ear 203 earth system science
advertisement

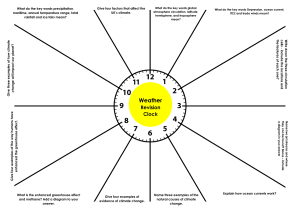
EAR 203, 2013-2014 Name: ________________________ Date: _________________________ Block: _____ EAR 203 EARTH SYSTEM SCIENCE SYRACUSE UNIVERSITY EXAM – CHAPTERS 1-9 REVIEW Chapter 1 1. Define the major global environmental problems. 2. Identify anthropogenic greenhouse gases, their sources and their effects. 3. Explain fundamental components of the Earth system and their interactions. 4. Differentiate between global warming and the greenhouse effect. 5. Explain the relationship between surface temperature and atmospheric CO 2 concentration. Describe how CO2 concentrations have changed (pay particular attention to graphs on pages 4-5). 6. Explain how ancient climate data (before direct measurement) is determined – PROXIES. 7. Explain the Gaia hypothesis and provide evidence supporting the hypothesis. 8. Know how past surface temperatures are determined. Chapter 2 1. What are systems? Feedback loops? 2. Explain how the components of systems interact with each other. 3. Describe the concept of a “feedback” - both positive and negative. 4. Diagram the equilibrium states of a system (both stable and unstable). 5. Diagram stability diagrams for White and Black Daisyworlds. 6. Explain how forcings in the Daisyworld system affect albedo. 7. Know how albedo affects climate. Chapter 3 (ignore electromagnetic radiation) 1. How is Earth warmed and cooled? 2. What are the most abundant gases in Earth’s atmosphere? 3. How do greenhouse gases warm the Earth’s surface? 4. Why is the greenhouse effect important to support life on the Earth? 5. How do clouds contribute to the greenhouse effect? 6. What are the different layers of Earth’s atmosphere? 7. What are the different mechanisms by which heat energy can be transferred (conduction, convection, radiation)? 8. Explain the water vapor feedback climate loop. 9. Explain the snow and ice albedo feedback climate loop. 10. Diagram the IR flux/temperature feedback climate loop. Chapter 4 1. Explain why the incoming solar energy varies with latitude and season. 2. Why do air masses rise or fall? 3. What is the Coriolis Effect? 4. Describe global atmospheric circulation patterns, why they occur, and how they affect the transport of energy and material around the globe. 5. Explain why Earth experiences different seasons throughout the year. 6. Explain how the concepts of thermal conductivity and heat capacity relate to global distribution of energy. 7. Explain how phase changes in water contribute to global heat distribution. 8. What role do water vapor and clouds play in global energy? 9. Why do weather and climate vary across the globe? EAR 203 – EXAM Chapters 1-9 Review Page 1 EAR 203, 2013-2014 Chapter 5 1. How do ocean currents form? 2. What role does ocean circulation play in the global climate system? 3. Compare and contrast surface ocean circulation and thermohaline ocean circulation. 4. What drive surface circulation? 5. What role does the differences in water density play in deep-ocean circulation? 6. How does the Coriolis Effect influence ocean circulation? 7. Explain the Ekman spiral/Ekman transport. What is the effect on water motion? 8. Explain how gyres form. 9. Describe the major surface currents: the Sub-tropical gyres and the eastern and western boundary currents. 10. What is coastal upwelling and downwelling? Equatorial upwelling? 11. Compare and contrast El Nino with normal conditions. Describe the adverse effects of El Nino. Chapter 6 1. What role does the cryosphere play in the global climate system? 2. Explain how ice forms on land and in the ocean. 3. Explain how glaciers and sea ice move. 4. Describe the ice, atmosphere heat flux feedback loop. Chapter 7 1. Explain the concept of plate tectonics and mantle convection. 2. How does plate tectonics relate to ocean history and the formation of ocean basins (Sea-floor Spreading, Wilson Cycle)? 3. Describe the three plate tectonic boundaries, explain the forces at work there, and give an example of each. 4. Describe Earth’s layers. Use both their chemical composition and in their physical properties (solid, plastic, liquid). 5. Explain how the magnetic striping patterns form in the sea floor, and explain why these stripes are symmetrical about the crests of the mid-ocean ridges. 6. Explain how convection currents beneath the plates move the crustal plates in different directions. 7. Describe the different forces acting on tectonic plates (slab pull, ridge push, mantle drag, negative buoyancy, trench suction). 8. What are the sources of heat driving convection currents? 9. Describe the two types of seismic waves and their characteristics. 10. How do we know about Earth’s interior, if we have never been there? 11. What is the source of Earth’s magnetic field? Explain how it forms. Chapter 8 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Explain the global carbon cycle. Why is Earth likely the only planet in our solar system that supports life? Explain why the composition of marine organisms determines the composition of sea water How do the long and short term organic carbon cycles differ? Describe the characteristics of the organic and inorganic carbon cycle. Explain how thermohaline circulation and the biological pump effects ocean chemistry. Chapter 9 1. Compare and contrast autotrophs and Heterotrophs. 2. What are the characteristics of life? 3. Explain how an ecosystem can impact the climate system (use the boreal forest as an example) 4. Explain why ecosystems are not divorced from their environment rather that the environment is part of the ecosystem (ecosystems are not static). 5. Explain the concepts of biomass and biodiversity. EAR 203 – EXAM Chapters 1-9 Review Page 2