Part 2: Biology Prefixes and Suffixes
advertisement

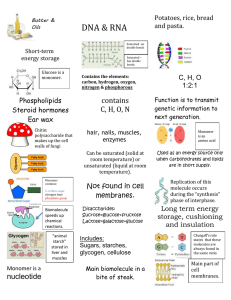
Mrs. Roberts – CTHS Pre-AP Biology Summer Assignment NAME: ____________________________________________________ ID: ____________________________ You have been given a summer assignment for Pre-AP biology. You will be expected to know the information covered in the summer assignment when you enter my class this upcoming school year. The summer assignment includes the scientific method, biomolecules, enzymes, and prefixes and suffixes you should know for biology. The summer assignment will count as your first grade in biology. You may use any resources available to you to complete the assignment including books and the internet. I strongly suggest not leaving this assignment until the first week of school to complete as many of your teachers will give you homework. THIS ASSIGNMENT IS DUE WITH CLASS MATERIALS, SIGNED SYLLABUS AND SIGNED SAFETY CONTRACT THE FIRST WEEK WE RETURN IN AUGUST! DUE FRIDAY, AUGUST 29th, 2014 ENZYMES and MACROMOLECULES Part One Directions: Answer the following questions. You may use any resource available to you including the internet to help you answer the following questions and fill in charts. 1.) What are the four types of biomolecules (macromolecules)? 2.) What is an enzyme? What role do enzymes play in our bodies? 3.) Draw out an enzyme substrate complex and label the enzyme, the substrate, and the active site. 4.) What type of biomolecule is an enzyme? 5.) What factors affect the action of an enzyme? Mrs. Roberts – CTHS Pre-AP Biology Summer Assignment 6.) What is a peptide bond? 7.) What is starch and where is it found? 8.) What is a monosaccharide, disaccharide, and polysaccharide? 9.) What is a monomer? 10.) What is a polymer? 11.) List three differences between RNA and DNA? 12.) What is ATP? 13.) What is a lipid? 14.) What is the difference between a saturated fat and an unsaturated fat? 15.) Describe the phospholipid bilayer include the following words in your description: hydrophobic, hydrophilic, head, tail, polar, nonpolar. Mrs. Roberts – CTHS Pre-AP Biology Summer Assignment Directions: Fill out the following tables for each of the four main types of biomolecules Carbohydrates Place your answers in this column: List names below: Name of monomer(s) Draw the structure of a monomer including elements present What elements make up this biomolecule and what ratio are they in? Give examples of the biomolecule (what type of Draw Structure here List elements and ratio below: Examples are: foods is it found in, or where is it found) What is the role of this biomolecule? List where the following polysaccharides are found List roles here: Proteins Place your answers in this column: List names below: Name of monomer(s) Draw the structure of a monomer including elements present What elements make up this biomolecule and what ratio are they in? Give examples of the biomolecule (what type of Starch: Cellulose: Gylcogen: Draw Structure here List elements and ratio below: Examples are: foods is it found in, or where is it found) What is the role of this biomolecule? List the importance of these proteins. List roles here: Enzymes: Hormones: Mrs. Roberts – CTHS Pre-AP Biology Summer Assignment Lipids Name of monomer(s) Draw the structure of a monomer including elements present What elements make up this biomolecule and what ratio are they in? Give examples of the biomolecule (what type of Place your answers in this column: List names below: Draw Structure here List elements and ratio below: Examples are: foods is it found in, or where is it found) What is the role of this biomolecule? Explain the difference between these fats List roles here: Nucleic acids Place your answers in this column: List names below: Name of monomer(s) Draw the structure of a monomer including elements present What elements make up this biomolecule and what ratio are they in? Give examples of the biomolecule (where inside the Saturated: Unsaturated: Draw Structure here List elements and ratio below: Examples are: cell do you find them?) What is the role of this biomolecule? Compare and contrast these nucleic acids. List roles here: DNA: RNA: ATP: Mrs. Roberts – CTHS Pre-AP Biology Summer Assignment Part 2: Biology Prefixes and Suffixes Directions: Review and study the following prefixes and suffixes that are used in biology. Choose ten prefixes and five suffixes and create a sentence using each. You should have 15 sentences! Prefix Meaning Example and definition of example A- Without, negative, not Asexual (without sex) Aer- Aerobic (with oxygen) Amyl- Starch Amylase (starch enzyme) Anti- Against Antibodies (proteins that work against invaders) Auto- Self Autotroph (self nourishing) Bi- Two Biennial (two year life span plant) Bio- Life Biology (the study of life) Cardi- Heart Cardiovascular Cata- Down, lower, under Catabolic Cephal- Head Cephalization Chlor- Green Chlorophyll Con- With, together Conjugation Crani- Skull Craniometer (instrument used to measure the skull) Cyto- Cell Cytosol Dactyl- Finger, toe, digit Dactylogram Derm- Skin dermis di- Two disaccharide Diplo- Double Diploid cell Un- Not Unsaturated (not saturated; capable of dissolving more of a substance) Uni- One Unicellular (having a single cell) Vas- vessel vasodilation (dilation of a blood vessel Zyg- Yoke, union Zygote (a fertilized cell) Macro- Large Macroeudution Mal- Bad, Abnormal Malformation Mrs. Roberts – CTHS Pre-AP Biology Summer Assignment Meta- After, behind Metastasis Micro- Small Microscopic Mill- Thousand Milliliter Flagell- Whip Flagella (whiplike structures) Re- Back again Regeneration (Re-growth of a body part) Ecto- Outer, external Ectotherm (An organism that uses external heat to regulate it’s body temperature) En- In Endothelium (Innermost layer of cells lining blood vessels) End-, Endo- within Endotherm (Organism that generates heat internally to maintain a constant body temperature) Erythro- red Erythrocyte (red blood cell) Eu- Good, well, true Eukaryote (Organism whose cells contains a “true” membrane bound nucleus) Ex- Out of, outer Exoskeleton (hard outer surface that provides support or protection for an organism) Extra- Outside, beyond Extracellular (locating or occurring outside a cell) Gam- United, jointed, sexual Gametes (egg or sperm that unite during sexual reproduction) Gastr Stomach, Belly Gastric juice (Acidic fluid secretes by the stomach) Glyco- Sugar, sweet Glycolysis (metabolic pathway that involves the splitting of sugars (glucose) into pyruvic acid) Haplo- Single haploid (having a single set of chromosomes Hem- Blood hemoglobin (iron containing protein in red blood cells) Hepat- Liver hepatitis (inflammation of the liver) Hetero- Other, different heterozygous (having two different alleles for a given trait) Homo- Same homozygous (having two alleles for a given trait that are the same) Hydro- Water hydrophilic (having an affinity for water; water loving) Hyper- Above, excessive Hypo- Under, beneath, lacking hyperthyroidism (condition resulting from the excessive production of thyroid hormones) hypodermic (of or pertaining to the parts under the skin) Im- Not Immobile (not moving) Inter- Between interstitial fluid (fluid filling space between cells) Mrs. Roberts – CTHS Pre-AP Biology Summer Assignment Intra- Within intraocular (occurring within the eyeball) Iso- Equal Lact- Milk isogamy (fusion of male and female gametes that are the same size and structure) lactose (milk sugar) Leuk- White leukocytes (white blood cells) Neo- New neonatal (of or relating to newborn infants) Neph- Kidney Nephrons (structure of kidneys and urinary system) Neuro- Nerve neuroblast (embryonic cell that develops into a nerve cell) Oste- Bone Ov- Egg osteoporosis (abnormal reduction in the amount of bone mass resulting in fragile porous bones) Ovum (female gamete, egg) Para- Around, near, beside parathyroid (near or within the thyroid gland) Path- Disease pathogen (disease causing agent) Phago- Eating Phil- Love phagocyte (a cell that engulfs and digests waste materials and microorganisms) philoprogenitive (relating to the love of children) Phob- Fear phobia (abnormal irrational fear of a specific thing) Phyto- Plant phytochrome (pigment involved in many plant responses to light) Pneum- Lung Pod- Foot, foot-like pneumococcus (microorganism that causes a disease of the lungs called bacterial pneumonia) podia (structures that resemble or function as feet) Poly- Many polysome (many ribosomes attached to a messenger RNA) Post- After postmortem (occurring after death) Pre- Before, prior prepuce (foreskin covering the human penis) Pro- Before, primary Pseudo- False protoderm (outer most primary meristem that forms the epidermis of roots and shoots) pseudoscience (practice that resembles science but is considered to be without scientific foundation) Psych- Soul, mind psychology (science that deals with mental processes and behavior) Sacchar- Sugar disaccharide (double sugar, example: sucrose - composed of glucose and fructose) Mrs. Roberts – CTHS Pre-AP Biology Summer Assignment Suffix Meaning Example and definition of example -asis Affected with, with Homeostasis (with a steady state) -emia blood Leukemia (form of cancer characterized by an abnormal increase In the number of white blood cells in the body) -itis Inflammation appendicitis (inflammation of the appendix) -kinesis Movement, motion cytokinesis (cell motion; division of the cytoplasm) -logy Science of, study of biology (science of life and living organisms) -lysis Decomposition, dissolving, destruction Tumor chemolysis (decomposition of organic substances through the use of chemical agents) adenoma (a benign glandular epithelial tumor) -osis Affected with, condition, abnormal process cirrhosis (chronic disease affecting the liver) -otomy Act of cutting, incision gastrotomy (incision in the stomach) -ous Characterized by, full of homozygous (union characterized by the joining of identical alleles for a single trait) -pathy Disease neuropathy (disease of the nervous system) -philic Love thermophilic (relating to the love of heat or hot environments) -phyll Leaf sporophyll (leaf that contains spores) -plasm Material forming cells cytoplasm (contents of a cell excluding the nucleus) -oma