www.studyguide.pk Product Life Cycle Theory
advertisement
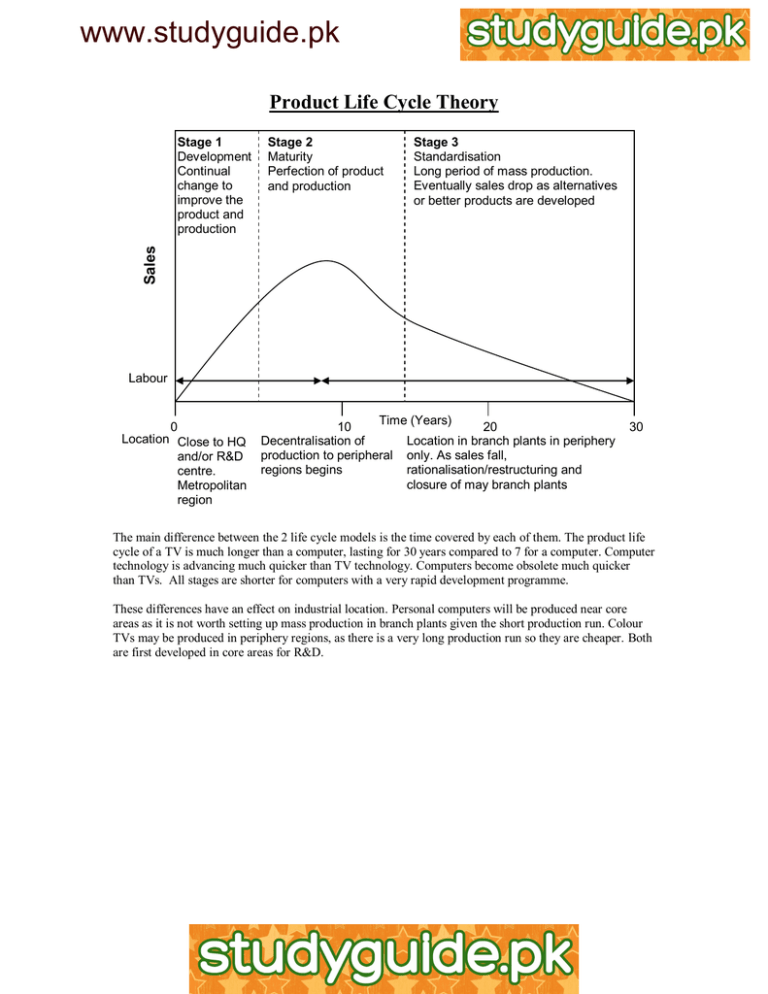
www.studyguide.pk Product Life Cycle Theory Stage 2 Maturity Perfection of product and production Stage 3 Standardisation Long period of mass production. Eventually sales drop as alternatives or better products are developed Sales Stage 1 Development Continual change to improve the product and production Labour 0 Location Close to HQ and/or R&D centre. Metropolitan region Time (Years) 10 20 Decentralisation of Location in branch plants in periphery production to peripheral only. As sales fall, regions begins rationalisation/restructuring and closure of may branch plants 30 The main difference between the 2 life cycle models is the time covered by each of them. The product life cycle of a TV is much longer than a computer, lasting for 30 years compared to 7 for a computer. Computer technology is advancing much quicker than TV technology. Computers become obsolete much quicker than TVs. All stages are shorter for computers with a very rapid development programme. These differences have an effect on industrial location. Personal computers will be produced near core areas as it is not worth setting up mass production in branch plants given the short production run. Colour TVs may be produced in periphery regions, as there is a very long production run so they are cheaper. Both are first developed in core areas for R&D. www.studyguide.pk The Location of Branch Plants in Mexico Branch plants (maquiladora) have developed in Mexico. These branch plants almost solely produce goods for the US market using Mexican labour. There are approximately 2100 maquiladora in Mexico employing 600,000 workers. They also receive government subsidies such as preferential tariffs & taxation. Most maquiladora are mature & labour intensive. They are situated near the US border in order to reduce transport costs. Companies use maquiladora in order to cut labour costs by exploiting Mexico’s slack wage laws. Maquiladora have had a large impact on employment in the USA and the growth of manufacturing employment in Mexico. This has continued since the development of NAFTA. There has been rapid economic development in the North of Mexico but this has caused environmental problems & has led to regional inequality. Location – International Scale It is popular with US companies because of cheap wages. Mexico is near to the US for markets and so transport costs are lower. Mexican plants are easily supplied with components by US companies. Location – Regional Scale Maquiladora are located very close to the US border. Transport costs & delivery costs are lower. Tijuana has good access to California. Also Branch managers can commute from the USA and so valuable staff are not lost. Location – Urban Scale Located near population centres that provide vast pools cheap labour e.g. Tijuana. Located on developed sites with good infrastructure – factory buildings Model of a TNC Company Headquarters Location Location Requirement Changes Metropolitan Areas Need for face to face contact Beginnings of suburbanisation Developments in telecommunications dispensing with need for physical proximity R&D Suburban areas, small cities Routine Assembly Plants Small Cities, Rural Areas Close to business services Close to government agencies Good environment to attract workers Low taxes Growth In Sunbelt USA and developing countries Cheap Labour Low taxes Location of different functions in a TNC Functions Headquarters Administration/distribution Production Major city Movement to and growth in smaller towns in amenity rich areas Regional urban centre Peripheral regions www.studyguide.pk Branch Plant Closure – Birdseye, Kirkby Reasons for Closure Workers would not accept better production techniques, although they disagree. They were not producing enough food even though they were still in profit. Workers believe the plant was not making enough money Also believe Unilever not prepared to pay the money to keep the factory open Grimsby plant is cheaper to operate as the workers are part time Prime minister believes closed because it couldn’t increase production and reduce costs. Events Plant was closed in March 1989, as it was outdated and inefficient. Production moved to a new plant at Grimsby with the loss of 380 jobs. The company still wanted to close the plant down even though they made profits of £1,516 mlln. The workers made a small attempt to avoid closure but other plants refused to help by going on strike. The Kirkby plant would not agree to slicker production methods, as Birdseye would not pay off workers fairly. Finally the plant did close, increasing unemployment to 21% of the Kirkby population. Location of Birds-eye The British HQ of Birdseye is Walton-on-Thames located near London. This is a core area near to financial services and government. There are better-qualified workers who are needed at the HQ but not the branch plants. Kirkby is located on Merseyside in the borough of Knowsley on the edge of Liverpool. Therefore Kirkby is in the NW with a periphery location as land and wages are cheaper. Transferability of Capital in TNCs Capital is not easily transferable in large multi-plant firms as all the money goes to the HQ rather than the branch. They are then unwilling to spend the profits on other plants. Unilever made a huge profit in Japan but did not want to use the money to save the Kirkby plant or pay for redundancies. There is some capital transfer as Unilever did finally pay £8000 as pay off for workers. The plant was relatively easy to close as the labour was unskilled and so could be found cheaper in many other places. There was little capital investment in the plant as some of it had already shut down. There were huge financial benefits in moving the factory and there was very little resistance from workers. Advantages of Grimsby Grimsby is nearer to the huge market of Europe and so transport costs are lower People work part-time so do not have overtime or holiday. Therefore labour is cheaper. The factory is more modern and so production is higher. Branch-plant Economies Branch-plant economies can be unreliable, as it is easy for the parent company to pull out. The plants do provide jobs for a large number of people but they are easily lost. The jobs are low paid and low skilled and so does not bring a lot of money to the area. Most of the profits go to the HQ and so little gets put back into the area.