Female Pelvis
advertisement
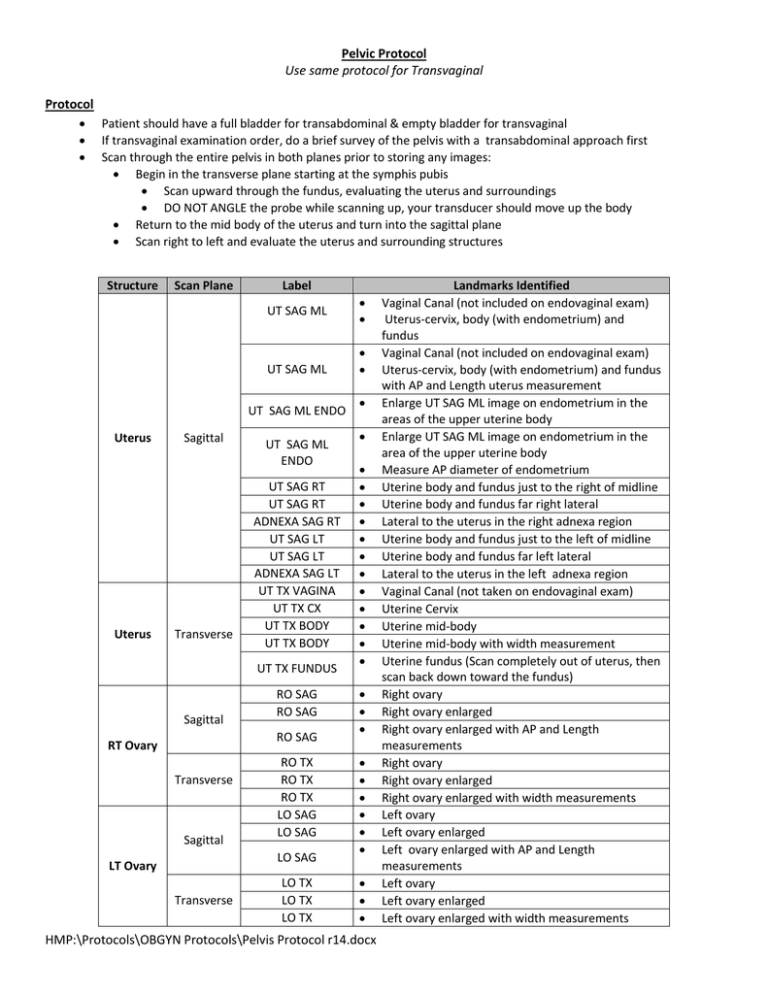
Pelvic Protocol Use same protocol for Transvaginal Protocol Patient should have a full bladder for transabdominal & empty bladder for transvaginal If transvaginal examination order, do a brief survey of the pelvis with a transabdominal approach first Scan through the entire pelvis in both planes prior to storing any images: Begin in the transverse plane starting at the symphis pubis Scan upward through the fundus, evaluating the uterus and surroundings DO NOT ANGLE the probe while scanning up, your transducer should move up the body Return to the mid body of the uterus and turn into the sagittal plane Scan right to left and evaluate the uterus and surrounding structures Structure Scan Plane Label UT SAG ML UT SAG ML UT SAG ML ENDO Uterus Uterus Sagittal Transverse UT SAG ML ENDO UT SAG RT UT SAG RT ADNEXA SAG RT UT SAG LT UT SAG LT ADNEXA SAG LT UT TX VAGINA UT TX CX UT TX BODY UT TX BODY UT TX FUNDUS Sagittal RO SAG RO SAG RO SAG RT Ovary Transverse Sagittal RO TX RO TX RO TX LO SAG LO SAG LO SAG LT Ovary Transverse LO TX LO TX LO TX HMP:\Protocols\OBGYN Protocols\Pelvis Protocol r14.docx Landmarks Identified Vaginal Canal (not included on endovaginal exam) Uterus-cervix, body (with endometrium) and fundus Vaginal Canal (not included on endovaginal exam) Uterus-cervix, body (with endometrium) and fundus with AP and Length uterus measurement Enlarge UT SAG ML image on endometrium in the areas of the upper uterine body Enlarge UT SAG ML image on endometrium in the area of the upper uterine body Measure AP diameter of endometrium Uterine body and fundus just to the right of midline Uterine body and fundus far right lateral Lateral to the uterus in the right adnexa region Uterine body and fundus just to the left of midline Uterine body and fundus far left lateral Lateral to the uterus in the left adnexa region Vaginal Canal (not taken on endovaginal exam) Uterine Cervix Uterine mid-body Uterine mid-body with width measurement Uterine fundus (Scan completely out of uterus, then scan back down toward the fundus) Right ovary Right ovary enlarged Right ovary enlarged with AP and Length measurements Right ovary Right ovary enlarged Right ovary enlarged with width measurements Left ovary Left ovary enlarged Left ovary enlarged with AP and Length measurements Left ovary Left ovary enlarged Left ovary enlarged with width measurements Pelvic Protocol Use same protocol for Transvaginal Normal Measurements Structure Uterus Measurements given are average measurements Uterus will be smaller for premenarche & postmenopausal uterus Endometrium Area of Interest Length Plane AP dimension or depth Sagittal Measureme nt 6-8.5cm nulliparous 8-10cm multiparous 3cm Width Transverse 2-3cm AP Sagittal 4-8mm Sagittal Only measure echogenic area Do not include the hypoechoic halo Ovaries Size varies w/ age, menstruation phase & menstrual status 6-10mm 7-14mm Length AP or depth Width Sagittal Sagittal Transverse Less than 8mm Less than 5 mm 2.5-5cm 1.5-3cm .6-2.2cm Comments Includes Vaginal canal and Uterine-Fundus, Body and Cervix Be careful on transvaginal scanning the cervix must be included or measurements will be off Widest portion of the uterine body from the anterior to posterior wall Calipers should be placed perpendicular to length Widest portion of the uterine body (level of cornua) Early Proliferative-Days 5-7 Thin bright echogenic line Late Proliferative-Days 10-14 3-line sign Secretory-Days 15-28, Thick echogenic stripe Post Menopausal-Asymptomatic Varies with hormone therapy Post Menopausal-Symptomatic Varies with hormone therapy Measure longest axis Calipers should be placed perpendicular to length Measure from left to right in the mid portion Tips You may need to apply pressure to the pelvis with the transducer in order to see ovaries. If transducer pressure is not working, pressure can be applied with your hand or by having the patient press down on themselves Look for free fluid in the posterior cul-de-sac Utilize 3D or 4D imaging to aid in pathology and endometrium shape details Ovaries are located between the uterus and the iliac vessels Pelvic muscles may mimic ovaries, evaluate structures in both planes prior to storing the image Patient Information Document first day of the last normal menstruation cycle Document if postmenopausal patient is currently on hormone therapy Document all symptoms in detail—area of pain, length of pain or bleeding, amount of bleeding, etc. Document clinical history of pregnancies, surgeries, or previous pathologies Pathology Gray scale sagittal and transverse images Gray scale sagittal and transverse images with 3 measurements (length, width and height) Color Doppler image document the presence of blood flow and Spectral Doppler image document type and velocity of blood flow HMP:\Protocols\OBGYN Protocols\Pelvis Protocol r14.docx






