Document 10426671
advertisement
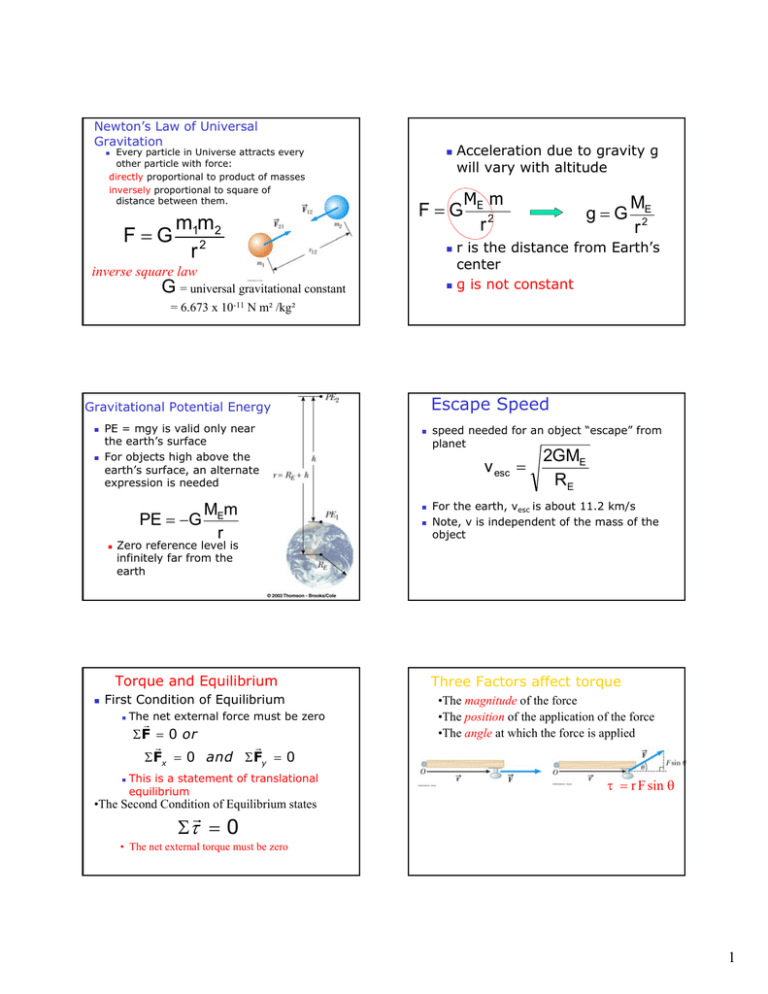
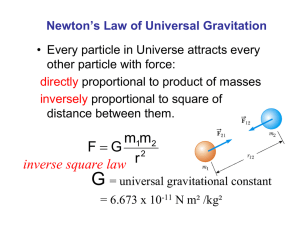
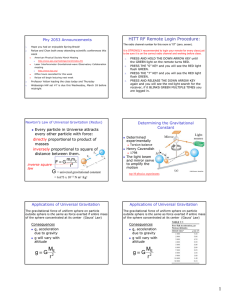
Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation Every particle in Universe attracts every other particle with force: directly proportional to product of masses inversely proportional to square of distance between them. F=G m1m2 r2 Acceleration due to gravity g will vary with altitude F=G mE1m M m2 r g=G 2 ME r2 r is the distance from Earth’s center g is not constant inverse square law G = universal gravitational constant = 6.673 x 10-11 N m² /kg² Escape Speed Gravitational Potential Energy PE = mgy is valid only near the earth’s surface For objects high above the earth’s surface, an alternate expression is needed PE = −G MEm r Zero reference level is infinitely far from the earth Torque and Equilibrium First Condition of Equilibrium The net external force must be zero r Σ F = 0 or r r Σ Fx = 0 and Σ Fy = 0 This is a statement of translational equilibrium speed needed for an object “escape” from planet v esc = 2GME RE For the earth, vesc is about 11.2 km/s Note, v is independent of the mass of the object Three Factors affect torque •The magnitude of the force •The position of the application of the force •The angle at which the force is applied τ = r F sin θ •The Second Condition of Equilibrium states r Στ = 0 • The net external torque must be zero 1 Torque direction: Right hand rule again Center of Gravity Force turns it in the counterclockwise direction In finding the torque produced by the force of gravity, all of the weight of the object can be considered to be concentrated at a single point Force turns it in the clockwise direction Center of gravity xcg = Σmi xi Σmi y i and ycg = Σmi Σmi 2