Industry Environment
advertisement

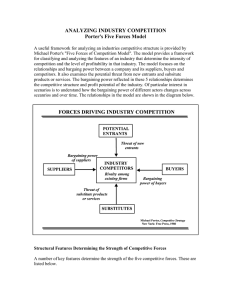
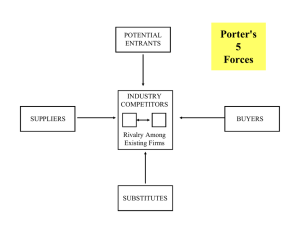
Topic 2 The External Environment 3 “Levels” to the External Environment • Remote Environment – Domestic & International Environment • Industry Environment – Industry Analysis and Competitive Analysis • Operating Environment The Firm’s External Environment •Economic •Social •Political •Technological •Ecological Remote Environment (Global and Domestic) Industry Environment (Global and Domestic) •Entry barriers •Supplier power •Buyer power •Substitute availability •Competitive rivalry Operating Environment (Global and Domestic) •Competitors •Creditors THE FIRM •Labor •Suppliers •Customers Remote … Economic Factors • Concern the nature and direction of the economy in which a firm operates • Types of factors • • • • • • General availability of credit Prime interest rates Level of disposable income Propensity of people to spend Inflation rates Trends in growth of gross national product Remote … Social Factors • Include beliefs, values, opinions, and lifestyles of people • “Recent” social trends • Entry of large numbers of women into labor market • Accelerating interest of consumers and employees in quality-of-life issues • Shift in age distribution of population Remote Political Factors • … define legal and regulatory parameters within which firms must operate • Types of factors – – – – – Fair-trade decisions Antitrust laws Tax programs Minimum wage legislation Pollution and pricing policies Remote Technological Factors • … focus on technological changes affecting industry • Types of changes • New products • Improvements in existing products • Manufacturing and marketing techniques Remote Ecological Factors • … involve relationships among human beings and other living things and air, soil, and water • Current concerns • Global warming • Loss of habitat and biodiversity • Air, water, and land pollution Remote Assessing the International Environment • Assess each non-domestic market, on the same factors … though the importance of each may differ • Notably … – – – – Economic Environment Political System Legal Environment Cultural Environment » (we will talk more about these) Forces Driving (#2) Industry Competition Potential Entrants Bargaining power of suppliers Threat of new entrants Industry Competitors Bargaining power of buyers Buyers Suppliers Rivalry Among Existing Firms Threat of substitute products or services Substitutes Porter’s 5 forces Model Industry Competition Threat of Entry • Seriousness of threat depends on – Reaction from existing firms – Barriers to entry • • • • • • Economies of scale Product differentiation Capital requirements Cost advantages independent of size Access to distribution channels Government policy Industry Competition Suppliers • A supplier group is powerful if: • It is dominated by a few companies and is more concentrated than industry to which it sells • Its product is unique, or differentiated, or has built up switching costs • It poses a threat of integrating forward into industry’s business • Industry is not an important customer of supplier group Industry Competition Buyers • A buyer group is powerful if: • It is concentrated or purchases in large volume • Products purchased from industry are standard or undifferentiated • Industry’s product is unimportant to quality of buyers’ products or services • Buyer poses credible threat of integrating backward Industry Competition Substitute Products • Relevance of substitutes • By placing a ceiling on prices charged, they limit profit potential of an industry • Substitutes deserving the most attention are those • Subject to trends improving their price-performance trade-off with the industry’s product • Produced by industries earning high profit Industry Competition Rivalry • Tactics of competitive rivalry • Price competition • Product introduction • Advertising slugfests • What Causes Rivalry to be Intense? – Size, slow growth, homogeneous products, high exit barriers …. Characteristics of Industry Structure • Structural attributes –Characteristics that give an industry its distinctive character • Variations among industries involves examining • • • • Concentration Economies of Scale Product Differentiation Barriers to Entry ***Common Mistakes in Identifying Competitors • Overemphasizing current and known competitors while ignoring potential entrants • Overemphasizing large competitors while ignoring small ones • Overlooking potential international competitors • Assuming competitors will continue to behave in the same way Operating Environment (#3) The operating environment, also called the competitive or task environment, comprises factors in the competitive situation that affect a firm’s success in acquiring needed resources or in profitably marketing its goods and services Factors in the Operating Environment • Firm’s competitive position … – Key success factors? ... market share, breadth of product line, experience, financial position, product quality, technological position, community reputation, etc. • The composition of its customers – Geographic, demographic, behavioral • Reputation among suppliers and creditors • Ability to attract capable employees