Web Ping- Pong Welcome to
advertisement

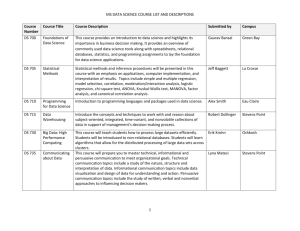
Welcome to Web Ping-Pong Introduction • What – Solution to slow web syndrome • Why – Information needs to reach destination – Accuracy • Time • Connection A Short History of the WEB: PREHISTORY • The development of hypertext, or the computer-aided reading of electronic documents • The development of the Internet protocols which made the global network possible 1957- USSR launched the first artificial earth satellite Sputnik • 1965-Douglas Engelbart produces 1st hypertext system • 1975-Alan Kay produces the 1st personal computer (later Apple Macintosh) • 1979-Charles Goldfarb invents SGML, as we know today HTML is the mark-up language of the Web, curiously HTML is an SGML application 1986-OSI protocols are introduced • 1987-CERN and US Laboratories connect to the Internet as the main means of exchanging data between laboratories • 1989-Tim Berners-Lee proposes a “networked” Hypertext system for CERN • 1990-the name ‘‘World-Wide-Web” is born • 1991-SLAC, Stanford Linear Accelerator Center in California becomes the 1st Web server in the USA • 1992- world has 50 servers • 1993- world has 250 servers 1994-Jim Clark founds MCC (later Netscape)--2500 servers • 1995-at one point 700 servers per day are registered, to date 73500 servers • 1996-various ISP’s suffer outages, bringing into question whether they will be able to handle the growing number of users • 1997-early morning July 17, human error at Network Solutions causes DNS. table for .com and .net to become corrupted SUMMARY • by the end of 1991, the Internet has grown to include: • 5,000 networks in 36 countries serving 700,000 host computers used by over 4 million people TODAY, the Internet has grown to include: • approximately 135,000 networks • in over 170 countries • serving approximately 30 million host computers • used by over 148 million people • the world now has approximately 2.2 million servers People Care!!! People Use!! Current Connection Map Current Network Issues • Age • Modernization – Cost – Time • Rural vs. Urban • Responsibility • Future Forecast – Better, Faster, Cheaper! Possible Improvements • Smart Hardware • Smart Software – Less Data Transferred – Pre-Pinging Paths • Pre-Pinging – How Used Today – How it works Current Message Path 2 Path with Pinging Web Usage • There are approximately 184 million people using the Internet (84.4% in the USA) • 32.7% use it 10-20 hours a week while 26.4% use it more then 20 • Wisconsin accounts for about 1.5% of the web usage world wide Where Used • Over half of the Web access is done in homes. This is an increase of 2% from last year • 37% of access is from an office • 6% is from a portable computer (i.e. laptop) Modem speeds • 75% have a connection speed of 28.8 to 56K • Only 16% have a T1 connection or better Growth • In 1991 NSFNET switched from a T1 connection installed 3 years earlier to a T3. This was before the Internet was introduced to the general public. • Only 39% of the population have been hooked up to the Web for more then 3 years. 45% for 1-3 S up e rio r W IS C O N S IN R ic e L a k e W a usa u E a u C la ire G re e n B a y M e no m o n ie A p p le to n M a n ito w o c N e e na h L a C ro s s e S te ve ns P o int F o nd d u L a c S he b o y ga n L e g e n d (po p u lat io n) L a rg e C it ie s (2 7 ,0 0 0 -6 2 8,0 0 0 ) M a d is o n M ilw a u k e e M e d iu m C it ie s (3 7 ,0 0 0 -9 6,0 0 0 ) S m a ll C it ie s (1 2 ,0 0 0 -8 0,0 0 0 ) R a c ine J a ne sv ille K e no s ha Menomonie Wausau 15 19 30 22 25 Stevens Eau Claire 15 Point 19 25 29 La Crosse 30 32 7 22 3 Madison Neenah 26 7 15 19 1 33 Controlled Map Milwaukee U0 8 10 V5 V1 16 13 7 V6 V7 9 17 11 V4 V2 5 14 V3 L(u0) 0 V1 V2 V3 (∞, -) (∞, -) (∞, -) (∞, -) (13, u0) (∞, -) (18, v5) (13, u0) (25, v5) (18, v5) (25, v5) (18, v5) (20, v4) (20, v4) V4 V5 (∞, -) (∞, -) (16, u0) (8, u0) (15, v5) (15, v5) V6 V7 (∞, -) (∞, -) (∞, -) (∞, -) (∞, -) (∞, -) (∞, -) (∞, -) (∞, -) (∞, -) (∞, -) (∞, -) Add to S U0 V5 V2 V4 V3 V1 Menomonie Wausau 15 19 30 22 25 Stevens Eau Claire 15 Point 19 25 29 La Crosse 30 32 7 22 3 Madison Neenah 26 7 15 19 1 33 Controlled Map Milwaukee Path Results Menomonie to Neenah • Typical Traffic • Total Weight 64 • Quickest Path – Eau Claire-La Crosse – Madison-Milwaukee – Neenah* • Pinging Included • Total Weight 81 • Quickest Path – Eau Claire-La Crosse – Madison-Neenah* Note: Shortest Path!! Conclusions from Data • Shift away from Big Cities/Hubs • # vertices down VS length increase – More direct path – heavier traffic • Less Hubs = less smart hardware • Traffic increase is a given with Pinging, but there are so many more path options with total weight lower in the current network that these paths are a better solution then with pinging included in the network. • Amount of traffic increases too high to offer benefits in overall global network ! Conclusion • Pre-Pinging Not Cure – Not efficient in Small or Big • Cost Issues – Hardware – Software – Size, Time Issues • Politics – Government – Telecommunications World Bibliography • Irvin Hause– Ameritic Telephone man >20years, Owner Wolf River Communications • World Wide Web – http://info.isoc.org/guest/zakon/internet/history/ – http://www.isoc.org/internet-history/cerf.html – http://www.inria.fr/actualites/cailiau-fra.html • Graph Theory Book • Dr. Wu • ADC Instructional Resource Material