Cell Structure and Organization Study Guide
advertisement
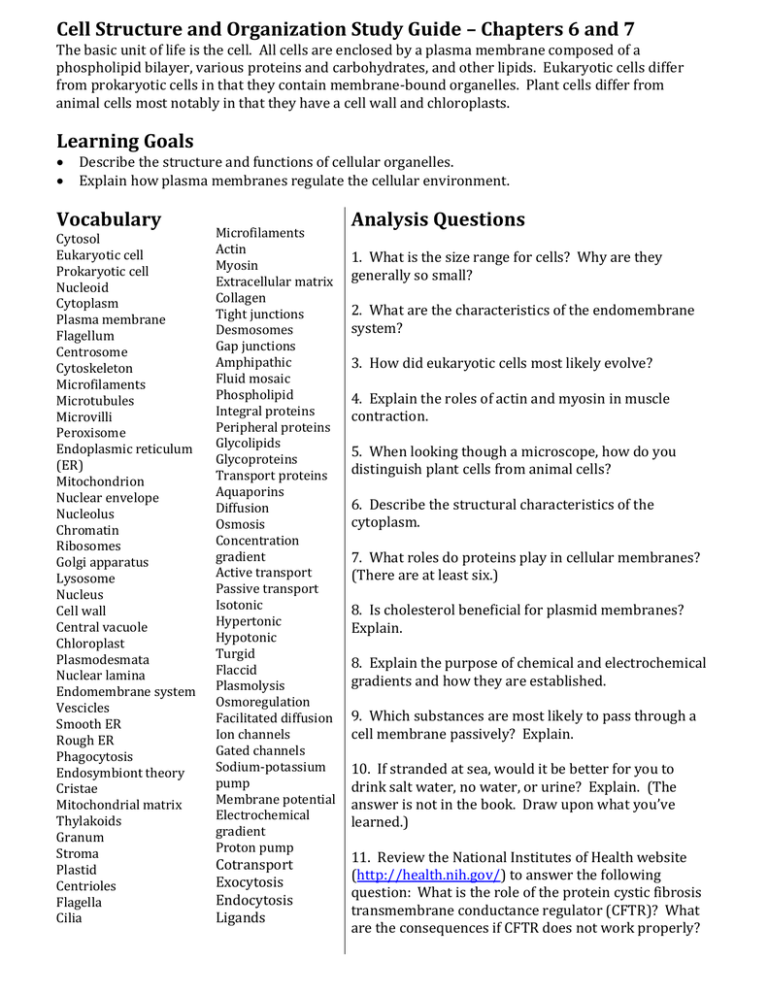
Cell Structure and Organization Study Guide – Chapters 6 and 7 The basic unit of life is the cell. All cells are enclosed by a plasma membrane composed of a phospholipid bilayer, various proteins and carbohydrates, and other lipids. Eukaryotic cells differ from prokaryotic cells in that they contain membrane-bound organelles. Plant cells differ from animal cells most notably in that they have a cell wall and chloroplasts. Learning Goals Describe the structure and functions of cellular organelles. Explain how plasma membranes regulate the cellular environment. Vocabulary Cytosol Eukaryotic cell Prokaryotic cell Nucleoid Cytoplasm Plasma membrane Flagellum Centrosome Cytoskeleton Microfilaments Microtubules Microvilli Peroxisome Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) Mitochondrion Nuclear envelope Nucleolus Chromatin Ribosomes Golgi apparatus Lysosome Nucleus Cell wall Central vacuole Chloroplast Plasmodesmata Nuclear lamina Endomembrane system Vescicles Smooth ER Rough ER Phagocytosis Endosymbiont theory Cristae Mitochondrial matrix Thylakoids Granum Stroma Plastid Centrioles Flagella Cilia Microfilaments Actin Myosin Extracellular matrix Collagen Tight junctions Desmosomes Gap junctions Amphipathic Fluid mosaic Phospholipid Integral proteins Peripheral proteins Glycolipids Glycoproteins Transport proteins Aquaporins Diffusion Osmosis Concentration gradient Active transport Passive transport Isotonic Hypertonic Hypotonic Turgid Flaccid Plasmolysis Osmoregulation Facilitated diffusion Ion channels Gated channels Sodium-potassium pump Membrane potential Electrochemical gradient Proton pump Cotransport Exocytosis Endocytosis Ligands Analysis Questions 1. What is the size range for cells? Why are they generally so small? 2. What are the characteristics of the endomembrane system? 3. How did eukaryotic cells most likely evolve? 4. Explain the roles of actin and myosin in muscle contraction. 5. When looking though a microscope, how do you distinguish plant cells from animal cells? 6. Describe the structural characteristics of the cytoplasm. 7. What roles do proteins play in cellular membranes? (There are at least six.) 8. Is cholesterol beneficial for plasmid membranes? Explain. 8. Explain the purpose of chemical and electrochemical gradients and how they are established. 9. Which substances are most likely to pass through a cell membrane passively? Explain. 10. If stranded at sea, would it be better for you to drink salt water, no water, or urine? Explain. (The answer is not in the book. Draw upon what you’ve learned.) 11. Review the National Institutes of Health website (http://health.nih.gov/) to answer the following question: What is the role of the protein cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR)? What are the consequences if CFTR does not work properly?