PHYSICS 140A : ASSIGNMENT #3 SOLUTIONS PdV TdS

PHYSICS 140A : ASSIGNMENT #3 SOLUTIONS
Problem 1. Solution:
First, let’s derive the expression of S. dE dS
=
=
TdS nC
V
!
dT
T
PdV
+ p
, for ideal gas, it can be written as: dV
T
!
dS = nC
V dT
T
+ nR dV
V
!
S = nC
V ln T + nR ln V + C ' = nC
V ln P + n ( C
V
+ R ) ln V + C
Therefore, we can get:
&
$
%
' S
' V
#
!
" p , N
= n ( C
V
V
+ R )
,
&
$$
' S
' p
#
"
V , N
= nC
V p
In addition, from the equation of state:
&
%
' T
' V
#
" p , N
= p nR
,
&
$$
' T
' p
#
"
V , N
=
V nR
Finally we get:
!
( T , S , N )
!
( p , V , N )
= 1
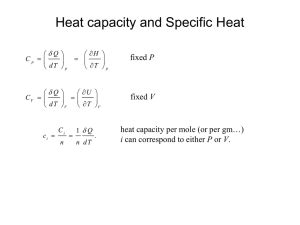
Problem 2. Solution:
C
!
=
'
& dQ dT
$
#
!
= %
& dE
+ dT pdV
$
#
!
=
C
V
+ p
'
%
&
(
V
(
T
$
#
!
Consider ideal gas for the following derivation.
(a) " ( T , V )
=
VT !
2
=
C
(
&
$
%
'
V
'
T
#
!
"
)
= 2 CT
( C
)
= C
V
+ p
&
$
%
' V
' T
#
!
"
)
= C
V
+ 2 pCT = C
V
+ 2 R
(b) !
( T , p )
=
Te p / p
0 =
Const
) ln T + p p
0
= ln T +
RT p
0
V
= ln Const .
)
1
T
+
R p
0
V
(
RT p
0
V 2
&
$
%
' V
' T
#
!
"
*
= 0
( C
)
= C
V
+ p
&
%
' V
' T
#
"
)
= C
V
+ R + p
0
V
T
(c) # ( T , p ) = p 3 V = const .
!
VT " 3 / 2
= C
The same procedure as (a) we can get: C
!
= C
V
+
3
2
R
Problem 3. Solution:
(a) The extensivity of S imposes a relation of:
S ( !
E , !
V , !
N ) = !
S ( E , V , N )
So we can easily get the constraint:
#
+
"
+
!
= 1
(b) Usually the stability of a system depends on the second order differential of a given function, e.g. potential energy, entropy.
As a standard procedure, we should evaluate
!
2 S
!
x i
!
x j
, in which x i
are dimensionless variables, e.g: E = E
0 x
1
. Since S tends to reach maximum, the matrix of
&
$
%
'
2 S
' x i
' x j
#
!
"
should be non-positive matrix. In other words, the eigenvalues of the following matrix should be non-positive.
$
%
&
$
* ( *
*)
*(
'
1 )
) (
*)
)
)(
'
1 )
( (
*(
(
)(
'
1 )
!
"
#
!
The final answer is $
,
#
,
" !
[ 0 , 1 ]
Problem 4. Solution: dH = TdS + Vdp , if H=const, then 0 = TdS + Vdp (*)
So we should express dS and dp in terms of dT and dV. dS
=
(
'
) S
) T
%
$
V dT
+
(
'
) S
) V
%
$
T dV
=
C
V
T dT
+
" p
!
T dV dV
=
)
(
*
V
*
T
&
% p dT
+
)
''
(
*
V
* p
&
$$
%
T dp
=
V
"
p dT
#
V
!
T dp
$ dp
=
" p dT
!
T
1
#
V !
T dV
Invoking them into (*), we can get:
V
)
(
* T
* V
&
%
H
=
!
p
+
1 #
V
!
C p
"
T p
T
#
T
!
2 p
Problem 5. Solution:
(a) For isothermal process of ideal gas with fixed N, ( F = ' T ( S = ' nRT ln
&
$$
%
V f
V i
#
!!
"
, where
!
S have obtained in the Problem 1. Or we can directly get the result from the expression:
dF
=
" SdT " pdV
+ µ
dN
=
" pdV !
( F = ' nRT ln
&
$$
%
V f
V i
#
!!
"
(b) d
" = !
SdT
!
pdV
!
Nd µ = !
pdV
= dF
* () = ' nRT ln
&
$$
%
V f
V i
#
!!
"