OUTLINE
advertisement

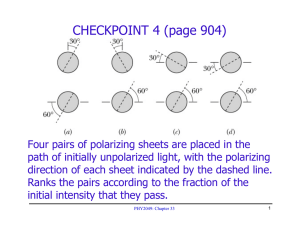
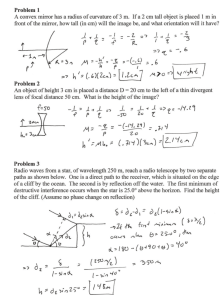
OUTLINE 1. Polarization (continued) 2. Reflection and refraction of light (Skip Section 33-10 on polarization by reflection and Brewster’s law.) 3. Plain mirrors CHECKPOINT 4 Four pairs of polarizing sheets are placed in the path of initially unpolarized light, with the polarizing direction of each sheet indicated by the dashed line. Which pair lets the largest fraction of light through? Which pair lets through the least? QUIZ 45° 45° (a) (b) • Initially unpolarized light is sent into a set of three polarizing sheets, either a or b. Which set lets more light through? a. (b completely blocks light.) • What fraction of the light’s initial intensity is transmitted? 1/8 CHECKPOINT (a) (b) Light travels from a medium with an index of refraction n1 into a medium with an index of refraction n2. In case a, is n2 larger or smaller than n1? n2 > n1. Chromatic dispersion White light violet red Prisms have double reflections and a limited resolution. To study a light spectrum, diffraction gratings (see Chapter 36) are used instead of prisms. See a demo in the lobby. Total internal reflection n2 n1 For a total reflection to occur, n1 has to be larger than n2. Quiz radius n2 ≈ 1 n1 = 1.33 A point source of light is located 3 m below the body of water. Find the diameter of the circle at the surface through which light emerges from the water. θ = 48.8° 2r = 6.84 m Plain mirrors i = –p All reflected rays extrapolate to point I, as if they all originated there. The viewer perceives a virtual image located at I. Quiz h A six-foot-tall gator stands in front of a mirror. In order for him to see himself from top to toe in the mirror, what is the minimum height required of the mirror? 3 ft. CHECKPOINT 1 • A person stands between two vertical, parallel mirrors A and B separated by distance d and looks into mirror A. How deep behind mirror A is the first, closest image of object O? 0.2d. • How deep behind mirror A is the second image? 1.8d. • How about the third image? 2.2d.