Botany Structure Competitive Review Questions 2008
advertisement

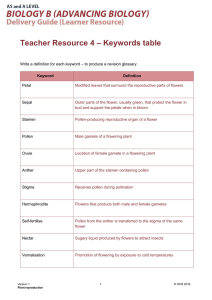
Botany Structure Competitive Review Questions 2008 1. What structure contains seeds in angiosperms? 2. What kind of veins do monocots have? 3. How are monocot flower parts arranged? 4. How many cotyledons does a bean seedling have? 5. Is an apple tree an angiosperm or a gymnosperm? 6. What structures do angiosperms use to hold their seeds for reproduction? 7. Is corn (a type of grass) a monocot or a dicot? 8. What does deciduous mean? 9. What is a cotyledon? 10. What kind of venation does corn have? 11. How many cotyledons does a palm tree have? 12. An example of a non-vascular plant is__. 13. A structure on the outside of plant leaves that prevents dehydration is the ___. 14. What does phloem carry? 15. Give an example of a plant that has a tap root. 16. Bacteria in the soil convert atmospheric nitrogen into a form that plants can use during the process of ____. 17. The function of lateral roots is to _____. 18. The function of root caps is to ___. 19. The function of the casparian strip is to__. 20. Define leaf node. 21. Stem growth in circumference takes place due to __ meristems. 22. Yearly increase in stem width occurs in ___. (monocots or dicots?) 23. What kind of wood_____ is found at the center of a tree trunk? 24. In translocation, what vascular tissue moves sugars? From where to where? 25. Excess water is released from leaves during the process of ___. 26. The function of endosperm is __. 27. The functions of the seed coat are __. 28. Free question. Is the answer A, B, or C ? 29. The function of a flower is __. 30. The Cohesion-Adhesion Theory explains___. Matching For questions 31 through 37, choose from the following letters 31. Stigma 32. Filament 33. Petal 34. Sepal 35. Ovary 36. Style 37. Anther A. supports stigma B. supports anther C. collects pollen D. releases pollen E. attracts pollinators F. protects flower bud G. contains eggs Botany Structure Competitive Review Answers 2008 1. flower/ fruit 2. parallel 3. in threes or multiples of three 4. two 5. angiosperm 6. flowers/ fruit 7. monocot 8. loses its leaves in winter 9. seed leaf 10. parallel 11. one 12. moss / liverwort / hornwort / horsetail / club moss / whisk fern 13. cuticle 14. products of photosynthesis 15. beet /carrot / radish / dandelion 16. nitrogen fixation 17. increase absorption of water and nutrients 18. protect (apical) meristems / root tip tissue 19. channel water into vascular tissue 20. the place where one or more leaves are attached to a stem 21. lateral 22. dicots 23. heartwood 24. phloem moves sugars from leaves (source) to areas where they are stored (sink) 25. transpiration 26. to provide a food source for the embryo 27. to protect the embryo and to prevent dehydration of the embryo 28. the answer is C 29. reproduction 30. causes phloem to move water and nutrients 31. collects pollen 32. supports anther 33. attracts pollinators 34. protects flower bud 35. contains eggs 36. supports anther 37. releases pollen NOTE: on the test, be able to label the following diagrams: parts of a seed, stomata, leaf cross-section, types of stems cross-sections, parts of a flower, leaf: types, venations, and margins