three branches of government
advertisement
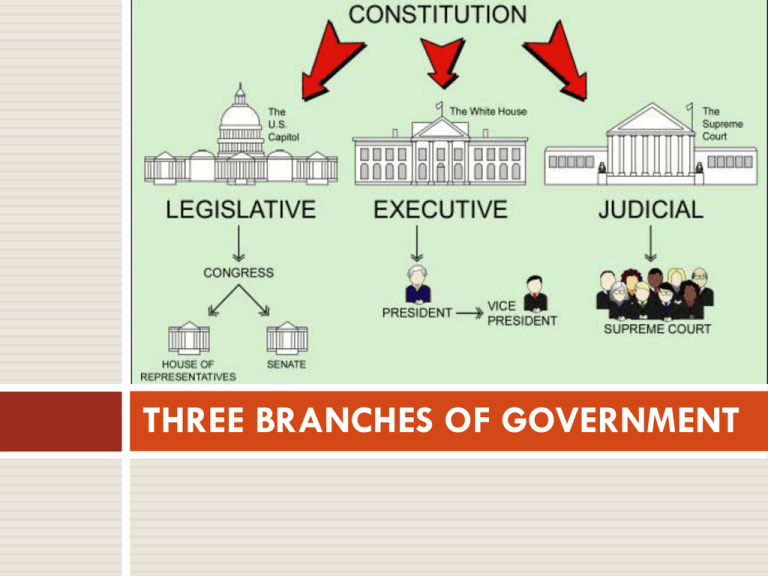
THREE BRANCHES OF GOVERNMENT Article I: The Legislature (pg. 248) U.S. CONGRESS HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES 435 members 2 yr. term; popular vote At least 25 years old U.S. citizen 7 yrs. Resident of state Reps based on population Power to: impeach, introduce tax bills Impeachment SENATE 100 members 6 yr. term; popular vote At least30 years old U.S. citizen 9 yrs. Resident of state 2 Senators per state Hold impeachment trial; act as jury Approves appointments to office and treaties Term U.S. CONGRESS HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES a census is taken every 10 years Presiding officer = Speaker of the House SENATE Vice President leads Senate meetings Votes in case of a tie Pro tempore= alternate presiding officer 1/3 of Senators elected every 2 years U.S. CONGRESS CURRENT SPEAKER John Boehner 8th District Ohio VICE PRESIDENT Joe Biden Senator Delaware Article I: The Legislature (makes laws) Section 6: Payment and Privileges (pg. 4) Section 8: Powers Granted to Congress (253- 254) Quickwrite: Read through the list of Congressional Powers. Which do you consider to be the most important? Explain your selection. Legislative Scavenger Hunt: Work with a partner to discover additional information about the legislative branch. WARM-UP: Article II: The Executive Complete the graphic organizer below using pgs. 256- 259 US book LEADER Second-in-command Powers/ duties Quailifications Advisors Article II: The Executive (Enforces Laws) Leader: President Second-in-Command: Vice President At least 35 years old Natural-born U.S. citizen Resident of the U.S. for 14 years Advisors: Cabinet: Title of each member is “Secretary” Current Cabinet Article II: The Executive Powers: Enforces Laws Commander-in-Chief of the Armed Forces Makes Appointements (ambassadors, judges of the Supreme Court, etc.) (Senate must approve) Makes treaties (with consent of 2/3 of the Senate) Chief Legislator- signs bills into law Enforces laws Duties Gives State of the Union Address WARM- UP 1. 2. Pick up the New York Times article titled “High School Student To Remove Antiwar Shirt”. Read and annotate the article to answer the following questions using complete sentences. What Constitutional Amendment is the focus of this article? What prompted the Vice Principal to ask Barber to turn his shirt “inside out or go home”? What court case did Berber reference when speaking to Principal Judith Coebly? What was the court’s ruling in that case? Do you think Barber’s Constitutional rights were violated? What about Brooklyn student, Yusra Awadeh? Explain your position. ARTICLE III: THE JUDICIARY U.S. SUPREME COURT (interprets laws) Supreme Court Justices Appointed by the President 2/3 approval by Senate Term: Life 9 Total Justices Chief Justice of the United States JOHN G. ROBERTS, JR. Acts as judge in Senate impeachment trials Associate Justices ANTONIN SCALIA ANTHONY M. KENNEDY CLARENCE THOMAS RUTH BADER GINSBURG STEPHEN G. BREYER SAMUEL A. ALITO, JR. SONIA SOTOMAYOR ELENA KAGAN Supreme Court Justices Supreme Court Cases Types of Cases Heard The Supreme Court hears three types of cases: 2/3 are cases appealed from lower federal courts 1/3 are cases appealed from state supreme courts Rarely, they hear cases that have not been previously heard by a lower court, such as between one state's government and another. The justices decide which cases they will hear, about 80 each year. They decide another 50 without hearing arguments. The cases they choose usually address constitutional issues or federal law. The Supreme Court gets about 7000 requests to hear cases per year, so there are many cases that don't get heard. If they decide not to hear a case, the decision of the lower court stands. Supreme Court Cases Typically, all nine of the justices hear each case.. Each case is decided by majority vote. In case of a tie, the decision of the lower court is upheld. Since the court only reviews cases which are appealed from a lower court, there is no evidence presented, and no witnesses are heard. There are simply briefs (written arguments) and oral argument by the parties. Each side has 30 minutes to present oral arguments, and the justices interrupt with questions while they are speaking. After the attorneys are finished speaking, the justices meet in secret to discuss the case and come to a decision. No official record is kept of this discussion. When the Supreme Court announces what they have decided in a case, they issue a formal document called a decision, and sometimes more than one. The conclusion of the court is a majority opinion. The justices that disagreed with the majority vote may issue one or more dissenting opinions, explaining their reasons for disagreeing. The decisions of the Supreme Court have an important impact on society! CHECKS AND BALANCES What are some examples? Quickwrite: How is the law making process an example of the Constitutional principle of checks and balances? In your response include the role all three branches play. LANDMARK CASES What Constitutional Amendment is the focus of this article? What prompted the Vice Principal to ask Barber to turn his shirt “inside out or go home”? What court case did Berber reference when speaking to Principal Judith Coebly? What was the court’s ruling in that case? Do you think Barber’s Constitutional rights were violated? What about Brooklyn student, Yusra Awadeh? Explain your position. Tinker v Des Moines