAdejimiJ O (2012):Supplementation of broiler feed with leaves of vernonia amygdalina and Azadirachtaindica protected birds naturally infected with Eimeriasp.Afr.j biotech.Vol.11(33).pp.8407-8413. 18. UgwokeCEC, U Nzekwe, GI Ameh () Phytochemical constituents and ethnobotany of the leaf extract of bitter leaf (Vernoniaamygdalina) DelJournal of Pharmaceutical and Allied Sciences (7) 3 . http://dx.doi.org/10.4314/jophas.v7i3.63409 How to Cite this Article: Odeyinka Odewusi, “A Study on the Natriuretic Effect of Vernonia Amygdalina Ethanolic Extract on Wistar Rats”, Science Journal of Medicine and Clinical Trials, Volume 2015, Article ID sjmct-168, 4 Pages, 2015. doi: 10.7237/sjmct/168 Science Journal of Medicine and Clinical Trials (ISSN: 2276-7487) Page 4 19. Terashima Y, Kondo K &Oiso Y (1999) Administration of oxytocin affectsvasopressin V2 receptor and aquaporin-2 gene expression in the rat.Life Sciences 641447–1453. 21. WaldumHL,Sundsfjord JA, Aanstad U , Burhol PG ( 1980)The effect ofsecretin on renal haemodynamics in man. Scandinavian Journal ofClinical and Laboratory Investigation 40, 475 –478. 20. Thrasher TN (1994):Baroreceptor regulation of vasopressin in rennin secretion:low pressure versus high pressure receptors(review).Front.Neuroendocrinol.,15:157-196. 22. Whitby LG,SmithAF,Beckett CJ (1989):Renal function in:Lecture notes on clinical chemistry,4th edition,Blackwill scientific publication.pp 150-174. How to Cite this Article: Odeyinka Odewusi, “A Study on the Natriuretic Effect of Vernonia Amygdalina Ethanolic Extract on Wistar Rats”, Science Journal of Medicine and Clinical Trials, Volume 2015, Article ID sjmct-168, 4 Pages, 2015. doi: 10.7237/sjmct/168