Chp.6 Circulatory System 2

Circulatory System
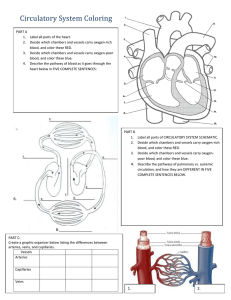
Blood vessels
Arteries, capillaries, veins are tube-like in construction
They transport blood to and from the heart and then to various body tissues
Blood vessels
Arteries
– Thick-walled muscular and elastic tubes that carry oxygenated blood from heart to capillaries
– Largest artery is the aorta
Blood vessels
Capillaries
– Minute, thin-walled vessels that connect smaller arteries to veins
– Provide tissues with nourishment and elimination of waste products
Blood vessels
Veins
– Thin-walled blood vessels
– Less elastic than arteries
– Contain cup-like valves to prevent back flow, and carry blood containing waste products from capillaries back to heart
– Located closer to outer surface off body than arteries
The Blood
Nutritive fluid circulating through the circulatory system
Approximately 80% water
Composed of red and white corpuscles, platelets, plasma and hemoglobin
The Blood
Sticky, salty fluid
Normal temperature of 98.6 degrees F
Makes up 1/20 of body weight
About 8-10 pints fill adult vessels
Bright red in arteries
Dark red in veins (except pulmonary)
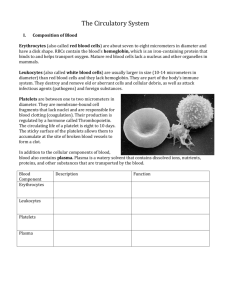
Blood Composition
Red Corpuscles (red blood cells)
– Also known as erythrocytes
– Produced in red bone marrow
– Contain hemoglobin (a complex iron protein that gives the blood its bright red color)
– Carry oxygen to cells
Blood Composition
White Corpuscles (white blood cells)
– Also called leucocytes
– Destroy disease-causing germs
Blood Platelets
– Smaller than red blood cells
– Important to clotting
Plasma
– Fluid part of the blood
– Straw-like in color
– About 90% water and contains proteins, sugar and oxygen
– Carries food and secretions to cells and carbon dioxide from cells
Chief functions of Blood
Carries water, oxygen, food, secretions to cells
Carries away carbon dioxide and waste
– To be eliminated through lungs, skin, kidneys and large intestine
Helps equalize body temperature
Protects from harmful bacteria and infections
– Through white blood cells
Clotting
– Which closes injured minute blood vessels and prevents excessive blood loss