Benefits and Liabilities Associated with Early Maturity and Determinacy in Cotton
advertisement

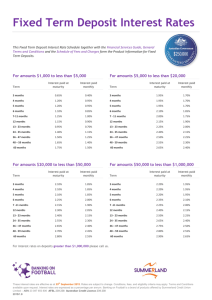
Benefits and Liabilities Associated with Early Maturity and Determinacy in Cotton What is Early Maturity and Determinacy? Physiologically, determinacy might be defined as the degree to which a plant segregates vegetative growth from reproductive growth. A plant that ceases all vegetative growth at the onset of fruiting is completely determinate. What is Early Maturity and Determinacy? Physiologically, earliness might be defined by the time required by the plant to reach a reproductive growth stage, and by the rate and duration of fruiting. What is Early Maturity and Determinacy? Agronomically, earliness is defined as the time required to mature a satisfactory crop and determinacy is defined as the plant’s ability to maintain vegetative growth and fruit form production after the onset of fruiting. Characteristics and Components of Early Maturity • • • • • Early fruit initiation (low fruiting node) Accelerated rate of fruiting bud development Accelerated rate of flowering Compressed fruiting interval Reduced rate of vegetative growth Characteristics and Components of Early Maturity • Early and sharply defined cessation of vegetative and reproductive growth (cutout) • Shorter boll maturation period • Shorter plant stature High fruit retention rates Accelerated Flowering and Cutout Early maturity traits: • Early fruit initiation • Increased plant determinacy reflected by plant heights High fruit retention rates Advantages of Early Maturity • Shorter growing season – Insect pest evasion and management – Avoidance of environmental adversities: • Cool planting temperatures • Heat stress • Cool temperatures during boll maturation • Inclement weather during harvest Escape from an environmental adversity (heat stress) due to early maturity in Pima S-7. Management Advantages – Reduced insecticide applications – Reduced numbers of irrigations – Increased flexibility in the development of management strategies Uses or Proposed Uses of Early Maturing Cultivars • Late planting to create a suicidal emergence of Pink Bollworm (Arizona). • Late planting following the failure of a medium or full season cultivar due to weather (general, U.S.). • Early or normal planting to avoid cool temperatures during boll maturation and resulting poor fiber quality (high plains, Texas). Uses or Proposed Uses of Early Maturing Cultivars • Early or normal planting to avoid rain and fog conditions at harvest (northern San Joaquin Valley, California). • Use in multiple cropping schemes, allowing production of food and cash crops in a single year (China, north Africa, general). Historically, insect pests have been the predominant motivation for the development of early maturing cultivars in the U.S. • Pre-1890 – Use of early maturing cultivars in northern cotton states due to short growing season. • 1900’s – Severe boll weevil pressure led to movement of early maturing cultivars into mid-south and the development of new early maturing cultivars. • 1970’s – Severe bollworm/budworm problems in midsouth renewed breeding efforts for earlier maturing cultivars. Reduction in growing season, 1960-1987 Season Reduction Years (planting – harvest) 1966-1987 28 days Location College Station, Texas Florence, 1968-1987 South Carolina Mississippi Delta, 1960-1987 Mississippi 33 days 38 days Cultivar Maturity Groups 3 Weeks 300 HU (30/13 C) Medium Short Full Pima S-6 SG 501 Pima S-7 DPL 20 DPL 5415 DPL 90 Short –Season Management for Pink Bollworm Control in the Imperial Valley of California, 1990-1994 • Primary Goal: Reduce pink bollworm populations area-wide through increasing time in which fields are free of the cotton host. • Secondary Goal: Cotton host avoidance of damaging late season insect populations. Management Program for Pink Bollworm in the Imperial Valley • Early termination of cotton crop with chemical defoliants. • Early mandatory destruction of plant residue in fields. • Switch from a full season to a medium season cotton variety (from DPL 90 to DPL5415), an unintended component. Boll set, standard cultivar Mandated termination Boll set, early maturing cultivar Pink bollworm population May June July Aug Sept Short-Season Management for Pink Bollworm Control, Imperial Valley, CA PreLate Season program Program Years (August) 1989 1990 1991 1992 1993 1994 Moths/trap/ night Larvae/100 bolls Lint yield (Kg/ha) 3.1 4.4 1.4 1.8 0.1 0.0 89 15 3 12.5 -- -- 1242 1177 1069 1133 1460 1503 Disadvantages of Early Maturity and Increased Determinacy • • • • Limitations on yield potential Inflexibility in response to injury Increased management oversight Increased susceptibility to: – Smog (ozone) damage – Foliar leaf spot diseases, nutrient deficiencies, and premature senescence – Verticillium wilt Cumulative Yield (lbs./acre) Sequential harvests of an early maturing (8709) and later maturing (91-311) cultivar 1700 1500 1300 1100 8709 91-311 900 700 500 300 155 166 176 Days after planting 201 Cumulative percent yield of an early maturing (8709) and later maturing (91-311) cultivar 100 90 80 70 60 8709 91-311 50 40 30 20 155 166 176 Days after planting 201 Early Foliar Decline, a Maturity Related Disorder of Pima Cotton Correlation of early foliar decline severity with plant growth traits, foliar potassium, and yield in 60 populations at Tulare, CA, in 2000. Early foliar Traits Decline rating Nodes above open bloom -0.64 Plant height -0.67 Foliar potassium -0.56 Lint yield -0.72 • In cotton, Maturity and Determinacy vary along along a continuous scale. • Benefits and liabilities also change on a scale. • Environment, management, and economics determine the appropriate level of earliness and determinacy for your situation.