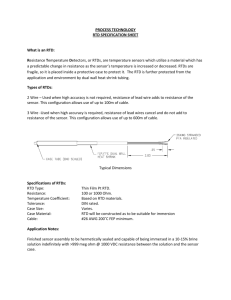
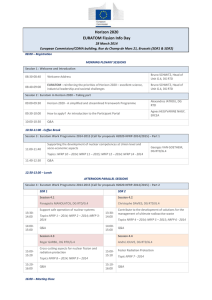
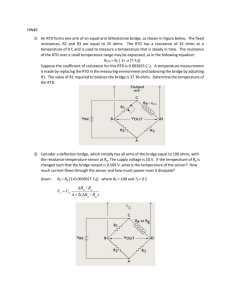
(RTD).
advertisement

Implementing the Right to Development in the aftermath of the global financial crisis: Challenges and Prospects Xigen Wang Professor of Law Wuhan University School of Law Wuhan PRC The global financial crisis of 2008 the fluctuation of exchange rates intensification of the debt crisis rising poverty rates higher unemployment the reduction of overseas investments and trade reduced economic growth increased social inequality Restrict the realization of the right to development (RTD). In order to implement RTD, the following measures should be taken immediately. Part 1: Reconstructing the idea of the RTD traditional models of justice a new concept of justice 1. Definition: “development - oriented justice” “people-centred development with justice” • Development-oriented Justice is to ensure that every human person and all peoples are entitled to participate in, contribute to, and enjoy economic, social, cultural and political development. It is a notion of global , substantial, fair, harmonized and people-oriented justice. 2. Features: Globalization Comparability Gregariousness Features Comprehensiveness Inclusiveness 3. Reshaping: • explain RTD under the framework of peoplecentred development with justice from the following five perspectives: (1)Subjects : Financial crisis RTD money-oriented development people-centred development “People” could be offered five characteristics and called : natural social person person economic person ecological political person person • The human person is the central subject of the development process and that development policy should therefore make the human being the main participant and beneficiary of development ------ Declaration on the Right to Development 1986 (2)Objects: The objects of RTD are encompassed by five elements: human dignity culture diversity common good development opportunity Objects greatest equal liberties (3)Contents : Financial economic crisis growth development RTD A. inclusive development economic justice B. social welfare culture development integrate integrate political justice economic and political justice (4)Time : • It is imperative to take the sustainable Development as a right • The RTD can be named as the Right to Sustainable Development. • Financial crisis derogated RTD: lead to an unsustainable development • Example : higher carbon emission Crisis carbon emission RTD ? • Supporter:carbon emission is a kind of RTD • Opponent:emision is an obligation not right Balance • It is necessary to release the tension between carbon emissions and the RTD. • As far as the developing country is concerned, the right to emissions is the right to development. • Opponent of this idea argues that emission is purely an obligation not a right. So our pressing need is encouraging each side to find consensus and resolution in defining the carbon emission. (5)Space : • A new right ------the right to regional development should be recognized as a subsidiary right of the RTD • “The world is not flat” ------- WORLD DEVELOPMENT REPORT 2009: Reshaping Economic Geography. Part 2.: Exploring crisis early warning and emergency response system 1. Evaluation Mechanisms: A minimum standard of RTD A general concept of RTD (UN Resolution 1979) RTD criteria and UN Declaration operational sub-criteria 1986) (A/HRC/15/W G.2/TF/2/Add.2) The Urgent task is to design a minimum standard of RTD based on the Criteria and Operational Sub-criteria on RTD (A/HRC/15/WG.2/TF/2/Add.2) food water basic medicines primary education The bottom line standard could be more recognized and practicable than the maximum one If the lowest demand concerning human survival, such as food, water, basic medicines, primary education, cannot be satisfied, an early warning mechanism will work 2. Early Warning Mechanism Treatment plan Executing agency Evaluation method Information analysis Outcome feedback 3. Emergency Response Mechanism • It recommends that to establish: – “The Overall Emergency Response Plan for a Minimum of RTD” and – Sub - mechanisms under the overall mechanism A • “Emergency Response Mechanism for food shortage” B • “Emergency Response Mechanism for Drinking Water Crisis” C • “Emergency Response Mechanism for Lacking of Basic Medicine” 4. Intervention Mechanism a pure autonomy of private law public law compulsion policy balance mechanism • More challenge, more intervention mechanisms are needed, especially for the non-reciprocal protection to the vulnerable groups. Part 3 : Mainstreaming RTD: ------Constructing a strategic system of the implementation of RTD subprime Text mortgage in crisis here classical financial bubbles liberalism financial crisis excessive consumption generation I generation II generation III freedom equality RTD 1. Ground: (1) Mainstreaming RTD has its normative ground in: Charter of the United Nations Universal Declaration of Human Rights Declaration on the Right to Development • Confirming that the right to development is an inalienable human right and that equality of opportunity for development is a prerogative both of nations and of individuals who make up nations. —— Declaration on the RTD (2) value consensus: universal fraternity theory in the classical natural law theory social solidarism value consensus global justice theory post-modernism the three generations of human rights theory Latin American dependency theory China's Confucian doctrines (benevolent love and people-centred principle) 2. Methodology : how to mainstream RTD • Steps should be taken to ensure the full exercise and progressive enhancement of the right to development, including the formulation, adoption and implementation of policy, legislative and other measures at the national and international levels- —— UN Declaration on the Right to Development Article 10 There are three different ways: A Soft law B Hard law C No law 3. Targets : • Three standards of mainstreaming human right: A the recognition from mainstream society B a set of complete system of rights and obligations C the implementation under the institutional framework(e.g. Law & policy) • Thus, the targets of mainstreaming RTD: Theoretically Obtain the same status as civil and political rights, economic, social and cultural rights Practically Technically supported and protected by developed subjects have a legally binding mechanism of remedy (similar to the ICCPR & ICESCR) • 4. obligation: • The RTD cannot be fully implemented into practice because of its ambiguous subjects, forms and procedures of accountability. I try to divide the obligation genealogy of RTD into two types: endogenous obligation and instrumental obligation. Instrumental obligation is derived from endogenous obligation. Obligation Genealogy of RTD Endog enous obligations Instrumental obligat -ions Extension values Mode Consideration Rules Moral obligation Humanities or interests Abstract No No Institutiona l obligation Corrective justice Integrity Yes Consti Public tutive law Merciful obligation Introspection Charity No No Contract obligation Autonomy Exchange Yes Regul Private ative law Interventio n obligation Heteronomy Mandatory Yes Public & social law 5. Steps: • pilot and implement of criteria and subStep1 criteria on RTD • establish Step2 the legal correlation between civil and political rights, economic, social and cultural rights and RTD; Link to treaty & trade law • draft “Operational Guidelines for Implementing the Step3 Step4 Declaration on the Right to Development”( subjects, objects, content and approaches of its implementation) • improve and integrate existed mechanisms on the international, regional and national level • lead to a Convention on the Right to Step5 Development Thanks!