Chapter 10
advertisement
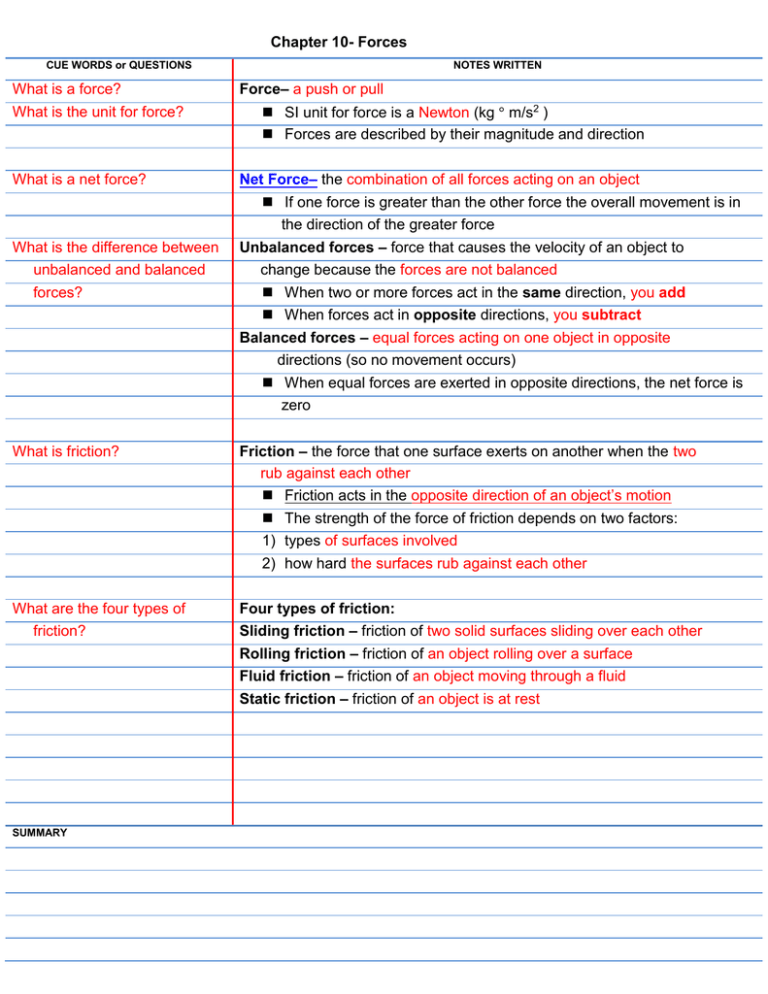
Chapter 10- Forces CUE WORDS or QUESTIONS What is a force? What is the unit for force? What is a net force? What is the difference between unbalanced and balanced forces? NOTES WRITTEN Force– a push or pull SI unit for force is a Newton (kg ° m/s2 ) Forces are described by their magnitude and direction Net Force– the combination of all forces acting on an object If one force is greater than the other force the overall movement is in the direction of the greater force Unbalanced forces – force that causes the velocity of an object to change because the forces are not balanced When two or more forces act in the same direction, you add When forces act in opposite directions, you subtract Balanced forces – equal forces acting on one object in opposite directions (so no movement occurs) When equal forces are exerted in opposite directions, the net force is zero What is friction? Friction – the force that one surface exerts on another when the two rub against each other Friction acts in the opposite direction of an object’s motion The strength of the force of friction depends on two factors: 1) types of surfaces involved 2) how hard the surfaces rub against each other What are the four types of friction? SUMMARY Four types of friction: Sliding friction – friction of two solid surfaces sliding over each other Rolling friction – friction of an object rolling over a surface Fluid friction – friction of an object moving through a fluid Static friction – friction of an object is at rest CUE WORDS or QUESTIONS What is gravity? NOTES WRITTEN Gravity – the force that pulls objects towards each other force of gravity between objects increases with greater mass and decreases with greater distance Mass – the measure of the amount of matter in an object Weight – mass x acceleration due to gravity (9.8 m/s2) How does air resistance effect free fall? Free fall – when the only force acting on an object is gravity Air resistance – fluid friction experienced by objects falling through air Air resistance is a force in the opposite direction of the object Air resistance is not the same for all objects (depends on surface area) Projectile (an object that is thrown horizontally) will fall at the same rate as an object thrown vertically What is the difference between compression and tension? What is Newton’s first law? Matter is considered elastic if it returns to its original shape after it is stretched or squeezed Compression – an elastic force that squeezes or pushes matter together Tension – an elastic force that stretches or pulls matter Newton’s First Law of Motion – an object at rest will remain at rest, and an object that is moving at constant velocity will continue moving at constant velocity, unless acted upon by and unbalanced force (called the law of inertia) The amount of inertia an object has depends on its mass – the greater the mass the greater the inertia Inertia– the tendency of an object to resist change in its motion What is Newton’s second law? Newton’s 2nd Law – acceleration depends on the net force acting on an object and on the object’s mass (force = mass x acceleration) The net force on an object is equal to the product of its acceleration & mass Force = Mass x Acceleration Acceleration = Force / Mass Mass = Force / Acceleration SUMMARY Chapter 10- Forces (page 2) CUE WORDS or QUESTIONS NOTES WRITTEN Newton – the force required to accelerate one kilogram of mass at 1 meter per second per second (kg.m/s2 is a Newton) What is Newton’s third law? Newton’s 3rd Law of Motion – if one object exerts a force on another object, then the second object exerts a force of equal strength in the opposite direction on the first object (action- reaction pairs) Newton called one force an action, and the other he called a reaction What is momentum? Momentum is the ‘quantity of motion’ (momentum = mass x velocity) Law of Conservation of Momentum states that the total momentum of the objects that interact does not change (momentum is not lost) The total momentum of any group of objects remains the same unless outside forces act on the objects (such as friction) When two objects collide in the absence of friction, momentum is not lost SUMMARY