Document 10430185
advertisement

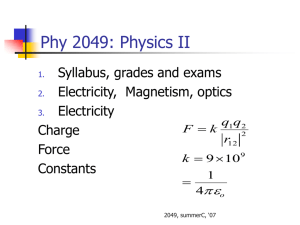
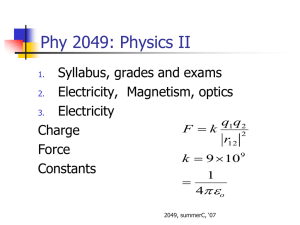
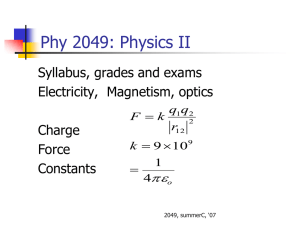
PHY 2049: Physics II Coulomb’s law: Two kinds of charges, positive and negative, unlike attract, like repel. Electrons and Protons: q = ± 1.602 x 10-19 C Current I = dq/dt 1 Amp. = 1 C/s Add forces as vectors F k q1 q 2 r12 2 rˆ PHY 2049: Physics II A rule Try to calculate the force magnitude by ignoring the signs of charges. Then assign the direction by looking at the signs. Never do both (using the charge signs in the calculation of the force and then assign the direction). PHY 2049: Physics II q1 = 2Q q2 = - 2Q q3 = -4Q E at origin [-0.344N, -0.218N], 212.38º Phy 2049: Physics II trial run In Fig. at right, the particles have charges q1 = -q2 = 300 nC and q3 = -q4 = 200 nC, and distance a = 4.0 cm. What is the direction of the force on particle 4? A. B. C. D. 3,1,2 PHY 2049: Physics II Balls are touched and then separated. Rank them by Charge left Magnitude of Force before After Charge transferred TALP: Take a look Problem PHY 2049: Physics II d Force on the center charge = 6kq2/d2 Direction: -x, 180º, PHY 2049: Physics II q1 = q4 = Q; q2 = q3 = q what is Q/q so that the force on 1 is zero All charges same sign. There is no solution. Q and q different sign. There is a possible solution. Is the answer the same if the force on 3 is to be zero PHY 2049: Physics II What is the force on the central chlorine ion? Suppose that we put in an electron that sits on a cesium site and neutralizes it, which way does the Chlorine move? PHY 2049: Physics II Electric Field Force F = qE E = k ∑ rˆ qi/ri2 •Electric field lines denote direction •Their density represents magnitude •They do not cross Physics II PHY 2049: Physics II Ek z qz 2 R 2 3/ 2 zˆ PHY 2049: Physics II Induction and charge transfer on contact Forces summed as vectors Electric fields PHY 2049: Physics II Physics II • Potentials add like numbers