Connected Mathematics 2 Essential Learnings multiplication, division)
advertisement

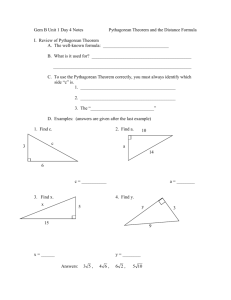
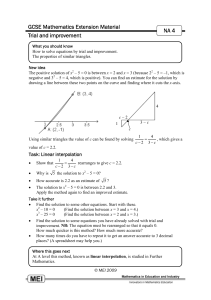
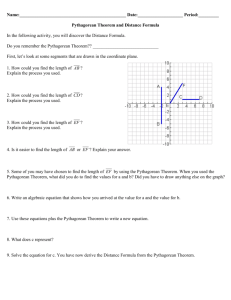
Connected Mathematics 2 Essential Learnings (as agreed upon by Junior High DCT 1/5/09) Edits from DCT on 3/3/09 noted in bold 1. Use models to represent integers and compute operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division) 7.1.1a, 7.1.1b, 7.1.5a, 7.6.2a, 7.6.2b, 7.6.2c 2. Use the relationship among fractions, decimals, and percents, including the concepts of ratio and proportion, in problem solving situations a. Write and convert comparison statements using the five number comparisions (percent, fractions, differences, scaling, ratio) b. Convert between fractions, decimals, and percents c. Use proportional thinking to solve problems 7.1.4a, 7.6.1a 3. Use vocabulary and understand concepts of exponents, read and write scientific notation 7.1.1d, 7.1.2c 4. Model linear functions a. Identify linear relationships in tables or graphs b. Create a table or graph for a linear relationship c. Determine the slope of a linear function from graphs and tables Expected mastery is looking solely at rise over run, no formal use of slope formula at this level. d. Solve one step equations 7.2.2a, 7.2.3b, 7.25.a, 7.2.5d 5. Find probabilities of basic independent events, understand that the range of probability options is from zero to one, and use informal basic counting techniques including creating tree diagrams and organized lists. 7.3.5a, 7.3.5b, 7.3.6a, 7.3.6b, 7.3.6c, 7.3.6d, 7.3.7a, 7.3.8a 6. Find the surface area of rectangular prisms and find volume of rectangular prisms 7.4.5c, 7.4.5d 7. Identify and compare similar shapes using ratio, proportion, or scale factor and understand the concepts related to similar polygons 7.4.3a, 7.4.3b PSD Math: Essential Learnings Version 1.0 D:\291206709.doc January 2009 K. Canine Connected Mathematics 3 Essential Learnings (as agreed upon by Junior High DCT 1/5/09) Edits from DCT on 3/3/09 noted in bold 1. Represent linear functions using written explanations, tables, equations (slopeintercept form only), and graphs a. Describe connections among these representations b. Convert from one function’s representation to another c. Determine the slope between two points using the formal slope formula 8.2.1a, 9.2.1b, 8.2.2a, 8.2.4a 2. Solve multi-step equations a. Simplify expressions using order of operations, combining like terms, distributive property b. Solve two step equations and equations with variables on both sides 8.2.5a 3. Display data (stem and leaf plots, histograms, scatter plots, box and whisker plots) and appropriately use measures of central tendencies 8.3.1a, 8.3.2a, 8.3.2b, 8.3.3a, 8.3.3b, 8.3.3c, 8.3.4a, 4. Use a model or counting technique (tree diagram, lists, multiplication principle, permutations – without formal use of permutation formula) to determine all the possible outcomes from an experiment 8.3.6a, 8.3.7a 5. Recognize and use equivalent representations of numerical radical expressions, rational and irrational numbers 8.1.1a, 8.1.2b, 8.1.2c, 6. Recognize Pythagorean relationships in right triangles and master using the Pythagorean Theorem to find the missing length of hypotenuses in right triangles (Apply the Pythagorean Theorem to solve real world problems) 8.4.5b, 8.5.4a 7. Find the surface area of cylinders and triangular prisms. 8.4.5a PSD Math: Essential Learnings Version 1.0 D:\291206709.doc January 2009 K. Canine Algebra 1 Essential Learnings Edits from DCT on 3/3/09 noted in bold 1. Solve multi-step equations and inequalities 8.2.5a, 8.6.2a, 9.2.2a, 9.2.5a 2. Apply the Pythagorean Theorem to solve real world problems and master using the Pythagorean Theorem to find any missing side length in a right triangle (Solve problems using the Pythagorean Theorem) 8.4.5b, 8.5.4b, 9.4.2b 3. Represent function relationships using written explanations, tables, equations, and graphs a. Describe connections among these representations b. Convert from one function’s representation to another 8.2.1a, 8.2.1b, 9.2.1a, 9.2.2a, 9.2.2b, 9.2.2c 4. Model linear functions a. Write equations of lines: slope-intercept form, standard form, pointslope form b. Graph linear functions c. Model linear relationships in scatter plots 8.2.1a, 8.2.2a, 8.3.1a, 9.2.1a, 9.2.2a, 9.2.4a, 9.2.5a, 9.3.3a 5. Find probabilities of compound events 8.3.6a, 8.3.6b, 8.3.6c, 9.3.5a, 9.3.5b, 9.3.5c 6. Solve problems using counting techniques, permutations, and combinations (including formal use of formulas) 8.3.7a, 9.3.6a 7. Simplify expressions using properties of exponents 9.1.4a 8. Solve systems of equations and inequalities a. Graphing b. Substitution c. Elimination d. In contexts 8.2.5a, 9.2.3b, 9.2.5a 9. Multiply polynomials and factor basic trinomials 9.2.5b, 9.6.2a PSD Math: Essential Learnings Version 1.0 D:\291206709.doc January 2009 K. Canine PSD Geometry Major Themes and Essential Learnings (as agreed upon by the Geometry Teachers 2/10/09) 1. Vocabulary and notation Use appropriate geometric vocabulary and notation in context. 2. Logic, reasoning, and proof Construct logical progressions of reasoning, for example writing conditional statements and their converses. 9.4.3, 10.4.3a, 10.4.3b 3. Congruency Describe, prove, and apply the properties of congruent angles and figures including vertical angles, angles formed by parallel lines cut by a transversal, triangles, polygons, and segments. 9.4.3a, 10.4.1a, 10.4.3a, 10.4.3b 4. Similarity Describe and apply the properties of similar figures including triangles and polygons. 9.4.3a, 9.5.1a, 9.6.1a, 10.4.1a, 10.4.3a, 10.4.3b, 10.5.1a, 10.6.1a, 5. Quadrilaterals Classify quadrilaterals. Apply properties of quadrilaterals (parallelograms, rectangles, squares, rhombuses, trapezoids, kites). 9.4.3a, 10.4.3a, 10.4.3b 6. Area & Volume Find the area of quadrilaterals and regular polygons including composite figures. Find the surface area and volume of prisms, cylinders, pyramids, cones, and spheres. 9.1.1b, 9.2.3c, 9.2.5b, 9.4.2a, 9.4.3a, 9.5.1c, 9.6.2a, 10.1.1b, 10.2.3c, 10.2.5b, 10.2.5c, 10.3.5e, 10.4.2b, 10.4.2c, 10.4.2d, 10.4.3a, 7. Right Triangles Apply tangent, sine, cosine ratios and the Pythagorean Theorem to solve for unknown parts of right triangles. Apply properties of special right triangles (30, 60, 90 and 45, 45, 90). 9.1.1b, 9.2.5b, 9.4.2b, 9.4.4a, 9.5.1a, 9.6.2a, 10.1.1b, 10.2.3c, 10.4.2a, 10.4.4a, 10.5.1a, 10.6.2a 8. Circles Find the measures of central angles, arcs, and circumference. Find the area of circles, sectors, and segments of a circle. 9.1.1b, 9.2.5b, 9.4.2a, 10.1.1b, 10.2.5b, 10.2.5c, 10.3.5e 9. Transformations Given a pre-image and image, describe the transformation (such as translation, reflection, and dilation) including compositions. 9.2.4, 9.4.1a, 10.2.4, 10.4.1b, 10.4.1c Necessary sub-skills Find the length of segments using the Pythagorean Theorem or distance formula. Find midpoints of segments. PSD Math: Essential Learnings Version 1.0 D:\291206709.doc January 2009 K. Canine