Module 14 8/12/2010
advertisement

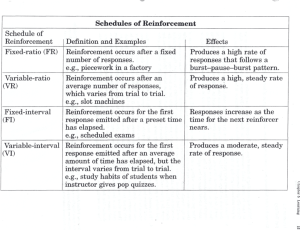
8/12/2010 Module 14 Module 14 Motivation • How do human needs and job designs influence motivation to work? • How do thought processes and decisions affect motivation to work? • What role does reinforcement play in motivation? 14.1 HUMAN NEEDS Human Needs and Job Design Maslow’s Hierarchy • Maslow described a hierarchy of needs topped by self-actualization • Alderfer’s ERG theory deals with existence,, relatedness and growth g needs • McClelland identified acquired needs for achievement, power and affiliation • Herzberg’s two-factor theory focuses on higher-order need satisfaction • The core characteristics model integrates motivation and job design • Motivation – level, direction and persistence of effort expended at work • Maslow’s hierarchy – Needs N d • Unfulfilled desires that stimulate people to act – Lower order needs • Physiological, safety and social needs – Higher order needs • Esteem and self-actualization 1 8/12/2010 HUMAN NEEDS HUMAN NEEDS Maslow’s Hierarchy Alderfer’s ERG Theory • Alderfer’s ERG Theory Existence Needs are desires for physiological and material well‐being. Relatedness needs are desires for satisfying interpersonal relationships. Relatedness Needs are desires for satisfying interpersonal relationships. Growth Needs are desires for continued psychological growth and development. HUMAN NEEDS HUMAN NEEDS McClelland’s Acquired Needs McClelland’s Acquired Needs • Three acquired needs that vary in strength among people • Two forms of need for power Need for Achievement Need for Power Need for Affiliation • is the desire to do something better, to solve problems, or to master complex tasks. • is the desire to control, influence, or be responsible for other people. • Is the desire to establish and maintain good relations with other people. – Need for personal power – Need for social power 2 8/12/2010 HUMAN NEEDS JOB DESIGN Herzberg Two-Factor Theory Core Characteristics Model Hygiene Factors found in the job context • working conditions g • interpersonal relations • organizational policies • salary Motivator Factors found in job content • sense of achievement • recognition • responsibility • advancement • personal growth. • Job design – Allocation of specific tasks to individuals and groups • Job enrichment – Adds opportunities for satisfying higher-order needs to a job by adding opportunities for planning and controlling work JOB DESIGN 14.2 Core Characteristics Model Thought Processes and Decisions Five Core Job Characteristics Skill variety Task identity • Equity theory explains how social comparisons can motivate individual behavior • Expectancy theory considers motivation = expectancy x instrumentality x valence Task significance Autonomy Feedback from the job itself • Goal-setting theory shows that wellchosen and well-set goals can be motivating 3 8/12/2010 THOUGHT PROCESSES THOUGHT PROCESSES Equity Theory Expectancy Theory • Equity theory explains how social comparisons can motivate individual behavior • Expectancy theory considers – Perceived negative inequity • Attempt to restore equity by working less or quitting – Perceived positive inequity • Attempt to restore equity by extra effort motivation = expectancy x instrumentality x valence Expectancy Instrumentality Valence • “Can I achieve the desired level of task performance?” • “What work outcomes will be received as a result of the performance?” • “How highly do I value work outcomes?” THOUGHT PROCESSES THOUGHT PROCESSES Expectancy Theory Goal Setting Theory • Goal-setting theory shows that wellchosen and well-set goals can be motivating 4 8/12/2010 14.3 REINFORCEMENT Reinforcement Law of Effect • Operant conditioning influences behavior by controlling its consequences • Positive reinforcement connects desirable behavior with pleasant consequences • Punishment connects undesirable behavior with unpleasant consequences • The law of effect states that behavior followed by a pleasant consequence is likely to be repeated; behavior followed by an unpleasant consequence is unlikely to be repeated. REINFORCEMENT REINFORCEMENT Operant Conditioning Operant Conditioning • Operant Conditioning – B. F. Skinner – Influences behavior by controlling its consequences. – Positive reinforcement strengthens a behavior by making a desirable consequence contingent on its occurrence. – Negative reinforcement strengthens a behavior by making the avoidance of an undesirable consequence contingent on its occurrence. – Punishment discourages by making an unpleasant consequence contingent on its occurrence. – Extinction discourages a behavior by making q the removal of a desirable consequence contingent on its occurrence. 5 8/12/2010 REINFORCEMENT REINFORCEMENT Operant Conditioning Positive Reinforcement • Positive reinforcement connects desirable behavior with pleasant consequences – Law of contingent reinforcement • Reward only when desirable behavior is demonstrated – Law of immediate reinforcement • Reward immediately after the desirable behavior is demonstrated REINFORCEMENT REINFORCEMENT Positive Reinforcement Punishment • Shaping • Punishment – Creating a new behavior by positive reinforcement of similar behaviors • Continuous reinforcement – Reward every time behavior is exhibited • Intermittent reinforcement – Connects undesirable behavior with unpleasant consequences • Deny a reward • No raise/pay reduction • Reprimand – Reward behavior periodically 6 8/12/2010 Module 14 Case • Pixar Animation Studios – Home of the Creative Geniuses 7