2/10 - MegCherry.com
advertisement
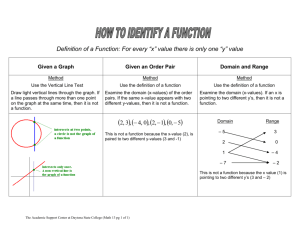
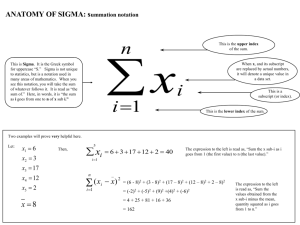
SP 225 Lecture 7 Measures of Center Using the Sigma Notation Alternative Sigma Notation x Means add the X values for all data points Sigma Example Data Point X value 1st 5 2nd 3 3rd 4 4th 2 x 5 3 4 2 14 Sigma with Complex Expression xy ( x y) x a First, multiply all x-values by their corresponding y-values. Second, add all products together First, add all x-values to their corresponding y-values. Second, add all sums together. First, add all x-values together. Second, add the value a to the sum. x 2 First, raise all x-values to the 2nd power. Second, add all terms together. Complex Expressions Examples Data Point 1st X-value Y-value 5 2 2nd 3 1 3rd 4 2 4th 2 1 xy (5 * 2) (3 *1) (4 * 2) (2 *1) 10 3 8 2 23 Complex Expressions Examples Data Point 1st X-value Y-value 5 2 2nd 3 1 3rd 4 2 4th 2 1 ( x y ) (5 2) (3 1) (4 2) (2 1) 7 4 6 3 20 Complex Expressions Examples Data Point 1st X-value 2nd 3 3rd 4 (5 3 4 2) 1 4th 2 14 1 15 5 If , a 1 x a Complex Expressions Examples Data Point 1st X-value x 2 5 2nd 3 3rd 4 5 3 4 2 25 9 16 4 4th 2 54 2 2 2 2 Sigma Worksheet Answers 1) 13 2) 5 3) 15 4) 51 5) 169 6) 153 7) 16 Upcoming Material Chapter 4 What is typical or average? Chapter 5 & 6 Is something unusual? Measures of Center Value at the center of or middle of a data set Mean Median Mode Notation denotes the sum of a set of values. x is the variable usually used to represent the individual data values. n represents the number of values in a sample. N represents the number of values in a population. Mean Found by adding all values and dividing by the number of values Notation x is pronounced ‘x-bar’ and denotes the mean of a set of sample values x = x n µ is pronounced ‘mu’ and denotes the mean of all values in a population µ = x N Median The middle value when the original data are arranged in increasing or decreasing order 5, 9, 1, 13, 4 1, 4, 5, 9, 13 Median is 5 If even number of data points, average the 2 median points Not sensitive to outliers Used when discussing national income ~ Often denoted by x (pronounced ‘x-tilde’) Mode The value that occurs most frequently When 2 values occur with greatest frequency, the data is bi-modal When more than two values occur with the same greatest frequency, the data is multimodal When no value is repeated, the value has no mode Only measure that can be used with nominal or qualitative data Round-off Rule Keep one more decimal place than the original data Problems for Discussion A sociologist wants to find the mean commuting time for all working US residents. She does an internet search and finds the mean commuting time for each of the 50 states. She adds those times and divides by 50. Is the result likely to be a good estimate of the mean commuting time for all workers? Calculating a Measure What is average or typical? Skewed A distribution is skewed if it is not symmetric and extends more to one side or the other Skew can be determined by examining differences between the mean, median and mode Skewed (cont.) In Class Activity Consensus Dissensus Polarization Income Inequality Answer the Question: What do you think does or does not influence opinion on income inequality? Justify your response using data from the GSS in 2-3 paragraphs. Analyze the response to 2-3 survey questions including a graph and measure of center for each survey question Include all SPSS output for each survey question