Tangent approximation Math 311-102
advertisement
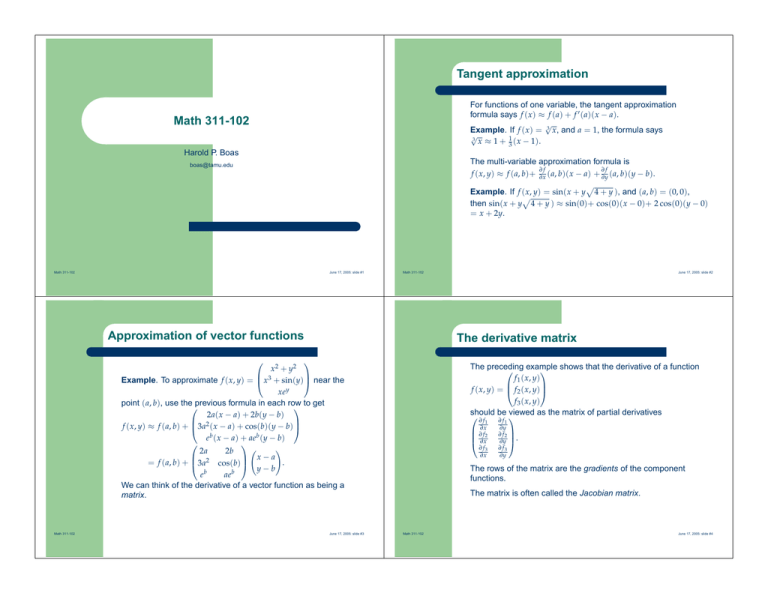
Tangent approximation For functions of one variable, the tangent approximation formula says f (x) ≈ f (a) + f 0 (a)(x − a). √ Example. If f (x) = 3 x, and a = 1, the formula says √ 3 x ≈ 1 + 13 (x − 1). Math 311-102 Harold P. Boas The multi-variable approximation formula is ∂f ∂f f (x, y) ≈ f (a, b)+ ∂x (a, b)(x − a) + ∂y (a, b)(y − b). p Example. If f (x, y) = sin(x + y 4 + y ), and (a, b) = (0, 0), p then sin(x + y 4 + y ) ≈ sin(0)+ cos(0)(x − 0)+ 2 cos(0)(y − 0) = x + 2y. boas@tamu.edu Math 311-102 June 17, 2005: slide #1 Math 311-102 Approximation of vector functions The derivative matrix x 2 + y2 Example. To approximate f (x, y) = x3 + sin(y) near the xey point (a, b), use theprevious formula in each row to get 2a(x − a) + 2b(y − b) f (x, y) ≈ f (a, b) + 3a2 (x − a) + cos(b)(y − b) b b e (x − a) + ae (y − b) Ã ! 2a 2b x−a 2 . = f (a, b) + 3a cos(b) y−b eb aeb We can think of the derivative of a vector function as being a matrix. Math 311-102 June 17, 2005: slide #2 June 17, 2005: slide #3 The preceding example shows that the derivative of a function f 1 (x, y) f (x, y) = f 2 (x, y) f 3 (x, y) should be viewed as the matrix of partial derivatives ∂ f1 ∂∂xf2 ∂x ∂ f3 ∂x ∂ f1 ∂y ∂ f2 ∂y . ∂ f3 ∂y The rows of the matrix are the gradients of the component functions. The matrix is often called the Jacobian matrix. Math 311-102 June 17, 2005: slide #4 Exercise Answers 4 sin(x) + 12 25 tan(y) + 5 z 16 3 z f (x, y, z) = 12 25 x + 25 sin(y) − 5 ze 4 3 − 5 x cos(x) + 5 y + yz 9 25 1. The Jacobian matrix equals 9 12 2 25 cos(x) 25 sec (y) 12 16 25 25 cos(y) 3 − 45 cos(x) + 45 x sin(x) 5 +z 1. Find the derivative matrix of f at (0, 0, 0). 2. Show that the matrix is orthogonal: the inverse equals the transpose. = 3. The matrix is a rotation matrix. Find the axis of rotation. 9 25 12 25 − 45 12 25 16 25 3 5 4 5 3 . −5 4 5 ¯ ¯ ¯ 3 z 3 z ¯ − 5 e − 5 ze ¯ ¯ ¯ y (0,0,0) 0 2. The columns of the matrix are orthonormal. 3 3. The vector 4 is an eigenvector with eigenvalue 1. 0 Math 311-102 June 17, 2005: slide #5 Math 311-102 June 17, 2005: slide #6