South Asia/East Asia 2: Population Geography (Pulsipher pp. 12-17) I. Global population data
advertisement

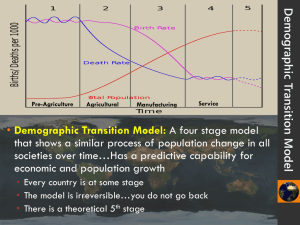
I. II. III. South Asia/East Asia 2: Population Geography (Pulsipher pp. 12-17) Global population data A. general facts 1. current world population = 7.3 billion 2. current US population = 323 million B. global population distribution Population change A. ways to alter a region’s population: 1. birth 2. death 3. migration B. World Population Data Sheet (online @ http://www.prb.org/) C. terms associated with population change: 1. crude birth rate (CBR): number of births per 1,000 population in 1 year period 2. crude death rate (CDR): number of deaths per 1,000 population in 1 year period 3. rate of natural increase (RNI) a. rate of natural increase (RNI) = (CBR – CDR)/1000 (percentage) b. ZPG (zero population growth): CBR - CDR = 0 4. rate of population growth a. includes migration 5. total fertility rate a. number of children an average woman bears b. replacement fertility 6. doubling time a. time (in years) it takes population to double at current rate of natural increase b. doubling time: 70/RNI c. J-curve d. changing death rate 1) agricultural advances 2) medical advances 7. population density = people/total area Demography A. study of population patterns and changes B. stages of demographic transition (fig 1.10) 1. Stage 1 – Pre-industrial a. high birth rates; high death rates b. equilibrium 2. Stage 2 a. falling death rates; high birth rates b. high rate of natural increase 3. Stage 3: demographic transition a. falling birth rates 4. Stage 4 a. population returns to equilibrium b. low birth rates and low death rates 5. demographic momentum C. population pyramids 1. structure of population pyramids South Asia/East Asia 2: Population Geography – p. 1 of 2 IV. V. a. 2 sided bar graph showing the distribution of population in various age categories (cohorts) b. horizontal axis = number of population in particular age groups c. vertical axis = different age groups 2. types of pyramids a. Stage 1: regular triangle shape 1) high birth and death rates 2) low rate of natural increase b. Stage 2-3: narrow top, wide base, concave sides 1) falling death rate; high birth rate 2) high rate of natural increase 3) tapered bottom/concave sides above dip: rapid decrease in fertility of a developing nation c. Stage 4: beehive shape 1) relatively stable population a) low birth rates; low death rates b) high median age c) modest to zero rate of natural increase 2) beehive w/indented base = zero or negative RNI 3. specialized pyramid examples D. Population data around the world 1. elderly 2. young 3. RNI a. Africa: fastest growing region b. Niger = 3.9% (highest in world) c. India = 1.5% d. China = 0.5% 4. case studies a. Italy b. Niger 5. China and India a. Mao v. post-Mao 1 child policy b. demographic time bomb c. China’s new policy d. missing girls: China, India Projections UN Revised Population Report 2008 A. current population increase B. projected year 2050 population 1. world population: 9.1 billion 2. developed nations v. developing nations: C. aging world ISSUE: Can the world handle the population increase? A. USA v. developing nations B. 2014 Astonishing Facts C. THE BIG QUESTION: “Can the earth continue to feed its growing population?” D. Your Ecological Footprint! South Asia/East Asia 2: Population Geography – p. 2 of 2