Learning
advertisement
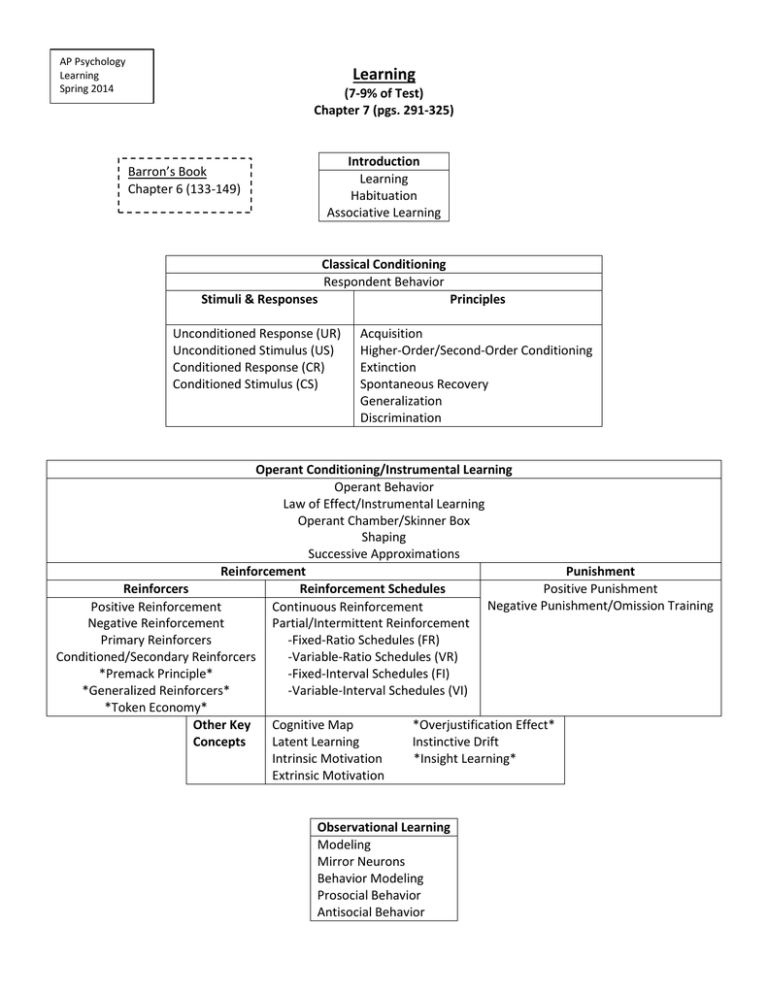
AP Psychology Learning Spring 2014 Learning (7-9% of Test) Chapter 7 (pgs. 291-325) Introduction Learning Habituation Associative Learning Barron’s Book Chapter 6 (133-149) Classical Conditioning Respondent Behavior Stimuli & Responses Principles Unconditioned Response (UR) Unconditioned Stimulus (US) Conditioned Response (CR) Conditioned Stimulus (CS) Acquisition Higher-Order/Second-Order Conditioning Extinction Spontaneous Recovery Generalization Discrimination Operant Conditioning/Instrumental Learning Operant Behavior Law of Effect/Instrumental Learning Operant Chamber/Skinner Box Shaping Successive Approximations Reinforcement Punishment Reinforcers Reinforcement Schedules Positive Punishment Negative Punishment/Omission Training Positive Reinforcement Continuous Reinforcement Negative Reinforcement Partial/Intermittent Reinforcement Primary Reinforcers -Fixed-Ratio Schedules (FR) Conditioned/Secondary Reinforcers -Variable-Ratio Schedules (VR) *Premack Principle* -Fixed-Interval Schedules (FI) *Generalized Reinforcers* -Variable-Interval Schedules (VI) *Token Economy* Other Key Cognitive Map *Overjustification Effect* Concepts Latent Learning Instinctive Drift Intrinsic Motivation *Insight Learning* Extrinsic Motivation Observational Learning Modeling Mirror Neurons Behavior Modeling Prosocial Behavior Antisocial Behavior Introduction: Be able to identify the 3 basic forms of learning. Know the two main principles of behaviorism. Classical Conditioning: Be able to explain the process of how a neutral stimulus becomes a conditioned stimulus. Be able to explain Ivan Pavlov’s research. Be able to describe basic classical conditioning principles. How do cognitive processes & biological predispositions affect classical conditioning? Understand John Garcia’s research on Taste Aversion. What have been some applications of Classical Conditioning? Be able to explain John Watson’s research with Little Albert. Operant Conditioning: Know the difference between Classical Conditioning & Operant Conditioning (Respondent v. Operant Behavior). Be able to describe Edward Thorndike’s research & his Law of Effect. Be able to explain BF Skinner’s research & beliefs. Understand the difference between positive reinforcement & negative reinforcement. Is Immediate Reinforcement or Delayed Reinforcement more effective? Know the difference between Continuous reinforcement & partial reinforcement. Which is most effective? Be able to differentiate between the 4 schedules of reinforcement & how each affects learning. Understand the difference between reinforcement & punishment. What are the drawbacks of using physical/corporal punishment on children? How do cognitive processes (latent learning & motivation) biological predispositions affect op. conditioning? Understand Robert Resocrla’s research. Understand Edward Tolman’s research into latent learning. What are some uses of operant conditioning (i.e at school, sports, work & home)? Be able to compare principles of classical conditioning to operant conditioning (Chart). Observational Learning: What is Observational Learning & what role do Mirror Neurons play in this type of learning? How do Mirror Neurons affect our emotions? Be able to describe Albert Bandura’s research & his conclusions. How are we affected by Behavior Modeling (both Prosocial & Antisocial)? Analyzing Data: Be able to interpret graphs that exhibit the results of learning experiments.







