9/18/2011 1
advertisement
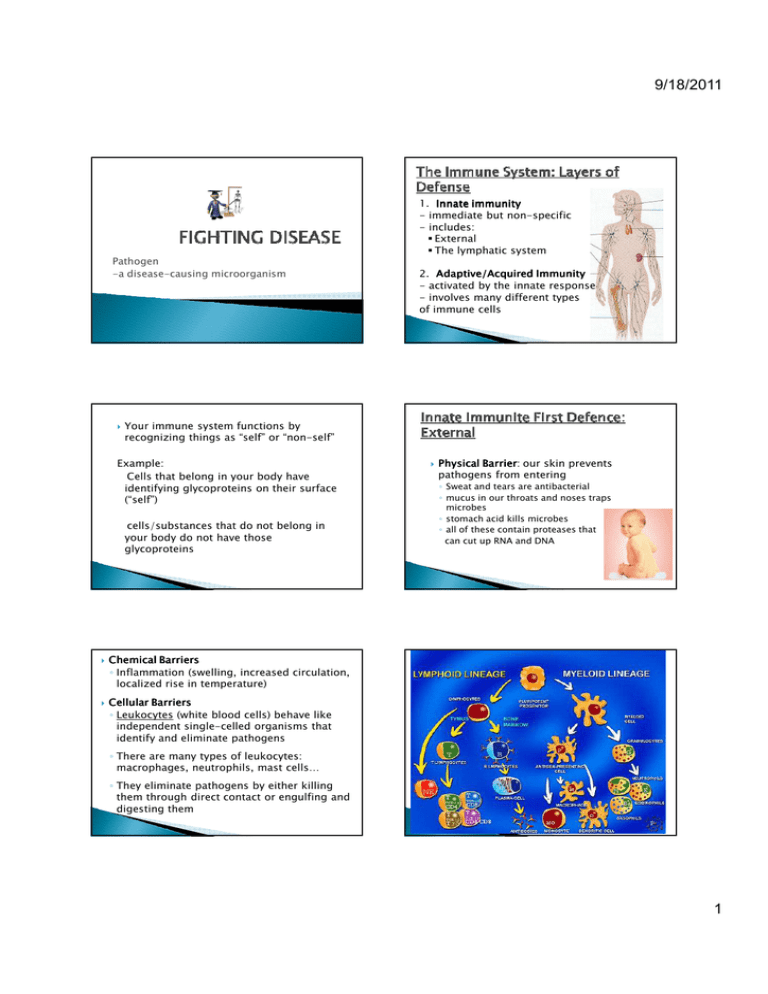
9/18/2011 1. Innate immunity - immediate but non-specific - includes: External The lymphatic system Pathogen -a disease-causing microorganism 2. Adaptive/Acquired Immunity - activated by the innate response - involves many different types of immune cells Your immune system functions by recognizing things as “self” or “non-self” Example: Cells that belong in your body have identifying glycoproteins on their surface (“self”) cells/substances that do not belong in your body do not have those glycoproteins Chemical Barriers ◦ Inflammation (swelling, increased circulation, localized rise in temperature) Cellular Barriers ◦ Leukocytes (white blood cells) behave like independent single-celled organisms that identify and eliminate pathogens Physical Barrier: Barrier our skin prevents pathogens from entering ◦ Sweat and tears are antibacterial ◦ mucus in our throats and noses traps microbes ◦ stomach acid kills microbes ◦ all of these contain proteases that can cut up RNA and DNA ◦ There are many types of leukocytes: macrophages, neutrophils, mast cells… ◦ They eliminate pathogens by either killing them through direct contact or engulfing and digesting them 1 9/18/2011 A complex network of organs that work to rid the body of infection Lymph, a transparent fluid that contains white blood cells (leukocytes leukocytes), leukocytes circulates through us It filters out and engulfs foreign bodies (ex. bacteria, viruses) Macrophages: white blood cells that seek and destroy foreign cells When injury happens: • Neutrophils (inflammatory) are the first cells to respond to injury • Macrophages clean up debris • Mast cells induce swelling, warmth, and redness • All 3 types of cells summon more immune system cells Adaptive immunity involves T cells and B cells T-cells seek out and kill invaders B-cell produce antibodies towards antigens Both produce memory cells that will allow the immune system to react FASTER and STRONGER next time, and (hopefully) preventing spread of infection Stronger than innate immunity Our immune systems have an “immulogical memory” ◦ The basis of vaccinations! Pathogens are remembered based on their specific structures: antigens ◦ antigens: anti-body gen-erators Passive vs. Active Immunity Active immunity body itself manufactures antibodies through fighting off a disease provides lasting protection Passive immunity antibodies are introduced into bloodstream of an individual, given from mother to child during pregnancy and breast-feeding short-term protection 2