Global Financial Crisis
advertisement

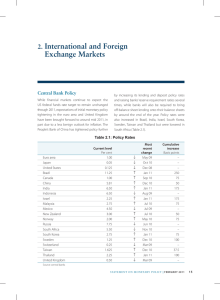
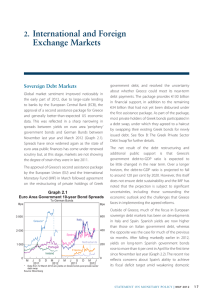
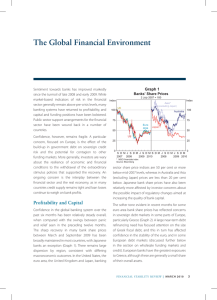
GLOBAL FINANCIAL CRISIS GLOBALIZATION LESSON 3 OBJECTIVES • Review events leading up to financial crisis that struck the US in 2008. • Explore the reverberations of said crisis on Europe and the global economy. • Identify if we have learned any lessons in the past 5 years. WARM UP • What have we learned about globalization so far? • Cultural, economic, political? • Effects on people? • Benefits? • Downsides? SUBPRIME MORTGAGE CRISIS • Global Pool of Money • World’s total investments • Doubled 2000 ($35t) – 2006 ($70t) b/c BRICS • Invested in US housing market via Mortgage-Backed Securities (MBS). Investments insured via Credit Default Swaps (CDS). • US Housing Bubble Bursts • Speculative – drove up prices, artificial values • Extended mortgages to subprime borrowers • ARM’s, NINA loans • Bubble bursts 06-07 – Values fall, ppl underwater or default on loan payments, banks see cash flow dry up, investors withdraw $ SUBPRIME MORTGAGE CRISIS • Collapse US Economy • Major US investment banks (Lehman Bros, Bear Sterns) assume massive losses, declare bankruptcy. AIG taken over by US govt. • Fed Reserve (TARP) & EU inject billions • Decline in production = loss of jobs = decline in spending • Global Effects • Banks unwilling to lend, economies slow as credit tightened • Internatl trade declines (decline US imports = decline global GDP = decline US exports = decline US GDP…) • Drop in US demand hurts rising economies • Stock values all over world drop w/loss confidence • Low interest rates = weaker $ = less profit trade partners • Too Big To Fail Explains It All LESSONS LEARNED? • Dodd-Frank reforms not enacted • Big Banks Bigger • No prosecution • Wall St Recovery, Main St Struggles • Debt Persists • Debt Ceiling Crisis EUROZONE • EU (28) • European Commission • Eurozone • Same currency (euro) • European Central Bank (monetary policy) • Separate national fiscal policies (budgets) EUROZONE DEBT CRISIS • When: Late 2009 • Why: Government Debts, Banking & Housing Crisis (similar to US – pool & securitize investments) & Slow, Uneven Economic Growth • Where: PIIGS and others • Who’s In Charge: European Commission, European Central Bank, IMF • Relief: Bailout, Loans, Lower Interest Rates, Austerity Budgets • Consequences: Economic & Political Changes, Social Upheaval ACTIVITY “Read” Interactive Charts on NY Times.com “It’s All Connected: An Overview of the Euro Crisis” http://www.nytimes.com/interact ive/2011/10/23/sundayreview/an-overview-of-the-eurocrisis.html and “Datapoints: It’s All Connected: A Spectator’s Guide to the Euro Crisis” http://www.nytimes.com/imagep ages/2011/10/22/opinion/201110 23_DATAPOINTS.html?ref=sundayreview Identify and define any terms with which you are unfamiliar! I know there will be some! • WHO called the euro zone “the ultimate contagion machine”? • WHAT are the major components of the debt crisis in Europe? • WHAT does “debt exposure” mean? • WHERE in Europe and around the world is the crisis having impact? • WHEN was the euro established as a form of currency? • WHY might rising borrowing costs, runs on banks and other financial troubles happen in certain European countries? • HOW much do borrowers in various European countries owe to banks of other nations?