Master Notes: Atomic Theory and Atom Structure
advertisement
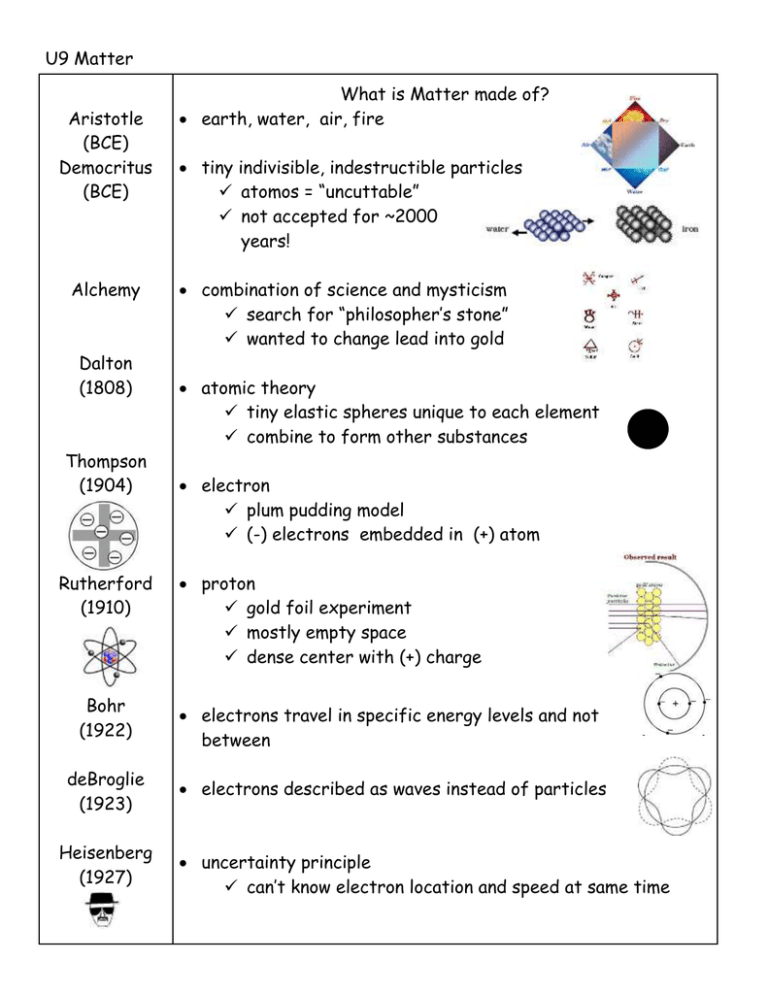
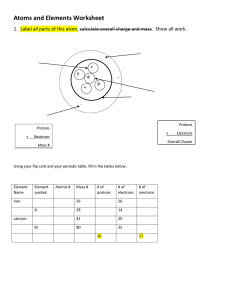
U9 Matter Aristotle (BCE) Democritus (BCE) Alchemy Dalton (1808) Thompson (1904) Rutherford (1910) Bohr (1922) deBroglie (1923) Heisenberg (1927) What is Matter made of? earth, water, air, fire tiny indivisible, indestructible particles atomos = “uncuttable” not accepted for ~2000 years! combination of science and mysticism search for “philosopher’s stone” wanted to change lead into gold atomic theory tiny elastic spheres unique to each element combine to form other substances electron plum pudding model (-) electrons embedded in (+) atom proton gold foil experiment mostly empty space dense center with (+) charge electrons travel in specific energy levels and not between electrons described as waves instead of particles uncertainty principle can’t know electron location and speed at same time Schrodinger (1930) electron probability cloud model Chadwick (1932) neutron in nucleus Gell-Mann quarks: tiny particles that make up protons and neutrons flavors: up, down, strange, charm, bottom, top Matter Atom Sub-atomic particles Structure anything that takes up space and has mass. smallest unit of an element that has all the properties of that element. proton neutron electron Location nucleus nucleus space outside nucleus Charge +1 0 -1 Mass ~1 amu ~1 amu ~1/2000 amu most of atom is empty space! Nucleus: overall (+) charge very small (~0.001% of atom’s volume) very dense (most of atom’s mass) analogy: nucleus = puck in center of hockey rink whole atom = entire arena and parking lot Standard Atomic Notation Element Info on PT atomic number = # protons (ID of element) in neutral atom: # protons = # electrons atomic mass (amu) = # protons + # neutrons element name atomic number: # protons = # electrons chemical symbol mass: # protons + # neutrons Changing # subatomic particles Δ # protons different element C has 6p+ add 1 proton 7p+ = N Δ # electrons (+) or (-) ion of same element neutral Na has 11p+ / 11e loses 1e- 11p+ /10e- Na+1 Δ # neutrons isotope of same element 12C has 6 p+ and 6 n0 add 1 n0 13C https://www.ted.com/talks/just_how_small_is_an_atom https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xazQRcSCRaY https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QbWKF9uDF7w https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IO9WS_HNmyg