Miss Daya's Virus Notes
advertisement
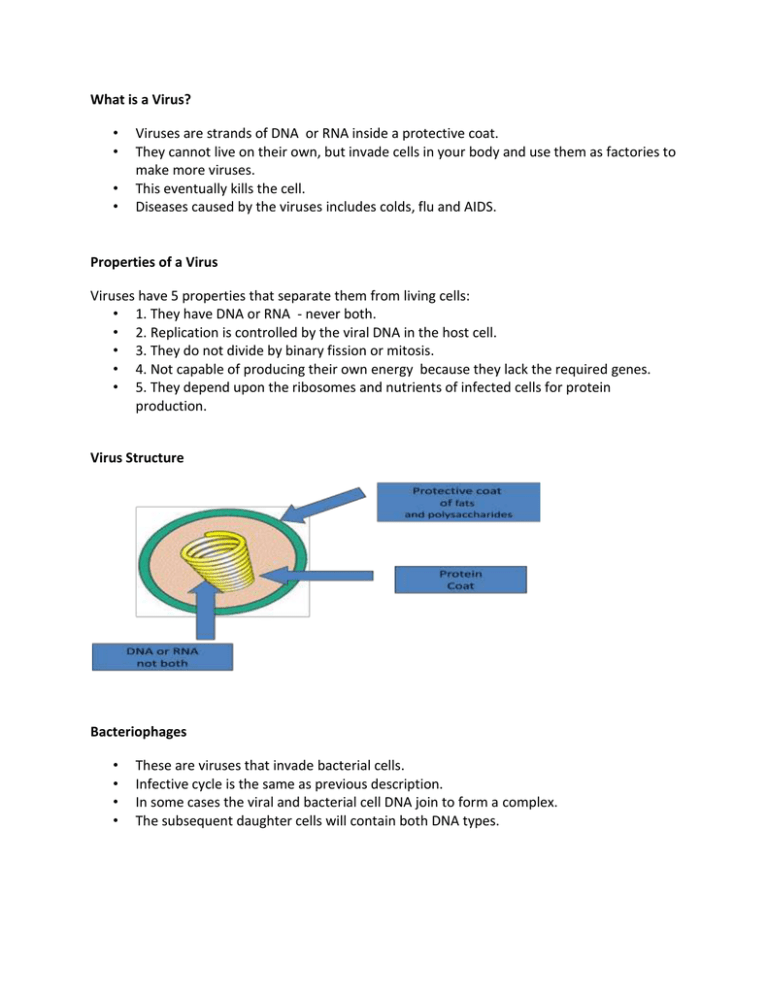
What is a Virus? • • • • Viruses are strands of DNA or RNA inside a protective coat. They cannot live on their own, but invade cells in your body and use them as factories to make more viruses. This eventually kills the cell. Diseases caused by the viruses includes colds, flu and AIDS. Properties of a Virus Viruses have 5 properties that separate them from living cells: • 1. They have DNA or RNA - never both. • 2. Replication is controlled by the viral DNA in the host cell. • 3. They do not divide by binary fission or mitosis. • 4. Not capable of producing their own energy because they lack the required genes. • 5. They depend upon the ribosomes and nutrients of infected cells for protein production. Virus Structure Bacteriophages • • • • These are viruses that invade bacterial cells. Infective cycle is the same as previous description. In some cases the viral and bacterial cell DNA join to form a complex. The subsequent daughter cells will contain both DNA types. Bacteriophages Structure • • • The Capsid- basically the “brain”. Contains a outer protein coat which is wrapped around the nucleic acid. – X-rays show that the capsid has 30 sides The Body- rod like structure that consists of a retractable sheath The Tail- 6 slender tail fibres which help anchor the virus to the host Invasion of Host Cell (Lytic Cycle) This is a cyclic process. 1. Virus contacts host cell. 2. Virus or DNA enters host cell. 3. Host cell DNA is broken up and new viral DNA or RNA is produced. 4. Viruses use protein from host cell membranes to make new protein coats. 5. Viral enzymes are produced that lyse the host cells. 6. Host cell membrane breaks. 7. New viruses are released. Lytic Cycle Animation: http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072556781/student_view0/chapter17/animation_quiz_2.htm Lysongenic Cycle • • • • Virus does not kill host cell right away Virus appears to be in a dormant state called lysogeny Dormant virus may be activated triggering lytic cycle Examples: cancer-causing viruses, HPV, Herpes Simplex, HIV 1. 2. 3. 4. Steps of Lysogenic Cycle Virus injects it’s own DNA/RNA into host cell Viral DNA combines with host DNA • New combined DNA called prophage Prophage is passed along to daughter cells by dividing naturally When activated, original viral DNA exits host cell and lytic cycle begins