Document 10286189
advertisement

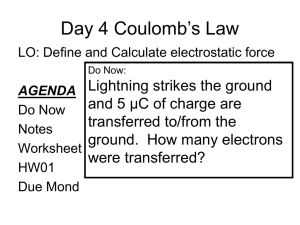
Northeastern Illinois University College Physics II Electric Field & Electric Charge Greg Anderson Department of Physics & Astronomy Northeastern Illinois University January 2012 c 2004-2012 G. Anderson College Physics II – slide 1 / 33 Northeastern Illinois University Overview Course Overview Electric Charge Coulomb’s Law Induced Charge Electrostatic Forces c 2004-2012 G. Anderson College Physics II – slide 2 / 33 Northeastern Illinois University Course Overview Introduction Lab Sections Outline: Electric Charges & Forces Electro-Magnetic Forces Electric Charge Coulomb’s Law Induced Charge Course Overview Electrostatic Forces c 2004-2012 G. Anderson College Physics II – slide 3 / 33 Northeastern Illinois University Course Overview Introduction Lab Sections Outline: Electric Charges & Forces Electro-Magnetic Forces Introduction ◆ If you click on my name in the previous page, you should be directed to the Physics homepage, provided your Acrobat Reader has been properly configured. Electric Charge Coulomb’s Law ◆ To go directly to the PHYS-202 course page select this link. Induced Charge Electrostatic Forces ◆ Press on CTRL-L to go to/leave full screen view. c 2004-2012 G. Anderson College Physics II – slide 4 / 33 Northeastern Illinois University Course Overview Introduction Lab Sections Outline: Electric Charges & Forces Electro-Magnetic Forces Lab Sections Three sections of the companion lab: PHYS-204 PHYS-204 PHYS-204 1 2 3 Physics II Lab Physics II Lab Physics II Lab W W W 12:00-1:50 3:25-5:15 7:05-8:55 Anderson Delzenero Delzenero Electric Charge Coulomb’s Law Induced Charge Electrostatic Forces Location: room SCI-237. Future handouts may be downloaded at: http://physics.neiu.edu/labs/204/ c 2004-2012 G. Anderson College Physics II – slide 5 / 33 Northeastern Illinois University Course Overview Introduction Lab Sections Outline: Electric Charges & Forces Electro-Magnetic Forces Electric Charge Coulomb’s Law Outline: Electric Charges & Forces ◆ Electric Charge ■ Quantization ■ SI Units ◆ Electric Charge in the Atom Induced Charge Electrostatic Forces ◆ Insulators and Conductors ◆ Conservation of Charge ■ Electric charge is conserved ■ Induced Charge ◆ Coulomb’s Law ◆ The Electric Field c 2004-2012 G. Anderson College Physics II – slide 6 / 33 Northeastern Illinois University Course Overview Introduction Lab Sections Outline: Electric Charges & Forces Electro-Magnetic Forces Electro-Magnetic Forces With the exception gravity, almost every force that you witness in everyday life is electro-magnetic in origin. ◆ EM forces bind electrons and nuclei into atoms. Electric Charge Coulomb’s Law ◆ EM forces bind atoms into molecules. O H H Induced Charge Electrostatic Forces ◆ EM forces bind atoms & molecules into solids. Electric forces are produced by electric charges. c 2004-2012 G. Anderson College Physics II – slide 7 / 33 Northeastern Illinois University Course Overview Electric Charge Electric Charge Quantization Active Learning Charged Constituents Q in Atoms & Molecules Materials: Insulators and Conductors Electric Charged is Conserved Charge Conservation Examples Producing Static Charge I Producing Static Charge II Active Learning Electric Charge Coulomb’s Law Induced Charge Electrostatic Forces c 2004-2012 G. Anderson College Physics II – slide 8 / 33 Northeastern Illinois University Course Overview Electric Charge Electric Charge Quantization Active Learning Charged Constituents Q in Atoms & Molecules Materials: Insulators and Conductors Electric Charged is Conserved Charge Conservation Examples Producing Static Charge I Producing Static Charge II Active Learning Coulomb’s Law Electric Charge Quantization Electric charge is quantized: A charged object has a surplus or deficit in the number of electrons relative to protons. ◆ e = fundamental unit of charge Qproton = +e, Qelectron = −e ◆ For any charge: Q = ne, n = 0, ±1, ±2, . . . SI Units: [Charge] = Coulomb = C Induced Charge Electrostatic Forces c 2004-2012 G. Anderson e = 1.6 × 10−19 C. College Physics II – slide 9 / 33 Northeastern Illinois University Course Overview Electric Charge Electric Charge Quantization Active Learning Charged Constituents Q in Atoms & Molecules Materials: Insulators and Conductors Electric Charged is Conserved Charge Conservation Examples Producing Static Charge I Producing Static Charge II Active Learning Coulomb’s Law Active Learning: Charge Quantization Electric charge is quantized. A charged object has a surplus or deficit of the number of electrons relative to protons. For any charged object: Q = ne, n = 0, ±1, ±2, . . . ◆ Let Ne be the number of electrons in an object ◆ Let Np be the number of protons in an object. ◮ Express n in terms of Ne and Np . Induced Charge Electrostatic Forces c 2004-2012 G. Anderson College Physics II – slide 10 / 33 Northeastern Illinois University Course Overview Electric Charge Electric Charge Quantization Active Learning Charged Constituents Q in Atoms & Molecules Materials: Insulators and Conductors Electric Charged is Conserved Charge Conservation Examples Producing Static Charge I Producing Static Charge II Active Learning Coulomb’s Law Active Learning: Charge Quantization Electric charge is quantized. A charged object has a surplus or deficit of the number of electrons relative to protons. For any charged object: Q = ne, n = 0, ±1, ±2, . . . ◆ Let Ne be the number of electrons in an object ◆ Let Np be the number of protons in an object. ◮ Express n in terms of Ne and Np . Induced Charge Electrostatic Forces n = Np − N e c 2004-2012 G. Anderson College Physics II – slide 10 / 33 Northeastern Illinois University Course Overview Electric Charge Electric Charge Quantization Active Learning Charged Constituents Q in Atoms & Molecules Materials: Insulators and Conductors Electric Charged is Conserved Charge Conservation Examples Producing Static Charge I Producing Static Charge II Active Learning Charge & Charged Constituents The total charge of any composite object is the sum of the charges of its charged constituents: electrons and protons. ◆ Ne electrons, each with charge −e contribute: Qelectrons = Ne (−e) = −Ne e ◆ Np protons, each with charge +e contribute: Qprotons = Np e Example − + Coulomb’s Law Induced Charge Together they give a total charge: Electrostatic Forces c 2004-2012 G. Anderson Q = (Np − Ne )e − + + Np = 3 − Ne = 4 − Q = −1e College Physics II – slide 11 / 33 Northeastern Illinois University Charges in Atoms and Molecules − Course Overview Electric Charge Electric Charge Quantization Active Learning Charged Constituents Q in Atoms & Molecules Materials: Insulators and Conductors Electric Charged is Conserved Charge Conservation Examples Producing Static Charge I Producing Static Charge II Active Learning Atoms are composed of negatively charged electrons bound to a nucleus of neutrons, protons. + − + − − O Coulomb’s Law Induced Charge Electrostatic Forces H + c 2004-2012 G. Anderson H + Charges in atoms & molecules are not always evenly distributed. e.g., water. College Physics II – slide 12 / 33 Northeastern Illinois University Course Overview Electric Charge Electric Charge Quantization Active Learning Charged Constituents Q in Atoms & Molecules Materials: Insulators and Conductors Electric Charged is Conserved Charge Conservation Examples Producing Static Charge I Producing Static Charge II Active Learning Materials: Insulators and Conductors − + + − + + − + + + − − + − + + − − − − + + + − − − − + + + + − − − − + + + + − − − + − − + + ◆ Conductor: Loosely bound charges (electrons) are free to move. Examples: Iron, copper, gold ◆ Insulator: Electrons are bound to nuclei and can’t Coulomb’s Law move. Examples: Wood, rubber, electrical tape Induced Charge Electrostatic Forces − ◆ Semi-Conductor: Neither a good conductor or good insulator. Examples: Silicon, germanium, carbon c 2004-2012 G. Anderson College Physics II – slide 13 / 33 Northeastern Illinois University Course Overview Electric Charge Electric Charge Quantization Active Learning Charged Constituents Q in Atoms & Molecules Materials: Insulators and Conductors Electric Charged is Conserved Charge Conservation Examples Producing Static Charge I Producing Static Charge II Active Learning Electric Charged is Conserved Electric Charge is Conserved: The total charge of an isolated system never changes. For an Isolated System: Qinitial = Qfinal Coulomb’s Law Induced Charge Electrostatic Forces c 2004-2012 G. Anderson College Physics II – slide 14 / 33 Northeastern Illinois University Course Overview Electric Charge Electric Charge Quantization Active Learning Charged Constituents Q in Atoms & Molecules Materials: Insulators and Conductors Electric Charged is Conserved Charge Conservation Examples Producing Static Charge I Producing Static Charge II Active Learning Charge Conservation Examples Examples of electric charge conservation: Pair production − γ + γ −→ e+ + e− Pair annihilation e+ + e− −→ γ + γ Ionization Coulomb’s Law Induced Charge H + γ −→ p+ + e− + + − H − + Electrostatic Forces c 2004-2012 G. Anderson College Physics II – slide 15 / 33 Northeastern Illinois University Producing Static Charge I Course Overview Electric Charge Electric Charge Quantization Active Learning Charged Constituents Q in Atoms & Molecules Materials: Insulators and Conductors Electric Charged is Conserved Charge Conservation Examples Producing Static Charge I Producing Static Charge II Active Learning ◆ When you rub a acrylic or glass rod with a paper towel or a silk cloth, the rod becomes positively charged. Coulomb’s Law Induced Charge Electrostatic Forces c 2004-2012 G. Anderson College Physics II – slide 16 / 33 Northeastern Illinois University Producing Static Charge I Course Overview Electric Charge Electric Charge Quantization Active Learning Charged Constituents Q in Atoms & Molecules Materials: Insulators and Conductors Electric Charged is Conserved Charge Conservation Examples Producing Static Charge I Producing Static Charge II Active Learning Coulomb’s Law Induced Charge Electrostatic Forces − + + + − − ◆ When you rub a acrylic or glass rod with a paper towel or a silk cloth, the rod becomes positively charged. ◮ The cloth strips electrons off of the rod. ◮ Charges are not created or destroyed, they are separated. ◮ The deficit of electrons in the glass rod is balanced by a surplus of electrons on the cloth. c 2004-2012 G. Anderson College Physics II – slide 16 / 33 Northeastern Illinois University Producing Static Charge II Course Overview Electric Charge Electric Charge Quantization Active Learning Charged Constituents Q in Atoms & Molecules Materials: Insulators and Conductors Electric Charged is Conserved Charge Conservation Examples Producing Static Charge I Producing Static Charge II Active Learning ◆ When you rub a PVC or plastic rod with a wool cloth: the rod becomes negatively charged. Coulomb’s Law Induced Charge Electrostatic Forces c 2004-2012 G. Anderson College Physics II – slide 17 / 33 Northeastern Illinois University Producing Static Charge II Course Overview Electric Charge Electric Charge Quantization Active Learning Charged Constituents Q in Atoms & Molecules Materials: Insulators and Conductors Electric Charged is Conserved Charge Conservation Examples Producing Static Charge I Producing Static Charge II Active Learning Coulomb’s Law + − − − + + ◆ When you rub a PVC or plastic rod with a wool cloth: the rod becomes negatively charged. ◮ The rod strips electrons off of the cloth. ◮ Charges are not created or destroyed, they are separated. Induced Charge Electrostatic Forces ◮ The surplus of electrons in the plastic rod is balanced by a deficit of electrons in the cloth. c 2004-2012 G. Anderson College Physics II – slide 17 / 33 Northeastern Illinois University Course Overview Electric Charge Electric Charge Quantization Active Learning Charged Constituents Q in Atoms & Molecules Materials: Insulators and Conductors Electric Charged is Conserved Charge Conservation Examples Producing Static Charge I Producing Static Charge II Active Learning Coulomb’s Law Active Learning Consider a glass rod which is initially electrically neutral, and a silk cloth which initially has charge q. The glass rod is rubbed with the silk. During the process the glass rod acquires a charge Q. The silk has charge: a. q + Q. Before: 0 q b. q − Q. Silk c. −Q. d. +Q. After: Q ? e. −q. Induced Charge Electrostatic Forces c 2004-2012 G. Anderson College Physics II – slide 18 / 33 Northeastern Illinois University Course Overview Electric Charge Electric Charge Quantization Active Learning Charged Constituents Q in Atoms & Molecules Materials: Insulators and Conductors Electric Charged is Conserved Charge Conservation Examples Producing Static Charge I Producing Static Charge II Active Learning Coulomb’s Law Active Learning Consider a glass rod which is initially electrically neutral, and a silk cloth which initially has charge q. The glass rod is rubbed with the silk. During the process the glass rod acquires a charge Q. The silk has charge: a. q + Q. Before: 0 q b. q − Q. Silk c. −Q. d. +Q. e. −q. Induced Charge After: Q ? Note: Q + (q − Q) = q Electrostatic Forces c 2004-2012 G. Anderson College Physics II – slide 18 / 33 Northeastern Illinois University Course Overview Electric Charge Coulomb’s Law Attraction & Repulsion Electrostatic Force Induced Charge Electrostatic Forces c 2004-2012 G. Anderson Coulomb’s Law College Physics II – slide 19 / 33 Northeastern Illinois University Course Overview Electric Charge Coulomb’s Law Attraction & Repulsion Electrostatic Force Induced Charge Attraction & Repulsion Charges of opposite sign attract. DCS Demos: ◆ 5A-10.10: Static Charge + − Producing ◆ Electrostatic Forces 5A-20.10: Coulomb’s Law Charges of the same sign repel. ◆ 5A-20.20: Coulomb’s Law with Pith Balls + + ◆ 5A-40.10: Induced Charge c 2004-2012 G. Anderson College Physics II – slide 20 / 33 Northeastern Illinois University Course Overview Electrostatic Force Electric force between two charged, static objects: Electric Charge Coulomb’s Law Attraction & Repulsion Electrostatic Force Induced Charge 1 Q1 Q2 Q1 Q2 F =k 2 = r 4πǫ0 r2 This is known as Coulomb’s law. Electrostatic Forces (magnitude of force) k = 8.988 × 109 N · m2 /C2 ≃ 9 × 109 N · m2 /C2 ǫ0 is known as the permittivity of free space. 1 = 8.85 × 10−12 C2 /N · m2 ǫ0 = 4πk c 2004-2012 G. Anderson College Physics II – slide 21 / 33 Northeastern Illinois University Course Overview Electric Charge Coulomb’s Law Induced Charge Charging by Induction Charging by Conduction Electrostatic Forces c 2004-2012 G. Anderson Induced Charge College Physics II – slide 22 / 33 Northeastern Illinois University Charging by Induction Course Overview Electric Charge Coulomb’s Law Induced Charge Charging by Induction Charging by Conduction Electrostatic Forces c 2004-2012 G. Anderson − − − − L M College Physics II – slide 23 / 33 Northeastern Illinois University Charging by Conduction Course Overview Electric Charge Coulomb’s Law Induced Charge Charging by Induction Charging by Conduction Electrostatic Forces c 2004-2012 G. Anderson College Physics II – slide 24 / 33 Northeastern Illinois University Course Overview Electric Charge Coulomb’s Law Induced Charge Electrostatic Forces Active Learning Net Force from Multiple Charges Vectors Adding Two Forces: F = F1 + F2 Action at a Distance? Electric Field Physics & Geometry Next Time c 2004-2012 G. Anderson Electrostatic Forces College Physics II – slide 25 / 33 Northeastern Illinois University Course Overview Electric Charge Coulomb’s Law Induced Charge Electrostatic Forces Active Learning Net Force from Multiple Charges Vectors Adding Two Forces: F = F1 + F2 Action at a Distance? Electric Field Physics & Geometry Next Time Active Learning Two uniformly charged spheres are fastened to frictionless pucks on an air table. The two charges satisfy Q2 = 3Q1 . Which force diagram is correct? A: F1 = −F2 Q1 C: F2 = −3F1 Q2 Q1 Q2 B: F1 = −F2 D: F1 = −3F2 Q1 Q1 c 2004-2012 G. Anderson Q2 Q2 College Physics II – slide 26 / 33 Northeastern Illinois University Course Overview Electric Charge Coulomb’s Law Induced Charge Electrostatic Forces Active Learning Net Force from Multiple Charges Vectors Adding Two Forces: F = F1 + F2 Action at a Distance? Electric Field Physics & Geometry Next Time Net Force from Multiple Charges When multiple charges are present, the net force on a given charge is the vector sum of the forces produced by the other charges. Q1 q Q2 Ftot = F1 + F2 c 2004-2012 G. Anderson (net force on q) College Physics II – slide 27 / 33 Northeastern Illinois University Course Overview Electric Charge Coulomb’s Law Induced Charge Electrostatic Forces Active Learning Net Force from Multiple Charges Vectors Adding Two Forces: F = F1 + F2 Action at a Distance? Electric Field Physics & Geometry Next Time Net Force from Multiple Charges When multiple charges are present, the net force on a given charge is the vector sum of the forces produced by the other charges. F2 Q1 q F 1 Q2 Ftot = F1 + F2 c 2004-2012 G. Anderson (net force on q) College Physics II – slide 27 / 33 Northeastern Illinois University Course Overview Electric Charge Coulomb’s Law Induced Charge Electrostatic Forces Active Learning Net Force from Multiple Charges Vectors Adding Two Forces: F = F1 + F2 Action at a Distance? Electric Field Physics & Geometry Next Time Net Force from Multiple Charges When multiple charges are present, the net force on a given charge is the vector sum of the forces produced by the other charges. F2 Ftot Q1 q F 1 Q2 Ftot = F1 + F2 c 2004-2012 G. Anderson (net force on q) College Physics II – slide 27 / 33 Northeastern Illinois University Course Overview Electric Charge Vectors Components: Coulomb’s Law Fx = F cos θ Fy = F sin θ Induced Charge Electrostatic Forces Active Learning Net Force from Multiple Charges Vectors Adding Two Forces: F = F1 + F2 Action at a Distance? Electric Field Physics & Geometry Next Time y Length: q F = Fx2 + Fy2 F Fy Angle wrt x-axis: θ tan θ = Fy /Fx x Fx c 2004-2012 G. Anderson College Physics II – slide 28 / 33 Northeastern Illinois University Adding Two Forces: F = F1 + F2 Graphical Method Course Overview Electric Charge Coulomb’s Law Algebraic Method Induced Charge Electrostatic Forces Active Learning Net Force from Multiple Charges Vectors Adding Two Forces: F = F1 + F2 Action at a Distance? Electric Field Physics & Geometry Next Time F1x F1y F2x F2y = = = = F1 cos θ1 F1 sin θ1 F2 cos θ2 F2 sin θ2 Fx Fy F tan θ = = = = F1x + F2x F F2y p1y + Fx2 + Fy2 Fy /Fx F F2 θ2 θ F1 θ1 c 2004-2012 G. Anderson College Physics II – slide 29 / 33 Northeastern Illinois University Course Overview Electric Charge Coulomb’s Law Induced Charge Electrostatic Forces Active Learning Net Force from Multiple Charges Vectors Adding Two Forces: F = F1 + F2 Action at a Distance? Electric Field Physics & Geometry Next Time Action at a Distance? Coulomb’s law appears to be a theory of “action at a distance.” Q1 Q2 F =k 2 r F + + F Q: What is the mediator of this interaction between these spacially separated objects? A: Electromagnetic Fields. c 2004-2012 G. Anderson College Physics II – slide 30 / 33 Northeastern Illinois University Course Overview Electric Charge Electric Field The electric field is the force/unit charge. Coulomb’s Law E = F/q Induced Charge Electrostatic Forces Active Learning Net Force from Multiple Charges Vectors Adding Two Forces: F = F1 + F2 Action at a Distance? Electric Field Physics & Geometry Next Time Newtons/ Coulomb F q Electric field produced by Q Q E Q 1 Q E=k 2 = r 4πǫ0 r2 Compute the electric field, then find the force on q: F = qE c 2004-2012 G. Anderson College Physics II – slide 31 / 33 Northeastern Illinois University Course Overview Physics & Geometry Imaginary sphere of radius r Electric Charge At a distance r from Q: Coulomb’s Law Induced Charge Electrostatic Forces Active Learning Net Force from Multiple Charges Vectors Adding Two Forces: F = F1 + F2 Action at a Distance? Electric Field Physics & Geometry Next Time c 2004-2012 G. Anderson r Q 1 Q E= ǫ0 4πr2 ◆ Surface Area: 4πr 2 ◆ Enclosed Charge Q College Physics II – slide 32 / 33 Northeastern Illinois University Course Overview Next Time Lecture 02: Electric Fields & Electric Charge II Electric Charge Coulomb’s Law Induced Charge Electrostatic Forces Active Learning Net Force from Multiple Charges Vectors Adding Two Forces: F = F1 + F2 Action at a Distance? Electric Field Physics & Geometry Next Time ◆ Review: Electric charges & forces ■ Electric charge, conserved and quantized. ■ Coulomb’s Law ◆ Coulomb’s Law ■ Attraction & Repulsion ■ Adding Force Vectors ◆ The Electric Field ■ Electric Field Lines ■ Electric Monopoles c 2004-2012 G. Anderson ■ Electric Dipoles College Physics II – slide 33 / 33